USS Olympia (C-6)
 USS Olympia (C-6), port bow, 10 February 1902. | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Olympia |
| Namesake: | The City of Olympia, Washington |
| Ordered: | 7 September 1888 |
| Builder: | Union Iron Works, San Francisco, California |
| Laid down: | 17 June 1891 |
| Launched: | 5 November 1892 |
| Sponsored by: | Miss Ann B. Dickie |
| Commissioned: | 5 February 1895 |
| Decommissioned: | 9 November 1899 |
| Commissioned: | January 1902 |
| Decommissioned: | 2 April 1906 |
| Commissioned: | 1916 |
| Decommissioned: | 9 December 1922 |
| Reclassified: |
|
| Refit: | 1901, 1902, 1916 |
| Struck: | 11 September 1957 |
| Identification: |
|
| Nickname(s): | "Queen of the Pacific", "The Winged O" |
| Fate: | Restored as Museum Ship |
| Status: | Museum ship. |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Protected cruiser |
| Displacement: | |
| Length: | 344 ft 1 in (104.88 m) |
| Beam: | 53 ft (16 m)[1][2] |
| Draft: | 21 ft 6 in (6.55 m) |
| Installed power: | 17,000 ihp (13,000 kW)[1] |
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | 21.7 knots (40.2 km/h; 25.0 mph)[2] |
| Range: | 6,000 nmi (11,000 km; 6,900 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph)[2] |
| Capacity: | 1,169 short tons (1,060 t) coal (maximum)[1] |
| Complement: | 33 officers and 395 enlisted |
| Armament: |
|
| Armor: | |
|
Olympia | |
|
USS Olympia (C-6) at the Independence Seaport Museum in 2007. | |
 | |
| Location | Penn's Landing Marina, South Columbus Blvd. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 39°56′37″N 75°8′27″W / 39.94361°N 75.14083°WCoordinates: 39°56′37″N 75°8′27″W / 39.94361°N 75.14083°W |
| Area | less than one acre |
| Built | 1892 |
| Built by | Union Iron Works of San Francisco |
| NRHP Reference # | 66000692[4] |
| Added to NRHP | 15 October 1966 |
USS Olympia (C-6/CA-15/CL-15/IX-40) is a protected cruiser that saw service in the United States Navy from her commissioning in 1895 until 1922. This vessel became famous as the flagship of Commodore George Dewey at the Battle of Manila Bay during the Spanish–American War in 1898. The ship was decommissioned after returning to the U.S. in 1899, but was returned to active service in 1902.
She served until World War I as a training ship for naval cadets and as a floating barracks in Charleston, South Carolina. In 1917, she was mobilized again for war service, patrolling the American coast and escorting transport ships.
After World War I, Olympia participated in the 1919 Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War and conducted cruises in the Mediterranean and Adriatic Seas to promote peace in the unstable Balkan countries. In 1921, the ship carried the remains of World War I's Unknown Soldier from France to Washington, D.C., where his body was interred in Arlington National Cemetery. Olympia was decommissioned for the last time in December 1922 and placed in reserve.
In 1957, the U.S. Navy ceded title to the Cruiser Olympia Association, which restored the ship to her 1898 configuration. Since then, Olympia has been a museum ship in Philadelphia, where it is now part of the Independence Seaport Museum. Olympia is the oldest steel US warship still afloat.[5] However, the Museum has been unable to fund essential maintenance for the aging vessel and attempts to secure outside funding have failed. Therefore, the current steward, under direction of the U.S. Navy, has put the ship up for availability to new stewards. It will take an estimated ten million dollars to restore Olympia to a stable condition.
Olympia was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1966.
