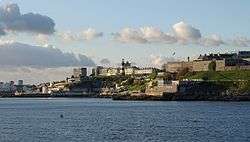Plymouth
| Plymouth | |
|---|---|
| City and Unitary authority | |
|
Plymouth Hoe viewed from Mount Batten | |
| Nickname(s): Britain's Ocean City | |
|
Motto: Turris fortissima est nomen Jehova "The name of Jehovah is the strongest tower"[1] | |
 Plymouth shown within Devon and England | |
| Coordinates: 50°22′17″N 4°08′32″W / 50.37139°N 4.14222°WCoordinates: 50°22′17″N 4°08′32″W / 50.37139°N 4.14222°W | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | South West England |
| Ceremonial county | Devon |
| City status | 1928 |
| Unitary Authority | 1998 |
| Government | |
| • Type | City Council |
| • Body | Plymouth City Council |
| • Administration | Conservative/UKIP (coalition) |
| • Lord Mayor | Pauline Murphy[2] |
| • HQ | Civic Centre Precinct |
| • Wards | 20 |
| • UK Parliament |
Plymouth Moor View Plymouth Sutton and Devonport South West Devon |
| Area[3] | |
| • Total | 30.83 sq mi (79.84 km2) |
| Area rank | 240th (of 326) |
| Highest elevation | 509 ft (155 m) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Population (mid-2014 est.) | |
| • Total | 261,546 |
| • Rank | 55th (of 326) |
| • Density | 8,500/sq mi (3,300/km2) |
| • Demonyms |
Plymothian (formal) Janner (informal) |
| Time zone | GMT (UTC0) |
| • Summer (DST) | BST (UTC+1) |
| Postcode district | PL1 – 9 |
| Area code(s) | 01752 |
| Website | www.plymouth.gov.uk |
Plymouth (![]() i/ˈplɪməθ/) is a city on the south coast of Devon, England, about 37 miles (60 km) south-west of Exeter and 190 miles (310 km) west-south-west of London, between the mouths of the rivers Plym to the east and Tamar to the west where they join Plymouth Sound to form the boundary with Cornwall.
i/ˈplɪməθ/) is a city on the south coast of Devon, England, about 37 miles (60 km) south-west of Exeter and 190 miles (310 km) west-south-west of London, between the mouths of the rivers Plym to the east and Tamar to the west where they join Plymouth Sound to form the boundary with Cornwall.
Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age, when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony – the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War the town was held by the Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646.
Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling imports and passengers from the Americas, and exporting local minerals (tin, copper, lime, china clay and arsenic) while the neighbouring town of Devonport became a strategic Royal Naval shipbuilding and dockyard town. In 1914 three neighbouring independent towns, viz., the county borough of Plymouth, the county borough of Devonport, and the urban district of East Stonehouse were merged to form a single County Borough. The combined town took the name of Plymouth which, in 1928, achieved city status. The city's naval importance later led to its targeting and partial destruction during World War II, an act known as the Plymouth Blitz. After the war the city centre was completely rebuilt and subsequent expansion led to the incorporation of Plympton and Plymstock along with other outlying suburbs in 1967.
The city is home to 261,546 (mid-2014 est.) people, making it the 30th most populous built-up area in the United Kingdom and the second-largest city in the South West, after Bristol. It is governed locally by Plymouth City Council and is represented nationally by three MPs. Plymouth's economy remains strongly influenced by shipbuilding and seafaring including ferry links to Brittany (Roscoff and St Malo) and Spain (Santander), but has tended toward a service-based economy since the 1990s. It has the largest operational naval base in Western Europe – HMNB Devonport and is home to Plymouth University.
History
Early history
Upper Palaeolithic deposits, including bones of Homo sapiens, have been found in local caves,[4] and artefacts dating from the Bronze Age to the Middle Iron Age have been found at Mount Batten showing that it was one of the main trading ports of the country at that time.[5] An unidentified settlement named 'TAMARI OSTIA' (mouth/estuaries of the Tamar) is listed in Ptolemy's Geographia and is presumed to be located in the area of the modern city.[6]
The settlement of Plympton, further up the River Plym than the current Plymouth, was also an early trading port, but the river silted up in the early 11th century and forced the mariners and merchants to settle at the current day Barbican near the river mouth.[7] At the time this village was called Sutton, meaning south town in Old English.[7] The name Plym Mouth, meaning "mouth of the River Plym" was first mentioned in a Pipe Roll of 1211.[8] The name Plymouth first officially replaced Sutton in a charter of King Henry VI in 1440.[9] See Plympton for the derivation of the name Plym.
Early defence and Renaissance

During the Hundred Years' War a French attack (1340) burned a manor house and took some prisoners, but failed to get into the town.[10] In 1403 the town was burned by Breton raiders.[11] On 12 November, 1439, the English Parliament made Plymouth the first town incorporated. In the late fifteenth century, Plymouth Castle, a "castle quadrate", was constructed close to the area now known as The Barbican; it included four round towers, one at each corner, as featured on the city coat of arms.[12] The castle served to protect Sutton Pool, which is where the fleet was based in Plymouth prior to the establishment of Plymouth Dockyard. In 1512 an Act of Parliament was passed for further fortifying Plymouth, and a series of fortifications were then built, including defensive walls at the entrance to Sutton Pool (across which a chain would be extended in time of danger).[13] Defences on St Nicholas Island also date from this time, and a string of six artillery blockhouses were built, including one on Fishers Nose at the south-eastern corner of the Hoe.[14] This location was further strengthened by the building of a fort (later known as Drake's Fort) in 1596, which itself went on to provide the site for the Citadel, established in the 1660s (see below).[15]
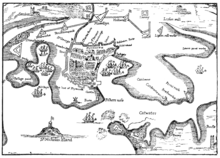
During the 16th century locally produced wool was the major export commodity.[16] Plymouth was the home port for successful maritime traders, among them Sir John Hawkins, who led England's first foray into the Atlantic slave trade,[17] as well as Sir Francis Drake, Mayor of Plymouth in 1581 and 1593.[18] According to legend, Drake insisted on completing his game of bowls on the Hoe before engaging the Spanish Armada in 1588.[18] In 1620 the Pilgrim Fathers set sail for the New World from Plymouth, establishing Plymouth Colony – the second English colony in what is now the United States of America.[19]
During the English Civil War Plymouth sided with the Parliamentarians and was besieged for almost four years by the Royalists.[20] The last major attack by the Royalist was by Sir Richard Grenville leading thousands of soldiers towards Plymouth, but they were defeated by the Plymothians at Freedom Fields Park.[20][21] The civil war ended as a Parliamentary win, but monarchy was restored by King Charles II in 1660, who imprisoned many of the Parliamentary heroes on Drake's Island.[20] Construction of the Royal Citadel began in 1665, after the Restoration; it was armed with cannon facing both out to sea and into the town, rumoured to be a reminder to residents not to oppose the Crown.[22] Mount Batten tower also dates from around this time.[23]
Plymouth Dock, naval power and Foulston



Throughout the 17th century Plymouth had gradually lost its pre-eminence as a trading port. By the mid-17th century commodities manufactured elsewhere in England cost too much to transport to Plymouth and the city had no means of processing sugar or tobacco imports, although it did play a relatively small part in the Atlantic slave trade during the early 18th century.[16]
In the nearby parish of Stoke Damerel the first dockyard, HMNB Devonport, opened in 1690 on the eastern bank of the River Tamar. Further docks were built here in 1727, 1762 and 1793.[1] The settlement that developed here was called "Dock" or "Plymouth Dock" at the time,[24] and a new town, separate from Plymouth, grew up. In 1712 there were 318 men employed and by 1733 it had grown to a population of 3,000 people.[7]
Before the latter half of the 18th century, grain, timber and then coal were Plymouth's main imports.[25] During this time the real source of wealth was from the neighbouring town of Plymouth Dock (renamed in 1824 to Devonport) and the major employer in the entire region was the dockyard.[7] The Three Towns conurbation of Plymouth, Stonehouse and Devonport enjoyed some prosperity during the late 18th and early 19th century and were enriched by a series of neo-classical urban developments designed by London architect John Foulston.[26] Foulston was important for both Devonport and Plymouth and was responsible for several grand public buildings, many now destroyed,[27] including the Athenaeum, the Theatre Royal and Royal Hotel, and much of Union Street.[26]
Local chemist William Cookworthy established his short-lived Plymouth Porcelain venture in 1768 to exploit the deposits of china clay that he had discovered in Cornwall. He was acquainted with engineer John Smeaton, the builder of the third Eddystone Lighthouse.[28]
The 1-mile-long (2 km) Breakwater in Plymouth Sound was designed by John Rennie in order to protect the fleet moving in and out of Devonport; work started in 1812. Numerous technical difficulties and repeated storm damage meant that it was not completed until 1841, twenty years after Rennie's death.[29] In the 1860s, a ring of Palmerston forts was constructed around the outskirts of Devonport, to protect the dockyard from attack from any direction.[30]
Some of the greatest imports to Plymouth from the Americas and Europe during the latter half of the 19th century included maize, wheat, barley, sugar cane, guano, sodium nitrate and phosphate[31] Aside from the dockyard in the town of Devonport, industries in Plymouth such as the gasworks, the railways and tramways and a number of small chemical works had begun to develop in the 19th century, continuing into the 20th century.[32]
Plan for Plymouth 1943
During the First World War, Plymouth was the port of entry for many troops from around the Empire and also developed as a facility for the manufacture of munitions.[33] Although major units of the Royal Navy moved to the safety of Scapa Flow, Devonport was an important base for escort vessels and repairs. Flying boats operated from Mount Batten.[33]

