Paschim Medinipur district
| Paschim Medinipur district | |
|---|---|
| District of West Bengal | |
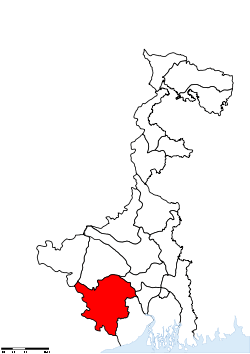 Location of Paschim Medinipur district in West Bengal | |
| Country | India |
| State | West Bengal |
| Administrative division | Burdwan |
| Headquarters | Midnapore |
| Government | |
| • Lok Sabha constituencies | Medinipur, Ghatal, Jhargram (ST) - all have assembly segments in adjoining districts, Arambagh - with one assembly segmant in the district |
| • Assembly seats | Dantan, Nayagram, Gopiballavpur, Jhargram, Keshiary, Kharagpur Sadar, Narayangarh, Sabang, Pingla, Kharagpur, Debra, Daspur, Ghatal, Chandrakona, Garbeta, Salboni, Keshpur, Medinipur, Binpur |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9,345 km2 (3,608 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 5,943,300 |
| • Density | 640/km2 (1,600/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 11.9 per cent |
| Demographics | |
| • Literacy | 79.04 per cent |
| • Sex ratio | 960 |
| Major highways | NH 6, NH 60 |
| Average annual precipitation | 2,111 mm |
| Website | Official website |

Paschim Medinipur district (Pron: pɔʃʧɪm med̪iːniːpur) or West Midnapore district (Pron: ˌmɪdnəˈpʊə) (Bengali: পশ্চিম মেদিনীপুর জেলা) (also known as Midnapore West) is the districts of the state of West Bengal, India. It was formed on 1 January 2002 after the Partition of Midnapore into Paschim Medinipur and Purba Medinipur.
Geography
Overview
Paschim Medinipur, located in the south-western part of West Bengal, was created with the partition of the erstwhile Midnapore district, then the largest district of India, on 1 January 2002. It ranks second in terms of geographical area (9,295.28 km2) amongst the districts of the state, next to South 24-Parganas (9,960 km2). It ranks third in terms of rural population (4.58 million) following South 24-Parganas (5.82 million) and Murshidabad (5.13 million). It ranked fourth in terms of percentage of tribal population (14.87) following Jalpaiguri (18.87), Purulia (18.27) and Dakshin Dinajpur (16.12) in 2011.[1]
Broadly speaking, there are two natural divisions of the district. NH 14 and NH 16 (old numbering NH 60) from Bankura to Balasore, cuts across the district and roughly is the dividing line between the two natural divisions. To the east of this road, the soil is fertile alluvial and the area is flat. To the west, the Chota Nagpur Plateau gradually slopes down creating an undulating area with infertile laterite rocks/ soil. The landscape changes from dense dry deciduous forests in the west to marshy wetlands in the east.[1]
The alluvial portion may be further subdivided into two divisions. First, it is a strip of purely deltaic country nearer to the Hooghly and the Rupnarayan, intersected by numerous rivers and watercourses subject to tidal influences. Second, it is rest of the eastern half of the district. It is a monotonous rice plain with numerous waterways and tidal creeks intersecting it. The tidal creeks are lined with embankments to prevent flooding of the fields. Much of the area is water-logged.[1]
Floods and drought
Paschim Medinipur district is subject to both floods and drought. Ghatal and parts of Kharagpur subdivision covering an area of 142,647 hectares (1,426.47 km2) are flood prone. Water logging during the rainy season affects Ghatal and the southern parts of Kharagpur subdivion and results in loss of crops in such areas as Sabang, Pingla and Narayangarh CD Blocks.335,248 hectares (3,352.48 km2) in Jhargram and Medinipur Sadar subdivisions are drought prone. The drought situation is particularly severe in Jhargram subdivision. Although the district is away from the sea, cyclones hit it frequently in October–November.[1]
Major cities and towns
Midnapore is the district headquarters. Other important towns and cities in the district include: Kharagpur, Jhargram, Ghatal, Belda, Chandrakona, Ramjibanpur, Garbeta, Balichak, Dantan, Mohanpur, Gopiballavpur, Nayagram, Keshiari, Keshpur, Narayangarh, Sabang, Daspur.Mohanpur.