As of 2013, Olympia's future was uncertain; repairs are desperately needed to keep her afloat. Two entities – one based on San Francisco and one in Port Royal, South Carolina (with four others, including one in Philadelphia and one in Washington, D.C. having dropped out)[6] – are vying to serve as a new steward, but it is a race against time due to the waterline deterioration of the hull. While the current entities remain in competition for the ship, no significant repairs have been made, although the current steward has done some minor repairs. In reaction to this gap in coverage, the National Trust for Historic Preservation (NTHP) has set up a fund repository that, if funds are raised, will be directly applied to immediate repairs of the vessel with the cooperation of the current steward. As of March 2012, the NTHP is considering a triple application by the Naval Historical Foundation, the Historic Naval Ships Association, and the National Maritime Association to have Olympia placed on the NTHP's list of the eleven most endangered "places". The steward applicants from San Francisco (Mare Island), and Beaufort, South Carolina, have endorsed the application. Despite these positive steps, Olympia is in critical danger due to the lack of funds.
Since 2011, Independence Seaport Museum has renewed its commitment to the continued preservation of the cruiser Olympia until the Transfer Application Process reaches its conclusion in summer 2014. The museum has invested in extensive stabilization measures including reinforcing the most deteriorated areas of the hull, expanding the alarm system, installing a network of bilge pumping stand pipes (which will provide greater damage control capability in the unlikely event of a hull breach), extensive deck patching and extensive repair and recoating of the ship’s rigging. Although still in need of dry docking and substantial restoration, the Olympia is in a more stable condition now than it has been for years. This work was made possible by donations from the National Trust for Historic Preservation, The U.S. Cruiser Sailors Association and many individual donors.
Of the six candidates that originally applied for stewardship of Olympia, only two remained as of 2013: an organization in California and an organization in South Carolina. In April, 2014 Independence Seaport Museum announced that neither of the two remaining organizations had presented a viable, long-term solution and that the ship would remain in Philadelphia and that the Seaport Museum would be launching a national fundraising campaign for her preservation.
Background
When the first Cleveland Administration took office in 1885, United States Secretary of the Navy William Collins Whitney continued the naval modernization program started during the preceding Arthur Administration. US naval policy at the time was focused on commerce raiding, which implied a defensive posture on the part of the United States.[7]
In 1887, Whitney authorized the construction of two coastal defense battleships, that were to become Texas and Maine.[8] The emphasis was still on large and fast commerce-raiding cruisers, capable of destroying an attacking fleet's supply line. President Grover Cleveland was defeated in the election of 1888, but before he left office, Whitney managed to have Congress authorize two additional cruisers, one of which was the large, 5,300 long tons (5,400 t) protected cruiser that was to become Olympia.[9]
Starting in 1887, the new Secretary of the Navy, Benjamin Tracy, began to rethink naval policy. Although Tracy allowed the design and construction of Olympia to continue, he was a follower of Alfred Thayer Mahan. As such, Tracy advocated a battle fleet capable of engaging enemy fleets in their home waters.[8] This meant a shift away from large, fast, commerce-raiding cruisers. As a result, Olympia, which would probably have been the first in a class of ships, was the only one of her type built.[10]
Design and construction
The newly formed Board on the Design of Ships began the design process for Cruiser Number 6 in 1889.[11] For main armament, the board chose 8-inch (200 mm) guns, though the number and arrangement of these weapons, as well as the armor scheme, was heavily debated. On 8 April 1890, the navy solicited bids but found only one bidder, the Union Iron Works in San Francisco, California.[12] The contract specified a cost of $1,796,000, completion by 1 April 1893, and offered a bonus for early completion .[13]