During the Second World War, Devonport was the headquarters of Western Approaches Command until 1941 and Sunderland flying boats were operated by the Royal Australian Air Force. It was an important embarkation point for US troops for D-Day.[34] The city was heavily bombed by the Luftwaffe, in a series of 59 raids known as the Plymouth Blitz.[32] Although the dockyards were the principal targets, much of the city centre and over 3,700 houses were completely destroyed and more than 1,000 civilians lost their lives. This was largely due to Plymouth's status as a major port.[35] Charles Church was hit by incendiary bombs and partially destroyed in 1941 during the Blitz, but has not been demolished, as it is now an official permanent monument to the bombing of Plymouth during World War II.[36]
The redevelopment of the city was planned by Sir Patrick Abercrombie in his 1943 Plan for Plymouth whilst simultaneously working on the reconstruction plan for London.[37] Between 1951 and 1957 over 1000 homes were completed every year mostly using innovative prefabricated systems of just three main types;[38] by 1964 over 20,000 new homes had been built transforming the dense overcrowded and unsanitary slums of the pre-war city into a low density, dispersed suburbia.[38][39] Most of the city centre shops had been destroyed and those that remained were cleared to enable a zoned reconstruction according to his plan.[38][39] In 1962 the modernist high rise of the Civic Centre was constructed, an architecturally significant example of mid twentieth century civic slab-and-tower set piece allowed to fall into disrepair by its owner Plymouth City Council but recently grade II listed by English Heritage to prevent its demolition.[38][40]
Post-war, Devonport Dockyard was kept busy refitting aircraft carriers such as the Ark Royal and, later, nuclear submarines while new light industrial factories were constructed in the newly zoned industrial sector attracting rapid growth of the urban population. The army had substantially left the city by 1971, with barracks pulled down in the 1960s,[39] however the city remains home to the 42 Commando of the Royal Marines.[39]
Government
Local government history
The first record of the existence of a settlement at Plymouth was in the Domesday Book in 1086 as Sudtone, Saxon for south farm, located at the present day Barbican.[1] From Saxon times, it was in the hundred of Roborough.[41] In 1254 it gained status as a town and in 1439, became the first town in England to be granted a Charter by Parliament.[1] Between 1439 and 1934, Plymouth had a Mayor.[42] In 1914 the county boroughs of Plymouth and Devonport, and the urban district of East Stonehouse merged to form a single county borough of Plymouth.[7] Collectively they were referred to as "The Three Towns".[43]
In 1919 Nancy Astor was elected the first ever female member of parliament to take office in the British Houses of Parliament for the constituency of Plymouth Sutton. Taking over office from her husband Waldorf Astor, Lady Astor was a vibrantly active campaigner for her resident constituents. Plymouth was granted city status on 18 October 1928.[44] The city's first Lord Mayor was appointed in 1935 and its boundaries further expanded in 1967 to include the town of Plympton and the parish of Plymstock.[7]
In 1945, Plymouth-born Michael Foot was elected Labour MP for the war-torn constituency of Plymouth Devonport and after serving as Secretary of State for Education and responsible for the 1974 Health and Safety at Work Act, went on to become one of the most distinguished leaders of the Labour party.
The 1971 Local Government White Paper proposed abolishing county boroughs, which would have left Plymouth, a town of 250,000 people, being administered from a council based at the smaller Exeter, on the other side of the county. This led to Plymouth lobbying for the creation of a Tamarside county, to include Plymouth, Torpoint, Saltash, and the rural hinterland.[45] The campaign was not successful, and Plymouth ceased to be a county borough on 1 April 1974 with responsibility for education, social services, highways and libraries transferred to Devon County Council. All powers returned when the city become a unitary authority on 1 April 1998 under recommendations of the Banham Commission.[46]
In the Parliament of the United Kingdom, Plymouth is represented by the three constituencies of Plymouth Moor View, Plymouth Sutton and Devonport and South West Devon and within the European Parliament as South West England.[47] In the 2015 general election all three constituencies returned Conservative MPs, who were Oliver Colvile (for Sutton and devonport), Gary Streeter (for Sutton and Devonport) and Johnny Mercer for Moor View.
City Council

The City of Plymouth is divided into 20 wards, 17 of which elect three councillors and the other three electing two councillors, making up a total council of 57.[48] Each year a third of the council is up for election for three consecutive years – there are no elections on the following "fourth" year, which is when County Council elections take place.[48] The total electorate for Plymouth was 188,924 in April 2015.[49] The local election of 7 May 2015 resulted in a political composition of 28 Labour councillors, 26 Conservative and 3 UKIP resulting in a Labour administration.[50] Plymouth City Council is formally twinned with: Brest, France (1963), Gdynia, Poland (1976), Novorossiysk, Russia (1990) San Sebastián, Spain (1990) and Plymouth, United States (2001).[51]
Plymouth was granted the dignity of Lord Mayor by King George V in 1935. The position is elected each year by a group of six councillors.[52] It is traditional that the position of the Lord Mayor alternates between the Conservative Party and the Labour Party annually and that the Lord Mayor chooses the Deputy Lord Mayor.[52] Conservative councillor Dr John Mahony is the incumbent for 2015–16.[2]

The Lord Mayor's official residence is 3 Elliot Terrace, located on the Hoe.[53] Once a home of Waldorf and Nancy Astor, it was given by Lady Astor to the City of Plymouth as an official residence for future Lord Mayors and is also used today for civic hospitality, as lodgings for visiting dignitaries and High Court judges and it is also available to hire for private events.[53] The Civic Centre municipal office building in Armada Way became a listed building in June 2007 because of its quality and period features, but has become the centre of a controversy as the council planned for its demolition estimating that it could cost £40m to refurbish it, resulting in possible job losses.[54]
Geography

Plymouth lies between the River Plym to the east and the River Tamar to the west; both rivers flow into the natural harbour of Plymouth Sound.[55] Since 1967, the unitary authority of Plymouth has included the, once independent, towns of Plympton and Plymstock which lie along the east of the River Plym.[7] The River Tamar forms the county boundary between Devon and Cornwall and its estuary forms the Hamoaze on which is sited Devonport Dockyard.[55]
The River Plym, which flows off Dartmoor to the north-east, forms a smaller estuary to the east of the city called Cattewater. Plymouth Sound is protected from the sea by the Plymouth Breakwater, in use since 1814.[56] In the Sound is Drake's Island which is seen from Plymouth Hoe, a flat public area on top of limestone cliffs.[57] The Unitary Authority of Plymouth is 79.84 square kilometres (30.83 sq mi).[3] The topography rises from sea level to a height, at Roborough, of about 509 feet (155 m) above Ordnance Datum (AOD).[58]
Geologically, Plymouth has a mixture of limestone, Devonian slate, granite and Middle Devonian limestone.[59] Plymouth Sound, Shores and Cliffs is a Site of Special Scientific Interest, because of its geology.[60] The bulk of the city is built upon Upper Devonian slates and shales and the headlands at the entrance to Plymouth Sound are formed of Lower Devonian slates, which can withstand the power of the sea.[59]
A band of Middle Devonian limestone runs west to east from Cremyll to Plymstock including the Hoe.[59] Local limestone may be seen in numerous buildings, walls and pavements throughout Plymouth.[59] To the north and north east of the city is the granite mass of Dartmoor; the granite was mined and exported via Plymouth. Rocks brought down the Tamar from Dartmoor include ores containing tin, copper, tungsten, lead and other minerals.[59] There is evidence that the middle Devonian limestone belt at the south edge of Plymouth and in Plymstock was quarried at West Hoe, Cattedown and Radford.[61]
Urban Form