Economy and politics
In 2006 the Ministry of Panchayati Raj named Paschim Medinipur one of the country's 250 most backward districts (out of a total of 640).[2] It is one of the eleven districts in West Bengal currently receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF).[2]
106 districts spanning 10 states across India, described as being part of Left Wing Extremism activities, constitute the Red corridor. In West Bengal the districts of Paschim Medinipur, Bankura, Purulia and Birbhum are part of the Red corridor. However, as of July 2016, there has been no reported incidents of Maoist related activities from these districts for the previous 4 years.[3] In the period 2009-2011 LWE violence resulted in more than 500 deaths and a similar number missing in Paschim Medinipur district.[4]
Divisions
Paschim Medinipur district is divided into the following administrative subdivisions: [5]
| Subdivision | Headquarters | Area km2 | Population (2011) | Rural Population % (2001) | Urban Population % (2001) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medinipur Sadar | Midnapore | 2,441.50 | 1,435,321 | 87.42 | 12.58 |
| Jhargram | Jhargram | 3,037,64 | 1,136,548 | 94.73 | 5.27 |
| Kharagpur | Kharagpur | 2,913.17 | 2,293,901 | 85.58 | 14.42 |
| Ghatal | Ghatal | 953.09 | 1,047,679 | 87.35 | 12.65 |
| Paschim Medinipur district | Midnapore | 9,368.00 | 5,913,457 | 88.10 | 11.90 |
Administrative subdivisions
The district comprises four subdivisions: Kharagpur, Medinipur Sadar, Ghatal and Jhargram. Kharagpur subdivision consists of Kharagpur municipality and ten community development blocks: Dantan–I, Dantan–II, Pingla, Kharagpur–I, Kharagpur–II, Sabang, Mohanpur, Narayangarh, Keshiari and Debra. Medinipur Sadar subdivision consists of Midnapore municipality and six community development blocks: Medinipur Sadar, Garhbeta–I, Garhbeta–II, Garhbeta–III, Keshpur and Shalboni. Ghatal subdivision consists of five municipalities (Ramjibanpur, Chandrakona, Khirpai, Kharar and Ghatal) and five community development blocks: Chandrakona–I, Chandrakona–II, Daspur–I, Daspur–II and Ghatal. Jhargram subdivision consists of Jhargram municipality and eight community development blocks: Binpur–I, Binpur–II, Jamboni, Jhargram, Gopiballavpur–I, Gopiballavpur–II, Nayagram and Sankrail.[6]
Midnapore is the district headquarters. There are 28 police stations, 29 development blocks, 8 municipalities and 290 gram panchayats in this district.[6][7]
Other than municipality area, each subdivision contains community development blocks which in turn are divided into rural areas and census towns. In total there are 12 urban units: 8 municipalities and 4 census towns.[7]
Kharagpur subdivision
- One municipality: Kharagpur.
- Dantan I community development block consists of rural areas with 9 gram panchayats and one census town: Chaulia
- Dantan II community development block consists of rural areas only with 7 gram panchayats.
- Pingla community development block consists of rural areas only with 10 gram panchayats.
- Kharagpur I community development block consists of rural areas with 7 gram panchayats and two census towns: Kharagpur Railway Settlement and Kalaikunda.
- Kharagpur II community development block consists of rural areas only with 9 gram panchayats.
- Sabang community development block consists of rural areas only with 13 gram panchayats.
- Mohanpur community development block consists of rural areas only with 5 gram panchayats.
- Narayangarh community development block consists of rural areas with 16 gram panchayats and one census town: Deuli.
- Keshiari community development block consists of only rural areas with 9 gram panchayats.
- Debra community development block consists of rural areas with 14 gram panchayats and one census town: Balichak.
Medinipur Sadar subdivision
- One municipality: Midnapore.
- Midnapore Sadar community development block consists of rural areas only with 9 gram panchayats.
- Garhbeta I community development block consists of rural areas with 12 gram panchayats and two census towns: Garbeta and Amlagora
- Garhbeta II community development block consists of rural areas only with 10 gram panchayats.
- Garhbeta III community development block consists of rural areas with 8 gram panchayats and three census towns: Durllabhganj, Dwari Geria and Naba Kola.
- Keshpur community development block consists of rural areas only with 15 gram panchayats.
- Salboni community development block consists of rural areas only with 10 gram panchayats.
Ghatal subdivision
- Five municipalities: Ramjibanpur, Chandrakona, Khirpai, Kharar and Ghatal.
- Chandrakona I community development block consists of rural areas only with 6 gram panchayats.
- Chandrakona II community development block consists of rural areas only with 6 gram panchayats.
- Daspur I community development block consists of rural areas only with 10 gram panchayats.
- Daspur II community development block consists of rural areas only with 14 gram panchayats.
- Ghatal community development block consists of rural areas only with 12 gram panchayats.