During the contract negotiations, Union Iron Works was granted permission to lengthen the vessel by 10 ft (3.0 m), at no extra cost, to accommodate the propulsion system. The contract was signed on 10 July 1890,[14] the keel laid on 17 June 1891, and the ship was launched on 5 November 1892.[15] However, delays in the delivery of components, including the new Harvey steel armor, slowed completion.[16] The last 1-pounder gun wasn't delivered until December 1894.[17]
Union Iron Works conducted the first round of trials on 3 November 1893; on a 68 nmi (126 km; 78 mi) run, the ship achieved a speed of 21.26 kn (39.37 km/h; 24.47 mph). Upon return to harbor, however, it was discovered that the keel had been fouled by sea grass, which required dry-docking to fix.[18]
By 11 December, the work had been completed and she was dispatched from San Francisco to Santa Barbara for an official speed trial. Once in the harbor, heavy fog delayed the ship for four days. On the 15th, Olympia sailed into the Santa Barbara Channel, the "chosen race-track for California-built cruisers,"[19] and began a four-hour time trial. According to the navy, she had sustained an average speed of 21.67 kn (40.13 km/h; 24.94 mph),[19] though she reached up to 22.2 kn (41.1 km/h; 25.5 mph)[18]—both well above the contract requirement of 20 kn (37 km/h; 23 mph).[19] While returning to San Francisco, Olympia participated in eight experiments that tested various combinations of steering a ship by rudder and propellers.[19] The new cruiser was ultimately commissioned on 5 February 1895.[15] For several months afterwards, she was the largest ship ever built on the western coast of the US, until surpassed by the battleship Oregon.[20]
Scientific American compared Olympia to the similar British Eclipse-class cruisers and the Chilean Blanco Encalada and found that the American ship held a "great superiority" over the British ships. While the Eclipse's had 550 short tons (500 t) of coal, compared to Olympia's 400 short tons (360 t), the latter had nearly double the horsepower (making the ship faster), more armor, and a heavier armament on a displacement that was only 200 short tons (180 t) greater than the other.[21]
Characteristics
The ship is 344 ft 1 in (104.88 m) in overall length, has a beam of 53 ft (16 m) and a draft of 21 ft 6 in (6.55 m). Her design displacement was 5,865 long tons (5,959 t), with a full combat load of up to 6,558 long tons (6,663 t) displacement. The ship is powered by a pair of vertical triple expansion engines, each supplied with steam from three coal-fired cylindrical boilers. Her engines were rated at 13,500 ihp (10,100 kW) with a top speed of 20 knots (37 km/h; 23 mph), though on trials she achieved 17,313 ihp (12,910 kW) and a top speed of 21.67 knots (40.13 km/h; 24.94 mph).
Olympia's crew numbered between 411 and 447 officers and enlisted.[15][21]
Armament
Olympia is armed with a variety of weapons. The primary armament was four 8 in (200 mm)/35 caliber guns in two twin Mark 6 gun turrets, one forward and one aft of the superstructure.[15] These guns could fire 260 lb (120 kg) projectiles, either armor-piercing or high explosive, at a muzzle velocity of 2,100 ft (640 m) per second. The Mark 6 turret was designed for depression of the guns to −4° and elevation to 13°.[22] By 1916, the turrets and guns were considered woefully obsolete, and were subsequently removed and replaced with open gun platforms, each with a single 4"/40. These guns were then later replaced with 5"/51-caliber guns in 1917.
The secondary battery was ten 5 in (127 mm)/40 caliber guns mounted in casemates, five on each side of the ship. Each is placed to avoid the flash from the main battery.[15][21] These guns fired 50 lb (23 kg) armor-piercing shells at a muzzle velocity of 2,300 ft (700 m) per second.[23] These also were replaced with 5"/51s during the 1917 refit. Fourteen 6-pounder (57 mm (2.24 in)) anti-torpedo-boat guns are mounted in sponsons. Six 1-pounder guns are mounted on deck, along with six 18 in (46 cm) above-water torpedo tubes.[15] In 1898, The Olympia also boasted two Gatling guns and an arsenal of revolvers and rifles.