On 27 April 1944 Sir Patrick Abercrombie's Plan for Plymouth to rebuild the bomb-damaged city was published; it called for demolition of the few remaining pre-War buildings in the city centre to make way for their replacement with wide, parallel, modern boulevards aligned east–west linked by a north–south avenue (Armada Way) linking the railway station with the vista of Plymouth Hoe.[37] A peripheral road system connecting the historic Barbican on the east and Union Street to the west determines the principal form of the city centre, even following pedestrianisation of the shopping centre in the late 1980s, and continues to inform the present 'Vision for Plymouth' developed by a team led by Barcelona-based architect David MacKay in 2003 which calls for revivification of the city centre with mixed-use and residential.[62] In suburban areas, post-War prefabs had already begun to appear by 1946, and over 1,000 permanent council houses were built each year from 1951–57 according to the Modernist zoned low-density garden city model advocated by Abercrombie.[39] By 1964 over 20,000 new homes had been built, more than 13,500 of them permanent council homes and 853 built by the Admiralty.[39] Plymouth is home to 28 parks with an average size of 45,638 square metres (491,240 sq ft).[63] Its largest park is Central Park,[64] with other sizeable green spaces including Victoria Park, Freedom Fields Park, Alexandra Park, Devonport Park and the Hoe.[63]
Climate
| Plymouth[65] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Along with the rest of South West England, Plymouth has a temperate oceanic climate (Köppen Cfb) which is generally wetter and milder than the rest of England. This means a wide range of exotic plants can be grown. The annual mean temperature is approximately 11 °C (52 °F). Due to the modifying effect of the sea the seasonal range is less than in most other parts of the UK.[66] As a result of this summer highs are lower than points further north in the UK, however the coldest month of February has mean minimum temperatures as mild as between 3 and 4 °C (37 and 39 °F). Snow is rare, not usually equating to more than a few flakes, but there have been exclusions, namely the European winter storms of 2009-10 which, in early January, covered Plymouth in at least 1 inch (2.5 cm) of snow; more on higher ground. Another period of notable snow occurred from 17–19 December 2010 when up to 8 inches (20 cm) of snow fell through the period – though only 2 inches (5.1 cm) would lie at any one time due to melt. Over the 1961–1990 period, annual snowfall accumulation averaged less than 7 cm (3 in) per year.[67] July and August are the warmest months with mean daily maxima over 19 °C (66 °F).[65]
South West England has a favoured location when the Azores High pressure area extends north-eastwards towards the UK, particularly in summer. Coastal areas have average annual sunshine totals over 1,600 hours.[66]
Rainfall tends to be associated with Atlantic depressions or with convection. The Atlantic depressions are more vigorous in autumn and winter and most of the rain which falls in those seasons in the south-west is from this source. Average annual rainfall is around 980 millimetres (39 in). November to March have the highest mean wind speeds, with June to August having the lightest winds. The predominant wind direction is from the south-west.[66]
Typically, the warmest day of the year (1971–2000) will achieve a temperature of 26.6 °C (80 °F),[68] although in June 1976 the temperature reached 31.6 °C (89 °F),[69] the site record. On average, 4.25 days[70] of the year will report a maximum temperature of 25.1 °C (77 °F) or above. During the winter half of the year, the coldest night will typically fall to −4.1 °C (25 °F)[71] although in January 1979 the temperature fell to −8.8 °C (16 °F).[72] Typically, 18.6 nights[73] of the year will register an air frost.
| Climate data for Mount Batten, Plymouth, 1981-2010, extremes 1960– | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.4 (57.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.3 (64.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
25.9 (78.6) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.9 (87.6) |
26.3 (79.3) |
23.0 (73.4) |
17.1 (62.8) |
16.1 (61) |
31.6 (88.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) |
8.8 (47.8) |
10.5 (50.9) |
12.6 (54.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
18.0 (64.4) |
19.9 (67.8) |
20.0 (68) |
18.1 (64.6) |
14.8 (58.6) |
11.8 (53.2) |
9.5 (49.1) |
14.0 (57.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 4.0 (39.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
4.8 (40.6) |
5.9 (42.6) |
8.8 (47.8) |
11.2 (52.2) |
13.3 (55.9) |
13.4 (56.1) |
11.6 (52.9) |
9.3 (48.7) |
6.4 (43.5) |
4.5 (40.1) |
8.1 (46.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.8 (16.2) |
−7 (19) |
−7 (19) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
2.9 (37.2) |
6.1 (43) |
5.9 (42.6) |
1.9 (35.4) |
−1 (30) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 108.3 (4.264) |
84.1 (3.311) |
78.0 (3.071) |
66.9 (2.634) |
63.8 (2.512) |
57.2 (2.252) |
62.3 (2.453) |
67.4 (2.654) |
73.7 (2.902) |
113.4 (4.465) |
113.4 (4.465) |
118.8 (4.677) |
1,007.4 (39.661) |
| Average precipitation days | 15.1 | 11.6 | 12.4 | 10.9 | 10.4 | 8.5 | 9.4 | 10.1 | 9.9 | 14.4 | 15.0 | 14.5 | 142.1 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 61.9 | 85.5 | 123.3 | 187.5 | 224.8 | 222.8 | 213.8 | 204.4 | 160.8 | 115.5 | 75.3 | 54.5 | 1,730.1 |
| Source: Met Office[74] | |||||||||||||
Education

The University of Plymouth enrolls 25,895 total students as of 2014/15 (22nd largest in the UK out of 165).[75] It also employs 3,000 staff with an annual income of around £160 million.[76] It was founded in 1992 from Polytechnic South West (formerly Plymouth Polytechnic) following the Further and Higher Education Act 1992.[77] It has a wide range of courses includeing those in marine focused business, marine engineering, marine biology and Earth, ocean and environmental sciences, surf science, shipping and logistics.[78] The university formed a joint venture with the fellow Devonian University of Exeter in 2000, establishing the Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry. The college is ranked 8th out of 30 universities in the UK in 2011 for medicine.[79] Its dental school was established in 2006, which also provides free dental care in an attempt to improve access to dental care in the South West.
The University of St Mark & St John (known as "Marjon" or "Marjons") specialises in teacher training, and offers training across the country and abroad.[80]
The city is also home to two large colleges. The City College Plymouth provides courses from the most basic to Foundation degrees for approximately 26,000 students.[81] Plymouth College of Art offers a selection of courses including media. It was started 153 years ago and is now one of only four independent colleges of art and design in the UK.[82]
Plymouth also has 71 state primary phase schools, 13 state secondary schools, eight special schools and three selective state grammar schools, Devonport High School for Girls, Devonport High School for Boys and Plymouth High School for Girls.[83] There is also an independent school Plymouth College.
The city was also home to the Royal Naval Engineering College; opened in 1880 in Keyham, it trained engineering students for five years before they completed the remaining two years of the course at Greenwich. The college closed in 1910, but in 1940 a new college opened at Manadon. This was renamed Dockyard Technical College in 1959 before finally closing in 1994; training was transferred to the University of Southampton.[84]
Plymouth is home to the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom (MBA) which conducts research in all areas of the marine sciences. The Plymouth Marine Laboratory is an offshoot of the MBA. Together with the National Marine Aquarium, the Sir Alister Hardy Foundation for Ocean Sciences, Plymouth University's Marine Institute and the Diving Diseases Research Centre, these marine-related organisations form the Plymouth Marine Sciences Partnership. The Plymouth Marine Laboratory, which focuses on global issues of climate change and sustainability. It monitors the effects of ocean acidity on corals and shellfish and reports the results to the UK government. It also cultivates algae that could be used to make biofuels or in the treatment of waste water by using technology such as photo-bioreactors. It works alongside the Boots Group to investigate the use of algae in skin care protects, taking advantage of the chemicals they contain that adapt to protect themselves from the sun.[85]
Demography
From the 2011 Census, the Office for National Statistics published that Plymouth's unitary authority area population was 256,384;[86] 15,664 more people than that of the last census from 2001, which indicated that Plymouth had a population of 240,720.[87] The Plymouth urban area had a population of 260,203 in 2011 (the urban sprawl which extends outside the authority's boundaries). The city's average household size was 2.3 persons.[88][89] At the time of the 2011 UK census, the ethnic composition of Plymouth's population was 96.2% White (of 92.9% was White British), with the largest minority ethnic group being Chinese at 0.5%.[86] The white Irish ethnic group saw the largest decline in its share of the population since the 2001 Census (-24%), while the Other Asian and Black African had the largest increases (360% and 351% respectively).[86][90] This excludes the two new ethnic groups added to the 2011 census of Gypsy or Irish Traveller and Arab. The population rose rapidly during the second half of the 19th century, but declined by over 1.6% from 1931 to 1951.
Plymouth's gross value added (a measure of the size of its economy) was 5,169 million GBP in 2013 making up 25% of Devon's GVA.[91] Its GVA per person was £19,943 and compared to the national average of £23,755, was £3,812 lower.[91] Plymouth's unemployment rate was 7.0% in 2014 which was 2.0 points higher than the South West average and 0.8 points higher than the average for Great Britain (England, Wales and Scotland).[92]
A 2014 profile by the National Health Service showed Plymouth had higher than average levels of poverty and deprivation (26.2% of population among the poorest 20.4% nationally). Life expectancy, at 78.3 years for men and 82.1 for women, was the lowest of any region in the South West of England.[93]
| Ethnic group | Representation, 2011 | Change since 2001 |
|---|---|---|
| White | 96.15% | -2% |
| Mixed | 1.28% | +98% |
| Asian | 1.52% | +157% |
| Black | 0.65% | +249% |
| Other | 0.39% | +83% |
Economy

