LGD-2226
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 328947-93-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 11560224 |
| UNII |
RI376RM5MT |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.470 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
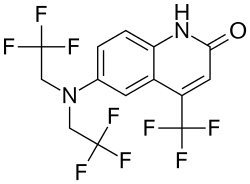
| Formula | C14H9F9N2O |
| Molar mass | 392.219 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| (verify) | |
LGD-2226 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator,[1] which is being developed for treatment of muscle wasting and osteoporosis.[2]
LGD-2226 is an orally active, potent and selective agonist for androgen receptors which was shown to have anabolic effects in both muscle and bone tissue, but with considerably less effects on prostate weight and lutenizing hormone levels than testosterone.[3][4]
Selective androgen receptor modulators may also be used by athletes to assist in training and increase physical stamina and fitness, potentially producing effects similar to anabolic steroids but with significantly less side effects. For this reason, SARMs have already been banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency since January 2008 despite no drugs from this class yet being in clinical use, and blood tests for all known SARMs are currently being developed,[5][6] including LGD-2226.[7]
References
- ↑ van Oeveren A, Motamedi M, Mani NS, Marschke KB, López FJ, Schrader WT, Negro-Vilar A, Zhi L. Discovery of 6-N,N-bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)amino- 4-trifluoromethylquinolin-2(1H)-one as a novel selective androgen receptor modulator. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2006 Oct 19;49(21):6143-6. doi:10.1021/jm060792t PMID 17034117
- ↑ Gao W, Dalton JT. Expanding the therapeutic use of androgens via selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs). Drug Discovery Today. 2007 Mar;12(5-6):241-8. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2007.01.003 PMID 17331889
- ↑ Miner JN, Chang W, Chapman MS, Finn PD, Hong MH, López FJ, Marschke KB, Rosen J, Schrader W, Turner R, van Oeveren A, Viveros H, Zhi L, Negro-Vilar A. An orally active selective androgen receptor modulator is efficacious on bone, muscle, and sex function with reduced impact on prostate. Endocrinology. 2007 Jan;148(1):363-73. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0793 PMID 17023534
- ↑ Hong MH, Sun H, Jin CH, Chapman M, Hu J, Chang W, Burnett K, Rosen J, Negro-Vilar A, Miner JN. Cell-specific activation of the human skeletal alpha-actin by androgens. Endocrinology. 2008 Mar;149(3):1103-12. doi:10.1210/en.2007-0530 PMID 18063690
- ↑ Thevis M, Kohler M, Schlörer N, Kamber M, Kühn A, Linscheid MW, Schänzer W. Mass spectrometry of hydantoin-derived selective androgen receptor modulators. Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 2008 May;43(5):639-50. doi:10.1002/jms.1364 PMID 18095383
- ↑ Thevis M, Kohler M, Thomas A, Maurer J, Schlörer N, Kamber M, Schänzer W. Determination of benzimidazole- and bicyclic hydantoin-derived selective androgen receptor antagonists and agonists in human urine using LC-MS/MS. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2008 May;391(1):251-61. doi:10.1007/s00216-008-1882-6 PMID 18270691
- ↑ Thevis M, Kohler M, Maurer J, Schlörer N, Kamber M, Schänzer W. Screening for 2-quinolinone-derived selective androgen receptor agonists in doping control analysis. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry. 2007;21(21):3477-86. doi:10.1002/rcm.3247 PMID 17985352