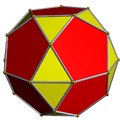
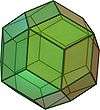
Icosidodecahedron
| Icosidodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Archimedean solid Uniform polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 32, E = 60, V = 30 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 20{3}+12{5} |
| Conway notation | aD |
| Schläfli symbols | r{5,3} |
| t1{5,3} | |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 | 3 5 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Ih, H3, [5,3], (*532), order 120 |
| Rotation group | I, [5,3]+, (532), order 60 |
| Dihedral Angle | 142.62° |
| References | U24, C28, W12 |
| Properties | Semiregular convex quasiregular |
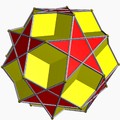
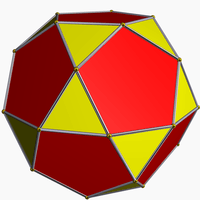 Colored faces |
 3.5.3.5 (Vertex figure) |
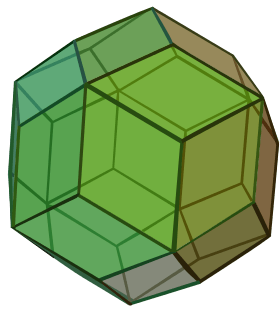 Rhombic triacontahedron (dual polyhedron) |
 Net |

In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon. As such it is one of the Archimedean solids and more particularly, a quasiregular polyhedron.
An icosidodecahedron has icosahedral symmetry, and its first stellation is the compound of a dodecahedron and its dual icosahedron, with the vertices of the icosahedron located at the midpoints of the edges of either.
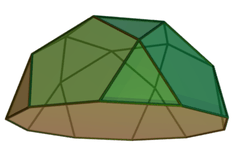
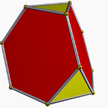
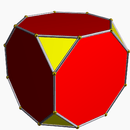
Its dual polyhedron is the rhombic triacontahedron. An icosidodecahedron can be split along any of six planes to form a pair of pentagonal rotundae, which belong among the Johnson solids.
The icosidodecahedron can be considered a pentagonal gyrobirotunda, as a combination of two rotundae (compare pentagonal orthobirotunda, one of the Johnson solids). In this form its symmetry is D5d, [10,2+], (2*5), order 20.
The wire-frame figure of the icosidodecahedron consists of six flat regular decagons, meeting in pairs at each of the 30 vertices.
Cartesian coordinates
Convenient Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of an icosidodecahedron with unit edges are given by the even permutations of:[1]
- (0, 0, ±φ)
- (±1/2, ±φ/2, ±1 + φ/2)
where φ is the golden ratio, 1 + √5/2.
Orthogonal projections
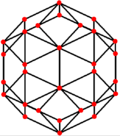
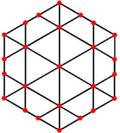
The icosidodecahedron has four special orthogonal projections, centered on a vertex, an edge, a triangular face, and a pentagonal face. The last two correspond to the A2 and H2 Coxeter planes.
| Centered by | Vertex | Edge | Face Triangle |
Face Pentagon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Projective symmetry |
[2] | [2] | [6] | [10] |
| Dual image |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Surface area and volume
The surface area A and the volume V of the icosidodecahedron of edge length a are:
Spherical tiling
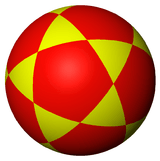
The icosidodecahedron can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and projected onto the plane via a stereographic projection. This projection is conformal, preserving angles but not areas or lengths. Straight lines on the sphere are projected as circular arcs on the plane.
 |
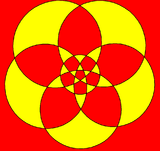 Pentagon-centered |
 Triangle-centered |
| Orthographic projection | Stereographic projections | |
|---|---|---|
Related polyhedra
The icosidodecahedron is a rectified dodecahedron and also a rectified icosahedron, existing as the full-edge truncation between these regular solids.