Armor
Olympia's conning tower is armored with 5 in (13 cm) thick steel plates. The ship has a 2 in (5.1 cm) thick armored deck that slopes on the sides; the slopes increase in thickness to 4.75 in (12.1 cm) amidships and 3 in (7.6 cm) at the ends. A 4 in (10 cm) thick glacis protects the engine rooms. Her main battery turrets are protected by 3.5 in (8.9 cm) of Harvey armor, while the barbettes upon which they rest have 4.5 in-thick (11 cm) nickel-steel armor. The 5-inch guns are protected by 4 in-thick (10 cm) gun shields.[15][21]
Service history
Upon commissioning in February 1895 Olympia departed the Union Iron Works yard in San Francisco and steamed inland to the U.S. Navy's Mare Island Naval Shipyard at Vallejo, where outfitting was completed and Captain John J. Read was placed in command.[24] In April, the ship steamed south to Santa Barbara to participate in a festival. The ship's crew also conducted landing drills in Sausalito and Santa Cruz that month. On 20 April, the ship conducted its first gunnery practice, during which one of the ship's gunners, Coxswain John Johnson, was killed in an accident with one of the 5-inch guns.[25] The ship's last shakedown cruise took place on 27 July.[26] After returning to Mare Island, the ship was assigned to replace Baltimore as the flagship of the Asiatic Squadron.[27]
On 25 August, the ship departed the United States for Chinese waters.[27] A week later, the ship arrived in Hawaii, where she remained until 23 October due to an outbreak of cholera. The ship then sailed for Yokohama, Japan, where she arrived on 9 November.[28] On 15 November, Baltimore arrived in Yokohama from Shanghai, China, to transfer command of the Asiatic Squadron to Olympia. Baltimore departed on 3 December; Rear Admiral F.V. McNair arrived fifteen days later to take command of the squadron.[29] The following two years were filled with training exercises with the other members of the Asiatic Squadron, and goodwill visits to various ports in Asia.[30] On 3 January 1898, Commodore George Dewey raised his flag on Olympia and assumed command of the squadron.[31]
Spanish–American War

As tensions increased and war with Spain became more probable, Olympia remained at Hong Kong and was prepared for action. When war was declared on 25 April 1898, Dewey moved his ships to Mirs Bay, China. Two days later, the Navy Department ordered the Squadron to Manila in the Philippines, where a significant Spanish naval force protected the harbor.[31] Dewey was ordered to sink or capture the Spanish warships, opening the way for a subsequent conquest by US forces.[32]
Battle of Manila Bay
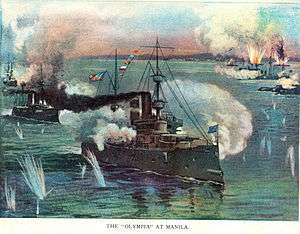
On the morning of 1 May 1898, Commodore Dewey—with his flag aboard Olympia—steamed his ships into Manila Bay to confront the Spanish flotilla commanded by Rear Admiral Patricio Montojo y Pasarón.[32] The Spanish ships were anchored close to shore, under the protection of coastal artillery, but both the ships and shore batteries were outdated.[33] At approximately 05:40, Dewey instructed Olympia's captain, "You may fire when you are ready, Gridley".[34] Gridley ordered the forward 8-inch gun turret, commanded by Gunners Mate Adolph Nilsson, to open fire, which opened the battle and prompted the other American warships to begin firing.[34][35]
Though shooting was poor from both sides, the Spanish gunners were even less prepared than the Americans. As a result, the battle quickly became one-sided. After initial success, Dewey briefly broke off the engagement at around 07:30 when his flagship was reported to be low on 5-inch ammunition. This turned out to be an erroneous report—the 5-inch magazines were still mostly full. He ordered the battle resumed shortly after 11:15. By early afternoon, Dewey had completed the destruction of Montojo's squadron and the shore batteries, while his own ships were largely undamaged. Dewey anchored his ships off Manila and accepted the surrender of the city.[34]
Word of Dewey's victory quickly reached the US; both he and Olympia became famous as the first victors of the war. An expeditionary force was assembled and sent to complete the conquest of the Philippines.[36] Olympia remained in the area and supported the Army by shelling Spanish forces on land. She returned to the Chinese coast on 20 May 1899. She remained there until the following month, when she departed for the US, via the Suez Canal and the Mediterranean Sea. The ship arrived in Boston on 10 October.[31] Following Olympia's return to the US, her officers and crew were feted and she was herself repainted and adorned with a gilded bow ornament.[36] On 9 November, Olympia was decommissioned and placed in reserve.[31]
Pre-World War I
Olympia was recommissioned into the fleet in January 1902 and assigned to the North Atlantic Squadron. Her first duty was to serve as the flagship of the Caribbean Division. Over the following four years, the ship patrolled the Atlantic and Mediterranean;[31] her voyages included a visit to Turkey.[37] In March through April 1903 she and four other U.S. Navy warships were involved in an intervention in Honduras.