Because of its coastal location, the economy of Plymouth has traditionally been maritime,[95] in particular the defence sector with over 12,000 people employed and approximately 7,500 in the armed forces.[96] The Plymouth Gin Distillery has been producing Plymouth Gin since 1793, which was exported around the world by the Royal Navy.[97] During the 1930s, it was the most widely distributed gin and has a controlled term of origin.[97] Since the 1980s, employment in the defence sector has decreased substantially and the public sector is now prominent particularly in administration, health, education, medicine and engineering.[96]
Devonport Dockyard is the UK's only naval base that refits nuclear submarines and the Navy estimates that the Dockyard generates about 10% of Plymouth's income.[94] Plymouth has the largest cluster of marine and maritime businesses in the south west with 270 firms operating within the sector.[98] Other substantial employers include the university with almost 3,000 staff,[76] as well as the Plymouth Science Park employing 500 people in 50 companies.[96] Several employers have chosen to locate their headquarters in Plymouth, including Hemsley Fraser.
Plymouth has a post-war shopping area in the city centre with substantial pedestrianisation.[39] At the west end of the zone inside a grade II listed building is the Pannier Market that was completed in 1959 – pannier meaning "basket" from French, so it translates as "basket market".[99] In terms of retail floorspace, Plymouth is ranked in the top five in the South West,[100] and 29th nationally.[101] Plymouth was one of the first ten British cities to trial the new Business Improvement District initiative.[102] The Tinside Pool is situated at the foot of the Hoe and became a grade II listed building in 1998 before being restored to its 1930s look for £3.4 million.[103]
Plymouth 2020
As of 2003, Plymouth Council has been undertaking a project of urban redevelopment called the "Vision for Plymouth" launched by the architect David Mackay and backed by both Plymouth City Council and the Plymouth Chamber of Commerce (PCC).[104] Its projects range from shopping centres, a cruise terminal, a boulevard and to increase the population to 300,000 and build 33,000 dwellings.[104]

In 2004 the old Drake Circus shopping centre and Charles Cross car park were demolished and replaced by the latest Drake Circus Shopping Centre, which opened in October 2006.[105] It received negative feedback before opening when David Mackay said it was already "ten years out of date".[105] In contrast, the Theatre Royal's production and education centre, TR2, which was built on wasteland at Cattedown, was a runner-up for the RIBA Stirling Prize for Architecture in 2003.[106]
There is a project involving the future relocation of Plymouth City Council's headquarters, the civic centre, to the current location of the Bretonside bus station; it would involve both the bus station and civic centre being demolished and a rebuilt together at the location with the land from the civic centre being sold off.[107] Other suggestions include the demolition of the Plymouth Pavilions entertainment arena to create a canal "boulevard" linking Millbay to the city centre. Millbay is being regenerated with mixed residential, retail and office space alongside the ferry port.[108]
Transport

The A38 dual-carriageway runs from east to west across the north of the city. Within the city it is designated as 'The Parkway' and represents the boundary between the urban parts of the city and the generally more recent suburban areas. Heading east, it connects Plymouth to the M5 motorway about 40 miles (65 km) away near Exeter; and heading west it connects Cornwall and Devon via the Tamar Bridge.[109] Regular bus services are provided by Plymouth Citybus, Stagecoach South West and Target Travel.[110] There are three Park and ride services located at Milehouse, Coypool (Plympton) and George Junction (Plymouth City Airport), which are operated by Stagecoach South West.[111]

A regular international ferry service provided by Brittany Ferries operates from Millbay taking cars and foot passengers directly to France (Roscoff) and Spain (Santander) on the three ferries, MV Armorique, MV Bretagne and MV Pont-Aven.[112] The Cremyll Ferry is a passenger ferry between Stonehouse and the Cornish hamlet of Cremyll, which is believed to have operated continuously since 1204.[113] There is also a pedestrian ferry from the Mayflower Steps to Mount Batten,[114] and an alternative to using the Tamar Bridge via the Torpoint Ferry (vehicle and pedestrian) across the River Tamar.[115]
The city's airport was Plymouth City Airport about 4 miles (6 km) north of the city centre.[116] The airport was home to the local airline Air Southwest,[117] which operated flights across the United Kingdom and Ireland.[118] In June 2003, a report by the South West RDA was published looking at the future of aviation in the south-west and the possible closure of airports.[119] It concluded that the best option for the south-west was to close Plymouth City Airport and expand Exeter International Airport and Newquay Cornwall Airport, although it did conclude that this was not the best option for Plymouth.[120] In April 2011, it was announced that the airport would close,[121] which it did on 23 December. However, FlyPlymouth plans to reopen the city airport by 2018, which will provide daily services to various destinations including London.[122]
Plymouth railway station, which opened in 1877,[123] is managed by Great Western Railway and also sees trains on the CrossCountry network.[124] Smaller stations are served by local trains on the Tamar Valley Line and Cornish Main Line.[125] First Great Western have come under fire recently, due to widespread rail service cuts across the south-west, which affect Plymouth greatly.[126] Three MPs from the three main political parties in the region have lobbied that the train services are vital to its economy.[127]
The Exeter to Plymouth railway of the LSWR needs to be reopened to connect Cornwall and Plymouth to the rest of the UK railway system on an all weather basis. There are proposals to reopen the line from Tavistock to Bere Alston for a through service to Plymouth.[128] On the night of 4 February 2014, amid high winds and extremely rough seas, part of the sea wall at Dawlish was breached washing away around 40 metres (130 ft) of the wall and the ballast under the railway immediately behind. The line was closed. Network Rail began repair work [129] and the line reopened on 4 April 2014.[130] In the wake of widespread disruption caused by damage to the mainline track at Dawlish by coastal storms in February 2014, Network Rail are considering reopening the Tavistock to Okehampton and Exeter section of the line as an alternative to the coastal route.[131]
Religion
Plymouth has about 150 churches and its Roman Catholic cathedral (1858) is in Stonehouse.[132][133] The city's oldest church is Plymouth Minster, also known as St Andrew's Church, (Anglican) located at the top of Royal Parade—it is the largest parish church in Devon and has been a site of gathering since AD 800.[132] The city also includes five Baptist churches, over twenty Methodist chapels, and thirteen Roman Catholic churches.[134] In 1831 the first Brethren assembly in England, a movement of conservative non-denominational Evangelical Christians, was established in the city, so that Brethren are often called Plymouth Brethren, although the movement did not begin locally.[135]
Plymouth has the first known reference to Jews in the South West from Sir Francis Drake's voyages in 1577 to 1580, as his log mentioned "Moses the Jew" – a man from Plymouth.[132] The Plymouth Synagogue is a Listed Grade II* building, built in 1762 and is the oldest Ashkenazi Synagogue in the English speaking world.[136] There are also places of worship for Islam, Bahá'í, Buddhism, Unitarianism, Chinese beliefs and Humanism.[137]
58.1% of the population described themselves in the 2011 census return as being at least nominally Christian and 0.8% as Muslim with all other religions represented by less than 0.5% each. The portion of people without a religion is 32.9%; above the national average of 24.7%. 7.1% did not state their religious belief.[138] Since the 2001 Census, the number of Christians and Jews has decreased (-16% and -7% respectively), while all other religions have increased and non-religious people have almost doubled in number.[139]
Culture

