Alexandria Canal (Virginia)
|
Alexandria Canal Tide Lock | |
|
Alexandria Canal Center with restored Tidal Basin and Tidal Lock | |
   | |
| Nearest city | Alexandria, Virginia |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 38°48′49.6″N 77°2′18.2″W / 38.813778°N 77.038389°WCoordinates: 38°48′49.6″N 77°2′18.2″W / 38.813778°N 77.038389°W |
| Area | 5.7 acres (2.3 ha) |
| Built | 1833 |
| Architect | Alexandria Canal Co. |
| NRHP Reference # | 80004305[1] |
| VLR # | 100-0099 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | January 15, 1980 |
| Designated VLR | November 20, 1979[2] |
The Alexandria Canal was a canal in the United States that connected the city of Alexandria to Georgetown in the District of Columbia.
In 1830, merchants from Alexandria (which at the time was within the jurisdiction of the federal District of Columbia) proposed linking their city to Georgetown to capitalize on the new Chesapeake and Ohio Canal (C&O Canal). Congress granted a charter to the Alexandria Canal Company in 1830.
Construction began soon afterwards on the Aqueduct Bridge, which would enable canal boats from the C&O Canal to cross the Potomac River without first unloading at Georgetown. The boats would then continue their trips downstream on a canal on the southwest side of the Potomac until they reached Alexandria's seaport.
Construction of the bridge and of the Alexandria Canal began in 1833. Both were completed a decade later.
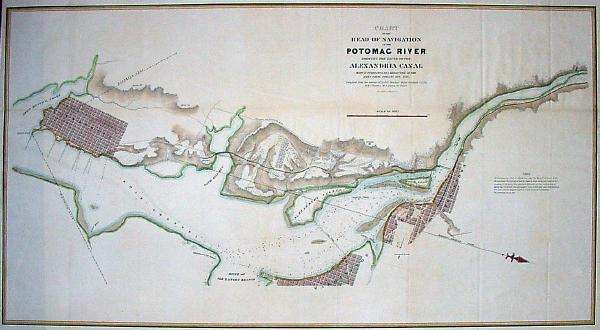
The canal ran southwards for seven miles through today's Arlington County and City of Alexandria, Virginia, dropping 38 feet through a series of four locks between Washington Street and the Potomac River in the northern portion of Alexandria. The Canal ended at a Tidal Basin (Pool No. 1) and a Tidal Lock (Lift Lock No. 1) located at the north end of Old Town Alexandria.
The canal was abandoned in 1886. Ten years after the canal closed, an electric trolley line was constructed in 1896 in Arlington on the bed of the towpath that traveled along the canal's west side. Arlington's S. Eads Street now approximates the canal's route in this area.
The Pennsylvania Railroad constructed a branch line to Rosslyn near and along the portion of the canal's route that passed through the area that lies between Arlington National Cemetery and the Potomac River. An open section of Metrorail's Blue Line now travels this route.
After the Key Bridge was completed in 1923, the old superstructure of the Aqueduct Bridge was removed. During the 1980s, Alexandria City archaeologists and the developer of the neighboring Trans-Potomac Canal Center excavated and restored the Tidal Basin and Lock. Aside from these two features, the abutments of the Aqueduct Bridge in Georgetown and Rosslyn, and a pier of the bridge in the Potomac River upstream of the Key Bridge, all of the canal's remnants have either been removed or remain underground.
References
- ↑ National Park Service (2009-03-13). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- ↑ "Virginia Landmarks Register". Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Retrieved 2013-05-12.
- Hahn, Thomas Swiftwater; Kemp, Emory L. (1992). The Alexandria Canal: Its History & Preservation. West Virginia University Press. ISBN 978-1-885907-01-1.
- Barr, Keith L. (1989). The Alexandria Canal: Tidewater Terminus of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal System. Alexandria Archaeology Publications.
- "Alexandria Canal". Alexandria Archaeology Museum. Government of the City of Alexandria, Virginia. Archived from the original on March 13, 2007. Retrieved July 16, 2014.
- "Alexandria Canal: History of the Alexandria Canal". Historic Alexandria. Government of the City of Alexandria, Virginia. Archived from the original on March 8, 2007. Retrieved July 16, 2014.
External links
- Maps and aerial photos
- Aqueduct Bridge abutment, Georgetown: Hybrid satellite image/map from WikiMapia
- Aqueduct Bridge pier, Potomac River: Hybrid satellite image/street map from WikiMapia
- Aqueduct Bridge abutment, Rosslyn: Hybrid satellite image/street map from WikiMapia
- Metrorail Blue Line on former Alexandria Canal route, Arlington: Hybrid satellite image/street map from WikiMapia
- S. Eads Street on former Alexandria Canal route, Arlington: Hybrid satellite image/street map from WikiMapia
- Restored Tidal Basin and Lock of Alexandria Canal, Alexandria: Hybrid satellite image/street map from WikiMapia