Starting on 2 April 1906, she became a training ship for midshipmen from the United States Naval Academy. In this role, she conducted three summer training cruises: 15 May – 26 August 1907, 1 June – 1 September 1908, and 14 May – 28 August 1909. Between the cruises, the ship was placed in reserve, first in Norfolk, Virginia and later at Annapolis, Maryland. On 6 March 1912, Olympia arrived in Charleston, South Carolina.[31] There she served as a barracks ship until 1916.[15] In late 1916, the ship was recommissioned into the fleet, when it became increasingly clear that the US would eventually enter World War I.[31]
World War I
.jpg)

After the U.S. entered the First World War by declaring war on Germany in April 1917, Olympia was mobilized as the flagship of the U.S. Patrol Force. She was tasked with patrolling the eastern seaboard of the US for German warships. She also escorted transport ships in the North Atlantic.[37] On 15 June 1917, she ran aground in Long Island Sound, and put in for repairs at the Brooklyn Navy Yard, which, along with the replacement of her 8-inch and 5"/40-caliber guns with 5"/51-caliber guns, took eight months.[38] Olympia departed Charleston on 28 April 1918 carrying an expeditionary force bound for Russia. Russia, which had previously been a member of the Allied Powers, was in the midst of civil war and had signed a separate peace with Germany.[31] On 9 June 1918, the ship arrived in Murmansk, Russia, and deployed the peace-keeping force.[37] She subsequently assisted in the occupation of Archangel.[31]
After the end of the war, Olympia sailed to the Mediterranean via Portsmouth, England.[31] In December 1918, the ship became the flagship for American naval forces stationed in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. While on this assignment, she continued in her old role of showing the flag and conducting goodwill visits in various Mediterranean ports.[37] This included a period of policing duty in the Adriatic Sea from 21 January to 25 October 1919; the Dalmatian coast was in a state of turmoil following the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Empire at the end of the war. On 18 August, she steamed to the Black Sea to aid the return of refugees from the Balkans who had fled during the war. She was back in the Adriatic by 19 September, and four days later had to deploy a landing party to prevent an incident between Italian and Yugoslav forces.[31]
Olympia briefly returned to Charleston on 24 November 1919.[31] The following year, she was reclassified CA-15.[39] She then prepared for another tour of duty in the Adriatic, departing from New York on 14 February 1920. This was concluded on 25 May 1921, when the ship returned to Charleston. A month after her arrival she was made the flagship of the Atlantic Fleet's training unit. She then participated in joint Army-Navy experiments in July, during which the ex-German warships Ostfriesland and Frankfurt were sunk off the Virginia Capes.[31] She was again reclassified as CL-15 that year.[39]
On 3 October 1921, Olympia departed Philadelphia for Le Havre, France, to bring the remains of the Unknown Soldier home for interment in Arlington National Cemetery. The cruiser departed France on 25 October 1921; she was escorted by a group of French destroyers for part of the voyage. At the mouth of the Potomac river on 9 November, the battleship North Dakota and the destroyer Bernadou joined Olympia as she sailed to the Washington Navy Yard. After transferring the remains ashore, the cruiser fired her guns in salute. She conducted a last training cruise for midshipmen in the summer of 1922.
Preservation of Olympia
On 9 December 1922, she was decommissioned for the last time in Philadelphia and placed in reserve. On 30 June 1931, the ship was reclassified IX-40,[31] to be preserved as a relic.
On 11 September 1957, she was released to the Cruiser Olympia Association, restored to her 1898 configuration and became a museum ship under their auspices. The main 8-inch guns and turrets, scrapped before World War I, were replaced with sheet metal fabrications. In January 1996, when faced with mounting debt and tremendous deferred maintenances, the Cruiser Olympia Society merged with the Independence Seaport Museum in Philadelphia.
Today, Olympia is a museum at the Independence Seaport Museum, at Penn's Landing in Philadelphia. She is the sole floating survivor of the US Navy's Spanish–American War fleet. Naval Reserve Officer Training Corps Midshipmen from Villanova University and the University of Pennsylvania regularly work on Olympia, functioning as maintenance crew.