Built in 1815, Union Street was at the heart of Plymouth's historical culture.[140] It became known as the servicemen's playground, as it was where sailors from the Royal Navy would seek entertainment of all kinds.[140] During the 1930s, there were 30 pubs and it attracted such performers as Charlie Chaplin to the New Palace Theatre.[140] It is now the late-night hub of Plymouth's entertainment strip,[141] but has a reputation for trouble at closing hours.[142]
Outdoor events and festivals are held including the annual British Firework Championships in August, which attracts tens of thousands of people across the waterfront.[143] In August 2006 the world record for the most amount of simultaneous fireworks was surpassed, by Roy Lowry of the University of Plymouth, over Plymouth Sound.[144] Since 1992 the Music of the Night has been performed in the Royal Citadel by the 29 Commando Regiment and local performers to raise money for local and military charities.[145]
The city's main theatres are the Theatre Royal (1,315 capacity),[146] its Drum Theatre (200 capacity),[147] and its production and creative learning centre, The TR2.[148] The Plymouth Pavilions has multiple uses for the city staging music concerts, basketball matches and stand-up comedy.[149] There are also three cinemas: Reel Cinema at Derrys Cross, Plymouth Arts Centre at Looe Street and a Vue cinema at the Barbican Leisure Park.[150] The Plymouth City Museum and Art Gallery is operated by Plymouth City Council allowing free admission – it has six galleries.[151] The Plymouth Athenaeum, which includes a local interest library, is a society dedicated to the promotion of learning in the fields of science, technology, literature and art. From 1961 to 2009 it also housed a theatre.[152]
Plymouth is the regional television centre of BBC South West.[153] A team of journalists are headquartered at Plymouth for the ITV West Country regional station, after a merger with ITV West forced ITV Westcountry to close on 16 February 2009.[154] The main local newspapers serving Plymouth are The Herald and Western Morning News with Radio Plymouth, BBC Radio Devon, Heart South West, and Pirate FM being the local radio stations with the most listeners. [155]
Sport
Plymouth is home to Plymouth Argyle F.C., who play in the fourth tier of English football league known as Football League Two. The team's home ground is called Home Park and is located in Central Park.[156] It links itself with the group of English non-conformists that left Plymouth for the New World in 1620: its nickname is "The Pilgrims".[157] The city also has four Non-League football clubs; Plymouth Parkway F.C. who play at Bolitho Park, Elburton Villa F.C. who play at Haye Road, Vospers Oak Villa F.C. who play at Weston Mill and Plymstock United F.C. who play at Deans Cross. All four clubs play in the South West Peninsula League.
Other sports clubs include Plymouth Albion R.F.C. and the Plymouth Raiders basketball club. Plymouth Albion Rugby Football Club is a rugby union club that was founded in 1875 and are currently competing in the third tier of Professional English Rugby. They play at the Brickfields.[158] Plymouth Raiders play in the British Basketball League – the top tier of British basketball. They play at the Plymouth Pavilions entertainment arena and were founded in 1983.[159] Plymouth cricket club was formed in 1843, the current 1st XI play in the Devon Premier League. Plymouth Devils were a speedway team in the British Premier League, but have recently folded. Plymouth was home to an American football club, the Plymouth Admirals until 2010. Plymouth is also home to Plymouth Marjons Hockey Club, with their 1st XI playing in the National League last season.
Plymouth is an important centre for watersports, especially scuba diving and sailing. The Port of Plymouth Regatta is one of the oldest regattas in the world, and has been held regularly since 1823. In September 2011, Plymouth hosted the America's Cup World Series for nine days.[160]
Public services

Since 1973 Plymouth has been supplied water by South West Water. Prior to the 1973 take over it was supplied by Plymouth County Borough Corporation.[161] Before the 19th century two leats were built in order to provide drinking water for the town. They carried water from Dartmoor to Plymouth. A watercourse, known as Plymouth or Drake's Leat, was opened on 24 April 1591 to tap the River Meavy.[162] The Devonport Leat was constructed to carry fresh drinking water to the expanding town of Devonport and its ever-growing dockyard. It was fed by three Dartmoor rivers: The West Dart, Cowsic and Blackabrook. It seems to have been carrying water since 1797, but it was officially completed in 1801. It was originally designed to carry water to Devonport town, but has since been shortened and now carries water to Burrator Reservoir, which feeds most of the water supply of Plymouth.[163] Burrator Reservoir is located about 5 miles (8 km) north of the city and was constructed in 1898 and expanded in 1928.[164]

Plymouth City Council is responsible for waste management throughout the city and South West Water is responsible for sewerage.[165][166] Plymouth's electricity is supplied from the National Grid and distributed to Plymouth via Western Power Distribution.[167] On the outskirts of Plympton a combined cycle gas-powered station, the Langage Power Station, which started to produce electricity for Plymouth at the end of 2009.[168]
Her Majesty's Courts Service provide a Magistrates' Court and a Combined Crown and County Court in the city.[169][170] The Plymouth Borough Police, formed in 1836, eventually became part of Devon and Cornwall Constabulary.[171] There are police stations at Charles Cross and Crownhill (the Divisional HQ) and smaller stations at Plympton and Plymstock.[172] The city has one of the Devon and Cornwall Area Crown Prosecution Service Divisional offices.[173] Plymouth has five fire stations located in Camel's Head, Crownhill, Greenbank, Plympton and Plymstock which is part of Devon and Somerset Fire and Rescue Service.[174] The Royal National Lifeboat Institution have an Atlantic 85 class lifeboat and Severn class lifeboat stationed at Millbay Docks.[175]
Plymouth is served by Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust and the city's NHS hospital is Derriford Hospital 4 miles (6 km) north of the city centre. The Royal Eye Infirmary is located at Derriford Hospital.[176] South Western Ambulance Service NHS Foundation Trust operates in Plymouth and the rest of the south west; its headquarters are in Exeter.[177]
The mid-19th century burial ground at Ford Park Cemetery was reopened in 2007 by a successful trust and the City council operate two large early 20th century cemeteries at Weston Mill and Efford both with crematoria and chapels. There is also a privately owned cemetery on the outskirts of the city, Drake Memorial Park which does not allow headstones to mark graves, but a brass plaque set into the ground.[178]
Landmarks and tourist attractions



After the English Civil War the Royal Citadel was built in 1666 on the east end of Plymouth Hoe, to defend the port from naval attacks, suppress Plymothian Parliamentary leanings and to train the armed forces. Guided tours are available in the summer months.[22] Further west is Smeaton's Tower, which was built in 1759 as a lighthouse on rocks 14 miles (23 km) off shore, but dismantled and the top two thirds rebuilt on the Hoe in 1877.[179] It is open to the public and has views over the Plymouth Sound and the city from the lantern room.[180] Plymouth has 20 war memorials of which nine are on The Hoe including: Plymouth Naval Memorial, to remember those killed in World Wars I and II, and the Armada Memorial, to commemorate the defeat of the Spanish Armada.[181]
The early port settlement of Plymouth, called "Sutton", approximates to the area now referred to as the Barbican and has 100 listed buildings and the largest concentration of cobbled streets in Britain.[182] The Pilgrim Fathers left for the New World in 1620 near the commemorative Mayflower Steps in Sutton Pool.[183] Also on Sutton Pool is the National Marine Aquarium which displays 400 marine species and includes Britain's deepest aquarium tank.[184]
One mile (two kilometres) upstream on the opposite side of the River Plym is the Saltram estate, which has a Jacobean and Georgian mansion.[185]
On the northern outskirts of the city, Crownhill Fort is a well restored example of a "Palmerston's Folly". It is owned by the Landmark Trust and is open to the public.[186]
To the west of the city is Devonport, one of Plymouth's historic quarters. As part of Devonport's millennium regeneration project, the Devonport Heritage Trail has been introduced, complete with over 70 waymarkers outlining the route.[187]
Plymouth is often used as a base by visitors to Dartmoor, the Tamar Valley and the beaches of south-east Cornwall.[188] Kingsand, Cawsand and Whitsand Bay are popular.[189]
The Roland Levinsky building, the landmark building of the University of Plymouth, is located in the city's central quarter. Designed by leading architect Henning Larsen, the building was opened in 2008 and houses the University's Arts faculty. It has been consistently considered one of the UK's most beautiful university buildings.[190]
- Images of landmarks

 National Armada memorial (Britannia)
National Armada memorial (Britannia) Naval War Memorial
Naval War Memorial The Parade, Barbican
The Parade, Barbican The Mayflower Steps Memorial
The Mayflower Steps Memorial Saltram House remodelled by the architect Robert Adam
Saltram House remodelled by the architect Robert Adam
Notable people

People from Plymouth are known as Plymothians or less formally as Janners.[191] Its meaning is described as a person from Devon, deriving from Cousin Jan (the Devon form of John), but more particularly in naval circles anyone from the Plymouth area.[192]
The Elizabethan navigator, Sir Francis Drake was born in the nearby town of Tavistock and was the mayor of Plymouth.[193] He was the first Englishman to circumnavigate the world and was known by the Spanish as El Draco meaning "The Dragon" after he raided many of their ships.[194] He died of dysentery in 1596 off the coast of Puerto Rico.[195] In 2002 a mission to recover his body and bring it to Plymouth was allowed by the Ministry of Defence.[196] His cousin and contemporary John Hawkins was a Plymouth man. Painter Sir Joshua Reynolds, founder and first president of the Royal Academy was born and educated in nearby Plympton, now part of Plymouth. William Cookworthy born in Kingsbridge set up his successful porcelain business in the city and was a close friend of John Smeaton designer of the Eddystone Lighthouse. On 26 January 1786, Benjamin Robert Haydon, an English painter who specialised in grand historical pictures, was born here. The naturalist Dr William Elford Leach FRS, who did much to pave the way in Britain for Charles Darwin, was born at Hoe Gate in 1791.
Antarctic explorers Robert Falcon Scott and Frank Bickerton both lived in the city.[197][198] Artists include Beryl Cook whose paintings depict the culture of Plymouth[199] and Robert Lenkiewicz, whose paintings investigated themes of vagrancy, sexual behaviour and suicide, lived in the city from the 1960s until his death in 2002.[200] Illustrator and creator of children's series Mr Benn and King Rollo, David McKee, was born and brought up in South Devon and trained at Plymouth College of Art. Jazz musician John Surman, born in nearby Tavistock, has close connections to the area, evidenced by his 2012 album Saltash Bells. The avant garde prepared guitarist Keith Rowe was born in the city before establishing the jazz free improvisation band AMM in London in 1965 and MIMEO in 1997. The musician and film director Cosmo Jarvis has lived in several towns in South Devon and has filmed videos in and around Plymouth.[201] In addition, actors Sir Donald Sinden and Judi Trott. George Passmore of Turner Prize winning duo Gilbert and George was born in the city, as was Labour politician Michael Foot whose family reside at nearby Trematon Castle.[202]
Notable athletes include swimmer Sharron Davies,[203] diver Tom Daley,[204] dancer Wayne Sleep,[205] and footballer Trevor Francis.[206] Other past residents include composer journalist and newspaper editor William Henry Wills, Ron Goodwin,[207] and journalist Angela Rippon and comedian Dawn French.[208] Canadian politician and legal scholar Chris Axworthy hails from Plymouth. America based actor Donald Moffat, whose roles include American Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson in the film The Right Stuff, and fictional President Bennett in Clear and Present Danger, was born in Plymouth.[209]
See also
- Grade I listed buildings in Plymouth
- Grade II* listed buildings in Plymouth
- Fortifications of Plymouth
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Brief history of Plymouth". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 20 July 2008.
- 1 2 "The Lord Mayor". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- 1 2 "Standard Area Measurements - Local Authorities - Dec 2010 (SAM_LAD_DEC_2010_UK)". UK Standard Area Measurements (SAM). Office for National Statistics. 31 December 2010. Retrieved 1 October 2011.
- ↑ Andrew T. Chamberlain; Keith W. Ray; Charlotte Henderson; Richard Welton Fisher (1994). A Catalogue of Quaternary Fossil-bearing Cave Sites in the Plymouth Area. Plymouth City Archaeology. ISBN 1-85522-345-7.
- ↑ Cunliffe, Barry (2004). "Britain and the Continent:Networks of Interaction". In Malcolm Todd. A Companion to Roman Britain. Blackwell Publishing. p. 3. ISBN 0-631-21823-8. Retrieved 23 June 2008.
- ↑ Denis Larionov & Alexander Zhulin. "Read the ebook Geographia classica, or, The application of antient geography to the classics by Samuel Butler". Ebooksread.com. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "The early history of Plymouth". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 19 July 2008.
- ↑ Gill, Crispin (1979). Plymouth, a new history. Newton Abbot: David and Charles. ISBN 9780715376171. (Quoted in Moseley, Brian (2 January 2011). "Plymouth – a History". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 24 October 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.)
- ↑ Moseley, Brian (24 June 2013). "Place names". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 27 September 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ Sumption, Jonathan (1999). "Sluys and Tournai: The War of the Alberts". The Hundred Years War: Trial by Battle. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 347. ISBN 0-8122-1655-5. Retrieved 29 June 2008.
- ↑ "Devon timeline". Devon County Council. Retrieved 29 June 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth City Council: coat of arms".
- ↑ "www.british-history.ac.uk/magna-britannia/vol6".
- ↑ See 1591 Spry Map of Plimmouth and surrounding areas, British Library
- ↑ "www.castlesfortsbattles.co.uk".
- 1 2 "Slave Ships in Plymouth". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 26 July 2008. Archived 2008-06-09 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Adventurers and Slavers". The National Archives. Retrieved 13 October 2007.
- 1 2 "Sir Francis Drake". The BBC. Retrieved 24 July 2008.
- ↑ Kellogg, William O. (2003). American History the Easy Way: The Easy Way. Barron's Educational Series (3rd ed.). Hauppauge, N.Y.: Barron's. p. 20. ISBN 0-7641-1973-7. Retrieved 14 November 2008.
- 1 2 3 "Siege". The BBC. 6 January 2003. Retrieved 6 July 2008.
- ↑ Jenny Mashford. "Plymouth City Council - Freedom Fields Park".
- 1 2 "Coast Walks: Point 3 – The Citadel". The BBC. 25 January 2008. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ↑ Jewitt, Llewellynn Frederick (1873). A history of Plymouth. Oxford University. p. 648.
- ↑ Carrington, Henry Edmund (1828). The Plymouth and Devonport guide. Oxford University. p. 1. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ↑ "Cargo and Trade, Ocean Landing Pier" (PDF). Plymouth City Museum and Art Gallery. Retrieved 26 July 2008.
- 1 2 Moseley, Brian (3 December 2011). "John Foulston (1772-1842)". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 15 May 2012. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ "Devonport, Devon". Architecture.com. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ "Information Sheet: Cookworthy's Plymouth Porcelain" (PDF). Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ↑ Moseley, Brian (26 February 2013). "Breakwater". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 17 May 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ Moseley, Brian (21 January 2011). "Palmerston's Forts and Batteries". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 17 May 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ Moseley, Brian (25 August 2012). "Imports (Port of Plymouth)". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 28 September 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- 1 2 "Characteristics of the City of Plymouth (Historical and industrial legacy)". Plymouth City Council. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 24 July 2008.
- 1 2 Moseley, Brian (21 February 2013). "The Great War, 1914-1918". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 28 November 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ "D-Day In Plymouth, Uk, And American Infantry". Cyber-heritage.co.uk. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ Gill, Crispin (1993). Plymouth. A New History. Devon Books. pp. 259–262. ISBN 0-86114-882-7.
- ↑ "Frosty response to church climb". BBC News. 17 November 2005. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- 1 2 Gould, Jeremy (March 2007). Architecture and the Plan for Plymouth: The Legacy of a British City. Architectural Review.
- 1 2 3 4 Gould, Jeremy (2010). Plymouth; Vision of a Modern City. English Heritage.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Gill, Crispin (1993). Plymouth. A New History. Devon Books. pp. 262–267. ISBN 0-86114-882-7.
- ↑ "Sale of Plymouth Civic Centre". English Heritage. 15 October 2010. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ "The hundreds of devon". GENUKI. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ↑ "List of Mayors and Lord Mayors from 1439 to date". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 8 December 2008.
- ↑ "Three Towns Amalgamation". The Times. UK. 9 February 1914.
- ↑ "The City of Plymouth". The Times. UK. 18 October 1928.
- ↑ "South West Regional Office of the Labour Party archives". The National Archives. 21 March 1972. pp. 38423/32. Retrieved 20 July 2008.
- ↑ Department of the Environment (18 July 1996). The Devon (City of Plymouth and Borough of Torbay) (Structural Change) Order 1996. Office of Public Sector Information. ISBN 0-11-062779-2. Retrieved 26 July 2008.