The icosidodecahedron contains 12 pentagons of the dodecahedron and 20 triangles of the icosahedron:
| Family of uniform icosahedral polyhedra | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [5,3], (*532) | [5,3]+, (532) | ||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| {5,3} | t{5,3} | r{5,3} | t{3,5} | {3,5} | rr{5,3} | tr{5,3} | sr{5,3} |
| Duals to uniform polyhedra | |||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| V5.5.5 | V3.10.10 | V3.5.3.5 | V5.6.6 | V3.3.3.3.3 | V3.4.5.4 | V4.6.10 | V3.3.3.3.5 |
The icosidodecahedron exists in a sequence of symmetries of quasiregular polyhedra and tilings with vertex configurations (3.n)2, progressing from tilings of the sphere to the Euclidean plane and into the hyperbolic plane. With orbifold notation symmetry of *n32 all of these tilings are wythoff construction within a fundamental domain of symmetry, with generator points at the right angle corner of the domain.[2][3]
| *n32 orbifold symmetries of quasiregular tilings: (3.n)2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Construction |
Spherical | Euclidean | Hyperbolic | ||||
| *332 | *432 | *532 | *632 | *732 | *832... | *∞32 | |
| Quasiregular figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Vertex | (3.3)2 | (3.4)2 | (3.5)2 | (3.6)2 | (3.7)2 | (3.8)2 | (3.∞)2 |
| *5n2 symmetry mutations of quasiregular tilings: (5.n)2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *5n2 [n,5] |
Spherical | Hyperbolic | Paracompact | Noncompact | ||||
| *352 [3,5] |
*452 [4,5] |
*552 [5,5] |
*652 [6,5] |
*752 [7,5] |
*852 [8,5]... |
*∞52 [∞,5] |
[ni,5] | |
| Figures |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Config. | (5.3)2 | (5.4)2 | (5.5)2 | (5.6)2 | (5.7)2 | (5.8)2 | (5.∞)2 | (5.ni)2 |
| Rhombic figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Config. | V(5.3)2 | V(5.4)2 | V(5.5)2 | V(5.6)2 | V(5.7)2 | V(5.8)2 | V(5.∞)2 | V(5.∞)2 |
Dissection
The icosidodecahedron is related to the Johnson solid called a pentagonal orthobirotunda created by two pentagonal rotunda connected as mirror images. The icosidodecahedron can therefore be called a pentagonal gyrobirotunda with the gyration between top and bottom halves.
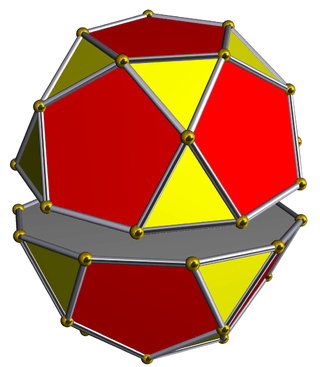 (Dissection) |
|
Related polyhedra
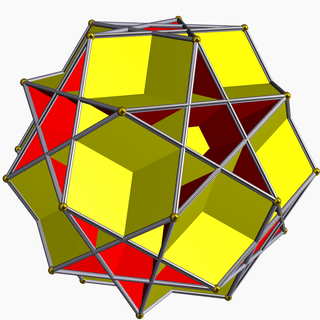
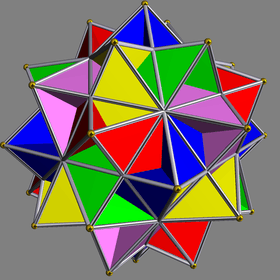
Eight uniform star polyhedra share the same vertex arrangement. Of these, two also share the same edge arrangement: the small icosihemidodecahedron (having the triangular faces in common), and the small dodecahemidodecahedron (having the pentagonal faces in common). The vertex arrangement is also shared with the compounds of five octahedra and of five tetrahemihexahedra.
Related polytopes
In four-dimensional geometry the icosidodecahedron appears in the regular 600-cell as the equatorial slice that belongs to the vertex-first passage of the 600-cell through 3D space. In other words: the 30 vertices of the 600-cell which lie at arc distances of 90 degrees on its circumscribed hypersphere from a pair of opposite vertices, are the vertices of an icosidodecahedron. The wire frame figure of the 600-cell consists of 72 flat regular decagons. Six of these are the equatorial decagons to a pair of opposite vertices. They are precisely the six decagons which form the wire frame figure of the icosidodecahedron.
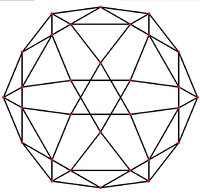
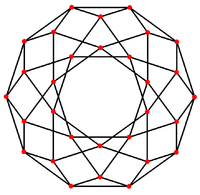
Icosidodecahedral graph
| Icosidodecahedral graph | |
|---|---|
|
5-fold symmetry Schlegel diagram | |
| Vertices | 30 |
| Edges | 60 |
| Automorphisms | 120 |
| Properties | Quartic graph, Hamiltonian, regular |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a icosidodecahedral graph is the graph of vertices and edges of the icosidodecahedron, one of the Archimedean solids. It has 30 vertices and 60 edges, and is a quartic graph Archimedean graph.[4]
 6-fold symmetry |
 10-fold symmetry |
See also
- Cuboctahedron
- Great truncated icosidodecahedron
- Icosahedron
- Rhombicosidodecahedron
- Truncated icosidodecahedron
Notes
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Icosahedral group". MathWorld.
- ↑ Coxeter Regular Polytopes, Third edition, (1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8 (Chapter V: The Kaleidoscope, Section: 5.7 Wythoff's construction)
- ↑ Two Dimensional symmetry Mutations by Daniel Huson
- ↑ Read, R. C.; Wilson, R. J. (1998), An Atlas of Graphs, Oxford University Press, p. 269
References
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X. (Section 3-9)
- Cromwell, P. (1997). Polyhedra. United Kingdom: Cambridge. pp. 79–86 Archimedean solids. ISBN 0-521-55432-2.
External links
- Eric W. Weisstein, Icosidodecahedron (Archimedean solid) at MathWorld.
- Klitzing, Richard. "3D convex uniform polyhedra o3x5o - id".
- Editable printable net of an icosidodecahedron with interactive 3D view
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra