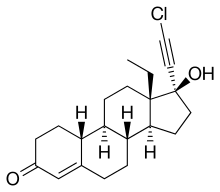
Chloroethynyl norgestrel
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | 2415-28-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 22790422 |
| ChemSpider | 18503812 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H27ClO2 |
| Molar mass | 346.89088 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Chloroethynyl norgestrel (developmental code name WY-4355) is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group related to norgestrel that was investigated as an oral contraceptive in the 1970s but was never marketed.[1][2][3][4] Similarly to other 19-nortestosterone derivatives, chloroethynyl norgestrel has weak androgenic and anabolic activity.[5]
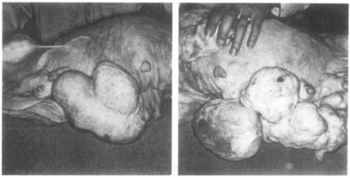
In combination with mestranol, similarly to ethynerone and anagestone acetate (and certain other progestogens, including progesterone and several other 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives), chloroethynyl norgestrel was found to produce striking mammary tumors in beagle dogs after administration at very high dosages (10- to 25-fold human clinical dosages) for prolonged periods of time.[1][3][4] This resulted in the discontinuation of its development, along with that of ethynerone and anagestone acetate, as well as the removal of several progestins, including chlormadinone acetate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and megestrol acetate, from various markets as contraceptives (although medroxyprogesterone acetate has since been reintroduced).[1][6] Subsequent research revealed that the risk is species-dependent and unique to canines and that there is no similar risk for humans.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 C.H. Lingeman (6 December 2012). Carcinogenic Hormones. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 149–. ISBN 978-3-642-81267-5.
- ↑ Tavassoli FA, Casey HW, Norris HJ (1988). "The morphologic effects of synthetic reproductive steroids on the mammary gland of rhesus monkeys. Mestranol, ethynerone, mestranol-ethynerone, chloroethynyl norgestrel-mestranol, and anagestone acetate-mestranol combinations". Am. J. Pathol. 131 (2): 213–34. PMC 1880606
 . PMID 3358452.
. PMID 3358452. - 1 2 Geil, R. G.; Lamar, J. K. (2009). "FDA studies of estrogen, progestogens, and estrogen/progestogen combinations in the dog and monkey". Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. 3 (1-2): 179–193. doi:10.1080/15287397709529557. ISSN 0098-4108.
- 1 2 Casey, H. W.; Giles, R. C.; Kwapien, R. P. (1979). "Mammary Neoplasia in Animals: Pathologic Aspects and the Effects of Contraceptive Steroids": 129–160. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-81267-5_4.
- ↑ Excerpta medica. Section 3: Endocrinology. 1978. p. 313.
- ↑ Christian Streffer; H. Bolt; D. Follesdal; P. Hall; J.G. Hengstler; P. Jacob; D Oughton; K. Prieß; E. Rehbinder; E. Swaton (11 November 2013). Low Dose Exposures in the Environment: Dose-Effect Relations and Risk Evaluation. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 135–. ISBN 978-3-662-08422-9.
- ↑ Benno Clemens Runnebaum; Thomas Rabe; Ludwig Kiesel (6 December 2012). Female Contraception: Update and Trends. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 134–. ISBN 978-3-642-73790-9.