Oregon's climate is generally mild. West of the Cascade Mountains, winters are chilly with frequent rain, while light snowfall occurs a few days a year; temperatures can get very cold, but only occasionally, as the result of Arctic cold waves. The high desert region of the state is much drier, with less rain, more snow, colder winters, and hotter summers. An oceanic climate (also called "marine west coast climate") predominates in Western Oregon, and a much drier semi-arid climate prevails east of the Cascade Range in Eastern Oregon. Major factors determining Oregon's climate include the large semi-permanent high pressure and low pressure systems of the north Pacific Ocean, the continental air masses of North America, and the Cascade mountains.[1] Oregon's population centers, which lie mostly in the western part of the state, are generally moist and mild, while the lightly populated high deserts of Central and Eastern Oregon are much drier.
Precipitation
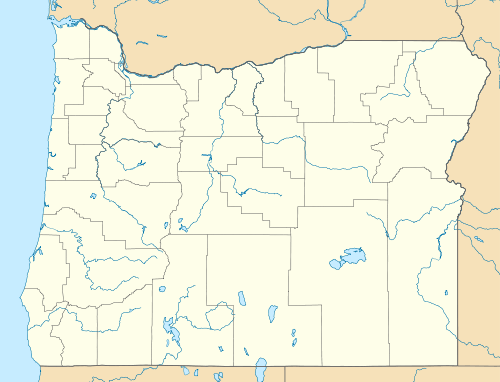
_Map.png)
Oregon rainfall varies widely from region to region.
Precipitation in the state varies widely: some western coastal slopes approach 200 inches (5,100 mm) annually, while the driest places, such as the Alvord Desert (in the rain shadow of Steens Mountain) in eastern Oregon, get as little as 5 inches (130 mm).[3]
The Pacific Ocean, the moisture-laden air above it, and the storms moving from it over the Oregon coast, are major factors in the state's precipitation patterns. As humid ocean air flows east from the ocean and encounters the Coast Range, it rises steeply, cools, and loses moisture through condensation, which produces heavy rain. The heaviest precipitation in the state occurs at 2,000 to 4,000 feet (610 to 1,220 m) above sea level in these coastal mountains. At lower elevations along the coast, orographic precipitation is less intense but still produces 60 to 80 inches (1,500 to 2,000 mm) a year.
In the Willamette Valley east of the Coast Range, storms blowing from the Pacific retain enough moisture to drop from 35 to 45 inches (890 to 1,140 mm) annually in the most heavily populated part of the state. East of the valley, the storm air rises again as it meets the Cascade Range, cooling once more and forming condensate at elevations often as low as 3,000 feet (910 m). Since volcanic peaks in the range are quite high—more than 11,000 feet (3,400 m) in the case of Mount Hood—most of the remaining Pacific moisture falls here in the form of rain or snow.
The remaining two-thirds of the state is relatively dry, classified as semi-arid, with large areas receiving no more than 12 inches (300 mm) a year. Exceptions occur at higher elevations in the Blue Mountains and the Wallowa Mountains to the northeast, which get 50 to 80 inches (1,300 to 2,000 mm) a year.
Across Oregon, the wet season runs from November through March, when the jet stream is strongest in the Northern Hemisphere. Precipitation is less in the months between winter and summer: April through June in the spring and September and October in the fall. Statewide, the dry months are July and August, when moisture arrives during afternoon thunderstorms, mainly in the mountains, and less often from storms that reach the north coast and adjacent counties.