The museum is seeking a national fundraising campaign to fund the preservation costs for Olympia. Historic steel-hulled ships should be dry-docked for maintenance every 20 years, but she has been in the water continuously since 1945. Essential repairs are estimated at $10 million.[40] Plans to scuttle Olympia, making her into an artificial reef, are under consideration.[5]
Plans were made to close Olympia to visitors on 22 November 2010, due a lack of operating funds.[41] These plans were scrapped, and Independence Seaport Museum agreed to keep the ship open with regular hours through 31 December, and then reduced hours through 31 March 2011.[42] The US Navy has expressed its willingness to let the museum "responsibly dispose" of the vessel. This could result in the ship being transferred, sold as scrap, or sunk as a reef. As such, the museum held a summit in early 2011 with the Navy, Navy Sea Systems Command, National Park Service, and the Pennsylvania Historical Museum Commission to determine what steps can be taken to save the cruiser.[42]
The TAPP Process
As a result of the summit, the Independence Seaport Museum (ISM) in Philadelphia searched for another non-profit organization to assume stewardship of Olympia to provide for her maintenance and restoration. On 6 March 2011, the ISM published a Transfer Application (TAPP) similar to a Request for Proposals. Those who qualified to apply for the TAPP include domestic governmental organizations and not-for-profit organizations with valid 501(c)(3) (charitable) IRS status. There were several organizations from the East, Gulf and West Coasts who submitted applications to preserve and display Olympia.[43] Only four were found to be acceptable, from Pennsylvania, California, South Carolina, and Washington DC.[44]
One TAPP applicant, an independent non-profit 501(c)(3) corporation known as Friends of the Cruiser Olympia,[45] was organized in 2009 with the goal of preserving Olympia and opening her to the public as a floating historic and educational museum that would preserve Olympia's structure, history, heritage, and tradition as a national treasure. The Friends of the Cruiser Olympia hosted a dinner on 23 June 2011, in the historic Mike Mansfield Room of the U.S. Capitol to raise awareness of their efforts to save, restore and preserve the Cruiser Olympia from destruction by neglect.[46] Participants included representatives of the U.S. Navy, Department of Defense, Navy League, Naval Historical Foundation, US Naval Academy Alumni Association, key Congressional staff from the House and Senate Armed Services Committees and the Pennsylvania Congressional Delegation, the US defense industry, and the international community.[47] With their support, the Friends submitted their TAPP application in September 2011 expressing their intention to keep her. The Friends application was found acceptable and the organization began preparations for Phase II of the TAPP process.
On 7 May 2011, the National Trust for Historic Preservation set up a national donation repository to allow donations received through it to be used directly for the much-needed temporary and future hull repairs. The Independence Seaport Museum, although originally committed to giving up the vessel, will manage any repair work undertaken, should funds become available.[48]
On 19 August 2011, the Mare Island Historic Park Foundation located at the closed Mare Island Naval Shipyard in Vallejo, California, submitted an expression of intent to acquire Olympia.[49] The Mare Island Historic Park Foundation had been operating for 18 years and operated two mansions, the oldest non-denominational chapel in the Navy, and a 50,000-square-foot (4,600 m2) museum in the oldest building on the former shipyard.[50] The Mare Island Historic Park Foundation intended to display the ship out of water in Mare Island's Dry Dock 1, a national historic landmark adjacent to the museum. By displaying the ship out of water, Mare Island Historic Park Foundation felt that future corrosion concerns with the hull would be eliminated and the venue would be enhanced by the ability to view not only the ship, but a historic graving dock as well.[51]
On 13 October 2011, a bill was introduced in the House of Representatives that would require production of silver dollars commemorating Olympia. The cost of each coin would include a surcharge of $10, which would be used for the restoration and preservation of the ship.[52][53] The bill, HR 3180, named the Friends of the Cruiser Olympia as participants in the coin design and recipients of the funds raised to ensure Olympia's ongoing restoration and preservation.[54]
As of May, 2013, only two organizations remain in the TAPP process: the Mare Island Historic Park and one from Beaufort, SC.[55]
In April, 2014, Independence Seaport Museum announced the end of the TAPP process as the two remaining organizations did not present a viable, long-term solution for the ship. The Olympia will remain in Philadelphia, and the Seaport Museum plans to launch a national fundraising campaign for her preservation.
