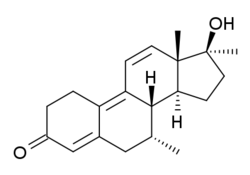
Dimethyltrienolone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | RU-2420 |
| CAS Number | 10110-86-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 44352223 |
| ChemSpider | 23208745 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 298.4192 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Dimethyltrienolone (developmental code name RU-2420), also known as 7α,17α-dimethyltrenbolone, as well as 7α,17α-dimethyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone or 7α,17α-dimethylestra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic, orally active, highly potent anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and 17α-alkylated derivative of 19-nortestosterone that was never introduced for medical use. It is the 7α,17α-dimethyl derivative of trenbolone and the 7α-methyl derivative of metribolone,[1] as well as the Δ9,11 analogue of metribolone and the Δ9,11, 17α-methylated derivative of trestolone. Dimethyltrienolone has among the highest known affinity of any AAS for the androgen (and progesterone) receptors, in studies being surpassed only by trenbolone and metribolone.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ D. Ganten; D. Pfaff (6 December 2012). Actions of Progesterone on the Brain. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 17–. ISBN 978-3-642-69728-9.
- ↑ Waszkowycz B, Clark DE, Frenkel D, Li J, Murray CW, Robson B, Westhead DR (1994). "PRO_LIGAND: an approach to de novo molecular design. 2. Design of novel molecules from molecular field analysis (MFA) models and pharmacophores". J. Med. Chem. 37 (23): 3994–4002. PMID 7966160.
- ↑ Loughney DA, Schwender CF (1992). "A comparison of progestin and androgen receptor binding using the CoMFA technique". J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 6 (6): 569–81. PMID 1291626.