Snow
Snowfall in Oregon is greatest in the Cascade Range. Based on data from ski resorts and a few official weather stations, average annual snowfall in the Cascades can range from 300 to 550 inches (760 to 1,400 cm).[3] The state's largest annual snowfall on record, 903 inches (2,290 cm), occurred at Crater Lake in the Cascades in 1950. In the Blue Mountains of eastern Oregon, snowfall totals can also be large, between 150 and 300 inches (380 and 760 cm). On the other hand, most winter precipitation in the Coast Range falls as rain, though heavy snow sometimes occurs.[3]
In most mountain areas in Oregon, the ground above 4,500 feet (1,400 m) is covered with snow from December through April. Snow depths, which vary with elevation and time of year, average an estimated 50 to 100 inches (130 to 250 cm) in the Cascades and 25 to 65 inches (64 to 165 cm) in the Blue Mountains at the end of January; by the end of April, they diminish to 40 to 120 inches (100 to 300 cm) in the Cascades and 5 to 45 inches (13 to 114 cm) in the Blues. Glaciers remain year-round on some Cascade peaks higher than 7,000 feet (2,100 m) above sea level.[3]
Annual snowfall along the coastal plain averages 1 to 3 inches (2.5 to 7.6 cm) a year, including years with none. Further inland, between the Coast Range and the Cascades, snowfall generally averages from 10 to 15 inches (25 to 38 cm) a year. East of the Cascades, in non-mountain settings, the annual totals range from 15 to 75 inches (38 to 191 cm), depending on location; they are smallest in the north-central region and the Snake River basin in the southeast and largest in the northeastern valleys and in the high plateaus of the south-central part of the state.[3]
Temperature
In addition to seasonal cycles in solar radiation (more in summer, less in winter), major factors affecting temperatures in Oregon include the moderating influence of the Pacific Ocean combined with variations in surface elevation, especially the Cascade Range. In general, temperatures on Earth drop by about 4 °F (2 °C) per each 1,000 feet (300 m) increase in elevation. Throughout the year, high elevations across the state tend to be cooler than low elevations. In addition, the Cascades, running north–south from border to border, generally retain relatively warm Pacific air masses on the western side of the state and relatively cool continental air masses on the eastern side. This prevailing pattern breaks down occasionally when dense cold air flows down the Columbia Gorge into the Willamette Valley and lowers temperatures more than usual from Portland to Eugene.
Oregon has a wide range of temperatures, though the extremes are rare.[3] The highest was recorded on July 29, 1898, in Hermiston, Oregon, and again on August 10, 1898, in [Redmond, Oregon], both east of the Cascades, when the temperature reached 122 °F (50 °C). The lowest occurred on February 9, 1933, in Ukiah, and again on February 10, 1933, in Seneca, also both east of the Cascades, when the temperature dropped to −54 °F (−48 °C). The temperature in the Willamette Valley is mild compared to the desert regions of the state, with high temperatures at or above 90 °F (32 °C) occurring only five to fifteen times per year, and low temperatures below 30 °F (−1 °C) similarly infrequent.[8] The hottest area of the state is the southwest; Jackson County is the warmest place in the state during summer.[9]
Selected climate charts
Map of locations in the charts below |
| Astoria
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Bend
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Brookings
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Burns
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Eugene
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Medford
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Newport
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Ontario
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Pendleton
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
| Portland
|
|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °F |
| Precipitation totals in inches |
|
| Metric conversion |
|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Average max. and min. temperatures in °C |
| Precipitation totals in mm |
|
See also
References
Works cited
- Allan, Stuart; Buckley, Aileen R.; Meacham, James E. (2001). Loy, William G., ed. Atlas of Oregon (2nd ed.). Eugene: University of Oregon Press. ISBN 0-87114-101-9.
- Taylor, George H.; Hannan, Chris (1999). The Climate of Oregon: From Rain Forest to Desert. Corvallis: Oregon State University Press. ISBN 978-0-87071-468-9.
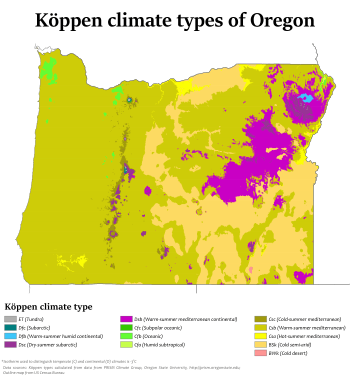

_Map.png)