Interim Repairs: 2014 - Today
While still seeking drydock repairs in the future, the Independence Seaport Museum commenced interim repairs in 2015 to stabilize the weaker portions of Olympia's hull.
Along with the Independence Seaport Museum's renewed commitment to the ship, the Olympia received multiple grants including $169,850.00 from the National Park Service's Maritime Heritage Program[56] to continue work on interim repairs of deteriorating hull plates and deck leaks. Between April and August 2015, Four 4-foot by 7-foot sections of the hull at the waterline were cleaned, scaled to bare metal, and treated with ceramic epoxy and new bottom paint. This was accomplished using a custom-made mobile surface-piercing cofferdam.[57]
Further work is planned for the Summer of 2016.
Awards
| Dewey Medal | Navy Expeditionary Medal | Spanish Campaign Medal |
| Philippine Campaign Medal | Dominican Campaign Medal | World War I Victory Medal with "WHITE SEA" clasp |
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 (2001) Jane's Fighting Ships of World War I, pg. 141. Random House, London. ISBN 1-85170-378-0
- 1 2 3 4 Ford (2001), p. 271.
- 1 2 Ford (2001), p. 272.
- ↑ National Park Service (2010-07-09). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- 1 2 Loviglio, Joann (6 September 2010). "Olympia, 2-war naval veteran, battles for survival". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 9 September 2010. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
- ↑ Associated Press (July 5, 2013). "Work Continues To Save Historic USS Olympia". CBS Philadelphia. Retrieved February 13, 2015.
- ↑ Friedman (1984), p. 22–23
- 1 2 Friedman (1985), p. 23
- ↑ Friedman (1984), p. 27
- ↑ Friedman (1984) p. 29
- ↑ Cooling, p. 11
- ↑ Cooling, p. 12
- ↑ Cooling, pp. 12–13
- ↑ Cooling, p. 13
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gardiner, Chesneau, & Kolesnik, p. 152
- ↑ Cooling, p. 18-21
- ↑ Cooling, p. 26
- 1 2 Cooling, p. 24
- 1 2 3 4 Wiggins, Marcus P (3 February 1894). "The Cruiser "Olympia"". Harper's Weekly. 38: 112.
- ↑ Cooling, p. 14
- 1 2 3 4 "The United States Protected Cruiser Olympia". Scientific American. 74: 177–178. 21 March 1896.
- ↑ DiGiulian, Tony (4 June 2008). "United States of America 8"/35 (20.3 cm) Marks 3 and 4 8"/40 (20.3 cm) Mark 5". navweaps.com. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
- ↑ DiGiulian, Tony (12 February 2008). "United States of America 5"/40 (12.7 cm) Marks 2, 3 and 4". navweaps.com. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
- ↑ Cooling, p. 28
- ↑ Cooling, p. 29
- ↑ Cooling, p. 31
- 1 2 Cooling, p. 32
- ↑ Cooling, pp. 33–35
- ↑ Cooling, p. 36
- ↑ Cooling, pp. 37–49
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "Olympia". Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. 17 August 2015. Retrieved 31 January 2016.
- 1 2 Cooling, p. 1
- ↑ Cooling, pp. 1–2
- 1 2 3 Cooling, p. 2
- ↑ Burr, p. 37
- 1 2 Cooling, p. 4
- 1 2 3 4 Miller & Miller, p. 180
- ↑ Burr, p. 41
- 1 2 "USS Olympia (Cruiser # 6, C-6, later CA-15, CL-15, and IX-40), 1895–1957". 10 October 1998. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
- ↑ "SOS! Philadelphia maritime museum says it can't afford to care for historic USS Olympia". Star Tribune. Minneapolis-St. Paul. Associated Press. 26 February 2010. Retrieved 2010-02-26.
- ↑ "Title unknown". Archived from the original on 9 September 2010.
- 1 2 Colimore, Edward (18 November 2010). "Spanish-American warship spared, at least for now". The Philadelphia Inquirer. Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ↑ Loviglio, Joann. "Museum seeks new owner for USS Olympia, historic 19th-century warship docked in Philadelphia". Star Tribune. Associated Press. Retrieved 2011-03-09.