- ↑ "Elected representatives". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- 1 2 "Plymouth wards". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 27 October 2009.
- ↑ "Electorate details, register statistics and annual performance". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- ↑ "About Plymouth City Council". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- ↑ "Twin towns". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
- 1 2 "Lord Mayoralty". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- 1 2 "Elliot Terrace". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- ↑ "Council opposes building listing". BBC News. 10 July 2007. Retrieved 20 November 2008.
- 1 2 3 "Devon's rivers: The Tamar". The BBC. 6 February 2008. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- ↑ Otter, R. A. (1994). "The Tamar Valley and Plymouth". Civil Engineering Heritage: Southern England. Thomas Telford. p. 48. ISBN 0-7277-1971-8. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- ↑ Report and Transactions. 9. Devonshire Association for the Advancement of Science. 1877. p. 426. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
- ↑ "Characteristics of the City of Plymouth (The geography)". Plymouth City Council. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 25 July 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Characteristics of the City of Plymouth (The geology)". Plymouth City Council. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 26 July 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth Sound Shores and Cliffs" (PDF). Natural England. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- ↑ "Characteristics of the City of Plymouth (Limestone)". Plymouth City Council. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 26 July 2008.
- ↑ harrisp. "Plymouth City Council - A vision for Plymouth".
- 1 2 "Parks and open spaces". Plymouth City Council. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ↑ "Central Park". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 17 February 2009.
- 1 2 "Climatological Normals of Plymouth – 1961–1990". Climatological Information for United Kingdom and Ireland. The Hong Kong Observatory. Retrieved 9 June 2008.
- 1 2 3 "About south-west England". The Met Office. Archived from the original on 25 February 2006. Retrieved 28 May 2006.
- ↑ "Climatological Normals of Plymouth – 1961–1990". NOAA. Retrieved 9 June 2011.
- ↑ "Average warmest day". Retrieved 9 June 2011.
- ↑ "1976 High". Retrieved 9 June 2011.
- ↑ ">25.1c days". Retrieved 9 June 2011.
- ↑ "Average coldest night". Retrieved 9 June 2011.
- ↑ "1979 minimum". Retrieved 9 June 2011.
- ↑ "Frost average". Retrieved 9 June 2011.
- ↑ "Plymouth climate".
- ↑ "2014/15 Students by HE provider, level, mode and domicile" (XLSX). Higher Education Statistics Agency. Retrieved 19 January 2016.
- 1 2 "University of Plymouth – an introduction". The University of Plymouth. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Our history". The University of Plymouth. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- ↑ "Undergraduate courses A-Z". The University of Plymouth. Retrieved 18 June 2008.
- ↑ "University guide 2011: Medicine". The Guardian. UK. 8 June 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- ↑ "The History of the University College". The University College Plymouth St Mark & St John. Retrieved 19 June 2008.
- ↑ "The College". City College Plymouth. Retrieved 19 June 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth College of Art home page". Plymouth College of Art. Retrieved 19 June 2008.
- ↑ "Schools". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 19 June 2008.
- ↑ Moseley, Brian (1 March 2007). "Royal Naval Engineering College HMS Thunderer". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 6 November 2010. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ "The Plymouth Marine Laboratory". South West England RDA. Retrieved 12 December 2008.
- 1 2 3 "Ethnic Group, 2011". Office for National Statistics. 30 January 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ↑ "Plymouth UA". Census 2001. The Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 15 February 2008.
- ↑ "Household Size, 2011". Office for National Statistics. 30 January 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ↑ "Household Composition - People, 2011". Office for National Statistics. 30 January 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ↑ "Ethnic Group, 2001". Office for National Statistics. 18 November 2004. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- 1 2 "Regional GVA NUTS3" (Excel). Office for National Statistics. December 2014. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ↑ "All people - Economically active - Unemployed (Model Based) Plymouth" (PDF). The Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ↑ "Health Profile 2014 Plymouth". National Health Service. August 2014. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- 1 2 "HMNB Devonport". The Royal Navy. Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ↑ "Plymouth's proud naval history". BBC Devon.
- 1 2 3 "Business and economy". Plymouth City Council. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 17 July 2008.
- 1 2 Andrews, Robert (2004). The Rough Guide to Devon & Cornwall. Peter Hack, Kate Hughes, Bea Uhart (2 ed.). Rough Guides. p. 139. ISBN 978-1-84353-312-2. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ↑ "Marine Sector". Plymouth City Council website. The University of Plymouth. Retrieved 22 July 2008.
- ↑ "History of pannier market". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- ↑ "Town Centre Performance & Retail Ranking Update, May 2007" (PDF). South West Regional Board. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- ↑ "Facts and figures". Plymouth City Council. Archived from the original on 10 February 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ↑ "Established BIDs". National BIDs Advisory Service. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- ↑ "Point 6 – Tinside Pool". The BBC. 25 January 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- 1 2 "A vision for Plymouth". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- 1 2 "Controversy over £200m shops plan". BBC News. 5 October 2006. Retrieved 13 October 2007.
- ↑ Laing, Jemima (5 October 2006). "Changing perceptions of Plymouth". BBC News. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ↑ "Civic centre demolition backed". BBC News. 25 September 2007. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ↑ "Dock regeneration plan boosted". BBC News. 19 December 2002. Retrieved 29 June 2008.
- ↑ Ordnance Survey. (3 October 2005). Lower Tamar Valley & Plymouth. Ordnance Survey. ISBN 0-319-23527-0. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Bus enquires and services". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Park and ride". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth Ferry Terminal Guide". Brittany Ferries website. Retrieved 11 April 2009.
- ↑ "Cremyll ferry". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Mount Batten Ferry general info". Mount Batten Ferry website. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Torpoint ferry". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "View of the aircraft parking area and runway at Plymouth City Airport". The BBC. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "About Us". Air Southwest. Archived from the original on 11 October 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth City Airport Flights". Plymouth City Airport. Archived from the original on 28 October 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Air strategy for the far South West published". The South West RDA. 6 June 2003. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "New blow for city airport". BBC News. 7 June 2003. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth City Airport to close in December". BBC News. 28 April 2011. Retrieved 30 December 2011.
- ↑ "FlyPlymouth vows to reopen Plymouth City Airport within two years". Plymouth Herald. 8 May 2015. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Plymouth Station celebrates 130th birthday". First Great Western. 28 March 2007. Archived from the original on 15 November 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Station Facilities: Plymouth (PLY)". National Rail Enquiries. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth ---> Gunnislake Train Timetable" (PDF). Network Rail. Retrieved 17 May 2008.
- ↑ Webster, Ben (25 February 2006). "Biggest cuts since Beeching will slash rural train services". The Times. London. Retrieved 31 May 2008.
- ↑ "MPs join forces against train cut". BBC News. 26 June 2005. Retrieved 31 May 2008.
- ↑ Harris, Nigel (2008). "Taking trains back to Tavistock". Rail. Bauer (590): 40–45.
- ↑ "UK storms destroy railway line and leave thousands without power". BBC Online. Retrieved 5 February 2014.
- ↑ "Dawlish's storm-damaged railway line reopens". BBC News. 4 April 2014. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ↑ "Network Rail chooses Dawlish alternative route". BBC News. 10 February 2014. Retrieved 10 February 2014.
- 1 2 3 "Places of worship". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 2 September 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth Cathedral 1858–2008: 150th Anniversary Celebrations". Roman Catholic Diocese of Plymouth. Retrieved 2 September 2008.
- ↑ "Christian". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 2 September 2008.
- ↑ "The Exclusive Brethren History". The BBC. 4 February 2004. Retrieved 13 July 2008.