- ↑ Jaffe, Alan (28 November 2011). "Preservation Row: Olympia suitors are narrowed to four". Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ "Friends of the Cruiser Olympia". Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ "Friends Host Reception and Dinner on Capitol Hill" (Press release). 14 June 2011. Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ "Friends of the Cruiser OLYMPIA Quarterdeck". Retrieved 2011-09-23.
- ↑ "The USS Olympia". National Trust for Historic Preservation. Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ "Mare Island Historic Park Foundation". Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ "328 Seawind Drive (Admirals Mansions at Mare Island), Vallejo, CA". Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ "Mare Island Historic Park Foundation Olympia Page". Retrieved 2013-04-04.
- ↑ "U.S.S. Cruiser Olympia Commemorative Coin Act Introduced". The Quarterdeck (Press release). 18 October 2011. Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ Zielinski, Michael. "House Bill Seeks U.S.S. Cruiser Olympia Commemorative Silver Dollars". Coin Update News. Retrieved 2011-10-20.
- ↑ "Bill Text 112th Congress (2011–2012) H.R.3180.IH". THOMAS. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- ↑ "Bringing Home the USS OLYMPIA (C-6) Newsletter" (PDF). Mare Island Museum. May 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ↑ "National Park Service awards $2.6 million in grants for maritime history education and preservation projects | MARAD". www.marad.dot.gov. Retrieved 2015-10-04.
- ↑ "Olympia Hull Repair". www.youtube.com. Retrieved 2016-10-15.
Bibliography
- Alden, John D. (1989). American Steel Navy: A Photographic History of the U.S. Navy from the Introduction of the Steel Hull in 1883 to the Cruise of the Great White Fleet. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-248-6. OCLC 22984787.
- Burr, Lawrence. US Cruisers 1883–1904: The Birth of the Steel Navy. New York City: Ospery Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84603-267-7. OCLC 437097869.
- Cooling, Benjamin Franklin (2007). USS Olympia: Herald of Empire. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-126-6. OCLC 183396685.
- Friedman, Norman (1984). U.S. Cruisers: An Illustrated Design History. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-718-6. OCLC 10949320.
- Friedman, Norman (1985). U.S. Battleships: An Illustrated Design History. United States Naval Institute Press.
- Gardiner, Robert; Chesneau, Roger; Kolesnik, Eugene M., eds. (1979). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships: 1860–1905. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-85177-133-5.
- Miller, Arthur P.; Miller, Marjorie L. (2000). Pennsylvania Battlefields and Military Landmarks. Stackpole Books. ISBN 0-8117-2876-5.
- Ford, Roger; Gibbons, Tony; Hewson, Rob; Jackson, Bob; Ross, David (2001). The Encyclopedia of Ships. London: Amber Books, Ltd. pp. 271–272. ISBN 978-1-905704-43-9.
- Jane's Fighting Ships of World War I. London: Random House Group, Ltd. 2001. p. 141. ISBN 1-85170-378-0.
- Munsey's Magazine Volume XXVI. October 1901, to March 1902. Page 880 (Article with paragraph discussing Driggs-Schroeder 6 pdr guns and their number used on the USS Olympia, USS Brooklyn, and USS New York in the Spanish–American War.)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to USS Olympia (C-6). |
- Photo gallery of Olympia at NavSource Naval History
- Cruiser Olympia at Spanish-American War Centennial website
- USS Olympia (C-6) at Historic Naval Ships Association
- Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) No. PA-428, "USS Olympia"
- Mare Island Museum's Olympia preservation page
 "Dewey, George". Appletons' Cyclopædia of American Biography. 1900. This article has information about Olympia at the end.
"Dewey, George". Appletons' Cyclopædia of American Biography. 1900. This article has information about Olympia at the end.- Greenwood, Richard F. (12 November 1974). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory—Nomination Form / U.S.S. Olympia" (pdf). National Park Service. Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- "Accompanying Photos" (pdf). National Park Service. Retrieved 2012-09-07.
- Historic footage of USS Olympia in 1921, receiving and transporting casket of the Unknown Soldier of World War I to America