- ↑ "Synagogue, Catherine Street, Plymouth". English Heritage. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- ↑ "Other faiths, religions and beliefs". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 2 September 2008.
- ↑ "Religion, 2011". Office for National Statistics. 30 January 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ↑ "Religion, 2001". Office for National Statistics. 18 November 2004. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- 1 2 3 "Union Street: night and day". The BBC. 24 July 2006. Retrieved 22 June 2008.
- ↑ Morris, Jonathan (14 November 2008). "Haven for casualties of the night". BBC News. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ Else, David (2007). England. Lonely Planet. p. 340. ISBN 1-74104-567-3. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "The British Firework Championships Plymouth". The British Firework Championships website. Archived from the original on 14 October 2008. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ↑ Pascoe, Ben (2 November 2006). "Rocket man sets record". The BBC. Retrieved 21 June 2008.
- ↑ "About Music Of The Night". Music of the Night. Archived from the original on 5 October 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Theatre Royal". The Theatre Royal. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Drum Theatre". The Theatre Royal. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "TR2". The Theatre Royal. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "About Us". The Plymouth Pavilions. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Cinemas". Plymouth City Council. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 17 November 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth City Museum and Art Gallery". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 17 November 2008.
- ↑ "The Plymouth Athenaeum Library". Independentlibraries.co.uk. Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- ↑ "Spotlight (address footnote)". BBC South West. Retrieved 17 November 2008.
- ↑ "The end of an era: Last night for Westcountry TV". The Herald. 13 February 2009. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- ↑ "Creative Sector". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 17 November 2008.
- ↑ "Divisional League Table". The Football League. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "History of Plymouth Argyle". The BBC. 18 February 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "History of Plymouth Albion RFC". Plymouth Albion R.F.C. website. Archived from the original on 31 May 2008. Retrieved 21 June 2008.
- ↑ "History". Plymouth Raiders website. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- ↑ "Plymouth hosts America's Cup World Series". The BBC. 23 February 2012. Retrieved 10 March 2013.
- ↑ The South West Water Authority Constitution Order 1973 (1973 No. 1307)
- ↑ Moseley, Brian (14 January 2013). "Water Supply to Plymouth". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 16 October 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ Moseley, Brian (8 July 2011). "Water Supply to Plymouth Dock/Devonport". The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History. Plymouth Data. Archived from the original on 17 May 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ↑ "The History of Dartmoor". Dartmoor National Park Authority. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Rubbish and recycling". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 31 May 2008.
- ↑ "About SWW". South West Water. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Western Power Distribution home page". Western Power Distribution. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Power station delayed for a year". BBC News. 6 March 2009. Retrieved 27 March 2009.
- ↑ "Magistrates' Court search". Her Majesty's Courts Service. Retrieved 17 November 2008.
- ↑ "Combined Crown and County Court search". Her Majesty's Courts Service. Retrieved 17 November 2008.
- ↑ "Our History – Devon & Cornwall Constabulary". Devon and Cornwall Constabulary. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- ↑ "Welcome to Plymouth City Centre & Waterfront – Devon & Cornwall Constabulary". Devon and Cornwall Constabulary. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- ↑ "Your Local CPS: Devon and Cornwall". The Crown Prosecution Service. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- ↑ "West Devon". Devon and Somerset Fire and Rescue Service. Archived from the original on 4 July 2007. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth Fleet". Royal National Lifeboat Institution. Retrieved 24 March 2009.
- ↑ "Plymouth Hospitals". Plymouth Hospitals. 29 August 2008. Retrieved 24 February 2013.
- ↑ "Welcome to the South Western Ambulance Service NHS Trust website". The South Western Ambulance Service NHS Trust. Retrieved 17 November 2008.
- ↑ "Drake Memorial Park". The Drake Memorial Park. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- ↑ "Coast Walks: Point 5 – Smeaton's Tower". The BBC. 25 January 2008. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ↑ "Smeaton's Tower". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 3 September 2008.
- ↑ "War memorials". Plymouth City Council. Retrieved 2 September 2008.
- ↑ "Plymouth's Historic Barbican". The BBC. 18 February 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "Point 8a – Mayflower Steps". The BBC. 7 January 2008. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ↑ Archived 10 October 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Saltram". The National Trust. Archived from the original on 10 June 2008. Retrieved 6 July 2008.
- ↑ "Crownhill Fort". The Landmark Trust. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ "Devonport Heritage Trail". DevonportOnline. Retrieved 29 April 2011.
- ↑ Gemma Thompson. "Plymouth City Council - The countryside". Plymouth.gov.uk. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ Archived 14 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "10 of the most beautiful university buildings in the UK". Times Higher Education. Retrieved 16 October 2014.
- ↑ "Anger over slave trader pub name". BBC News. 27 March 2008. Retrieved 27 October 2009.
- ↑ Routledge, Cyril Tawney; Kegan Paul (1987). Grey Funnel Lines: Traditional Song & Verse of the Royal Navy, 1900–1970. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul. ISBN 978-0-7102-1270-2.
- ↑ "Sir Francis Drake". BBC. Retrieved 3 December 2008.
- ↑ Rasor, Eugene (2004). English/British Naval History to 1815: A Guide to the Literature. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 190. ISBN 0-313-30547-1. Retrieved 2 September 2008.
- ↑ "Sir Francis Drake (c.1540 – c.1596)". The BBC. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Mission to rescue Drake's body". BBC News. 12 November 2001. Retrieved 27 October 2009.
- ↑ "Robert Falcon Scott". The BBC. Archived from the original on 6 January 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Antarctic explorer Frank Bickerton". BBC. Retrieved 8 June 2008.
- ↑ "Painter Beryl Cook dies aged 81". BBC News. 28 May 2007. Retrieved 8 June 2008.
- ↑ "Controversial artist". BBC. 30 January 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Music - Cosmo Jarvis". BBC. Retrieved 24 February 2013.
- ↑ "Gilbert & George Britannica Online Encyclopaedia". Britannica Online Encyclopaedia.
- ↑ "New centre to honour Plymouth Olympian Sharron Davies". Plymouth City Council. 14 March 2007. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Thomas Daley Biography". The British Olympic Association. Retrieved 12 February 2007.
- ↑ "About Sleep". Wayne Sleep's website. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Trevor Francis". Sporting Heroes. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- ↑ "Plymouth's movie maestro". BBC. 30 January 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "The talented Angela Rippon". This Is Hampshire. 19 August 2000. Archived from the original on 25 July 2009. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ↑ "Donald Moffat Biography (1930-)", Filmreference.com. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
Further reading
- Dunning, Martin (2001). Around Plymouth. Frith Book.
- Gill, Crispin (1993). Plymouth: A New History. Devon Books.
- Robinson, Chris (2004). Plymouth Then & Now. Plymouth Prints.
- Casley, Nicholas (1997). The Medieval Incorporation of Plymouth and a Survey of the Borough's Bounds. Old Plymouth Society.
- Carew, Richard (1555). The Survey of Cornwall. N.B. Carew refers to Plymouth Hoe as "the Hawe at Plymmouth"
- Abercrombie, Patrick; Watson, James; Stamp, Laurence; Robinson, Gilbert (27 April 1944). A Plan for Plymouth. Underhill. N.B. the publication carries the date 1943, although published on 27 April 27, 1944 A Plan for Plymouth – The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History
- W Best Harris - Plymouth - Plymouth Council of Social Service (undated)
- W Best Harris - Stories From Plymouth's History - Self-Published, Plymouth (undated)
- W Best Harris - The Book of Plymouth - Guild of Social Service, Plymouth (undated)
- W Best Harris - The New Book of Plymouth - Guild of Social Service, Plymouth (undated)
- W Best Harris - The Second Book of Plymouth - Guild of Social Service, Plymouth, 1957
- W Best Harris - Place Names of Plymouth, Dartmoor and the Tamar Valley - Self-Published, Plymouth, 1983
- W Best Harris - Welcome to Plymouth - Plymouth City Council (undated)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Plymouth. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Plymouth. |
- Plymouth City Council website
- The Encyclopaedia of Plymouth History – at Internet Archive Wayback Machine
- Plymouth at DMOZ