Jhargram subdivision
- One municipality: Jhargram.
- Binpur I community development block consists of rural areas only with 10 gram panchayats.
- Binpur II community development block consists of rural areas with 10 gram panchayats] and one census town: Silda.
- Jamboni community development block consists of rural areas only with 10 gram panchayats.
- Jhargram community development block consists of rural areas only with 13 gram panchayats.
- Gopiballavpur I community development block consists of rural areas only with 7 gram panchayats.
- Gopiballavpur II community development block consists of rural areas only with 7 gram panchayats.
- Nayagram community development block consists of rural areas only with 12 gram panchayats.
- Sankrail community development block consists of rural areas only with 10 gram panchayats.
Demographics
According to the 2011 census Paschim Medinipur district has a population of 5,943,300,[8] roughly equal to the nation of Eritrea[9] or the US state of Missouri.[10] This gives it a ranking of 14th in India (out of a total of 640).[8] The district has a population density of 636 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,650/sq mi) .[8] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 14.44%.[8] Paschim Medinipur has a sex ratio of 960 females for every 1000 males,[8] and a literacy rate of 79.04%.[8]
Culture
Tourism
- Chilkigarh (Kanak Durga Temple and park)
- Belpahari
- Jhargram
- Gopegarh Heritage Park
- Hatibari forest banglow and jhilli pakhiralay
- kankrajhore
- Garrasini asharam,near Belpahari
- Kaniashar pahar,near Belpahari
- Gurguripal Heritage Park
- Parimalkanan park,c.k.t
- Gangani [Garhbeta]
- Deer park[Jhargram]
- Rameshwar Temple,near Rohini(On the bank of Subarnarekha river with nearby green forest called TAPOBAN)
- Gourya Temple, Near Kharagpur
- ECO Park DURGAHURI, Near SANKRAIL
- Bisnu Temple, kultikri
- Rashikananda Memorial, Rohini
- Prayag Film City or Midnapore Film City or Chandrakona Film City at Chandrakona Road [11]
Notable personalities
- Sahid Kshudiram Basu (Mouboni, Anandapur PS, Keshpur Development Block)
- Iswar Chandra Vidyasagar (Birsingha, Ghatal PS)
- Raja Narasingha Malla Deb - (Jhargram)
Education
Universities and colleges
- Ambigeria Government College[12]
- Belda College
- Bhatter College
- Chaipat S.P.B. Mahavidyalaya
- Chandrakona Vidyasagar Mahavidyalaya
- Debra Thana Sahid Kshudiram Smriti Mahavidyalaya
- Garhbeta College
- Ghatal Rabindra Satabarsiki Mahavidyalaya
- Gourav Guin Memorial College
- Hijli College
- Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
- Institute of Science & Technology
- Jhargram Raj College
- K.D. College of Commerce and General Studies
- Kharagpur College
- Kharagpur Homeopathic Medical College and Hospital
- Midnapore College(formerly known as Day college)
- Midnapore Homoeopathic Medical College and Hospital
- Midnapore Law College
- Midnapore Medical College and Hospital
- Narajole Raj College
- Pingla Thana Mahavidyalaya
- Raja Narendra Lal Khan Women's College
- Sabang Sajani Kanta Mahavidyalaya
- Sankrail Anil Biswas Smriti Mahavidyalaya
- Santal Bidroha Sardha Satabarsiki Mahavidyalaya
- Iswar Chandra Vidyasagar Polytechnic - Jhargram
- Seva Bharati Mahavidyalaya
- Seva Bharati Krishi Vigyan Kendra
- Silda Chandra Sekhar College
- Subarnarekha Mahavidyalaya
- Sukumar Sengupta Mahavidyalaya
- Vidyasagar Teachers' Training College
- Vidyasagar University
- Vivekananda Satavarshiki Mahavidyalaya
Healthcare
The table below (all data in numbers) presents an overview of the medical facilities available and patients treated in the hospitals, health centres and sub-centres in 2014 in Paschim Medinipur district.[13]
| Subdivision | Health & Family Welfare Deptt, WB | Other State Govt Deptts |
Local bodies |
Central Govt Deptts / PSUs |
NGO / Private Nursing Homes |
Total | Total Number of Beds |
Total Number of Doctors |
Indoor Patients |
Outdoor Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitals |
Rural Hospitals |
Block Primary Health Centres |
Primary Health Centres | ||||||||||
| Jhargram | 1 | 6 | 2 | 25 | - | - | - | 7 | 41 | 838 | 87 | 73,696 | 1,033,410 |
| Medinipur Sadar | 2 | 5 | 1 | 15 | 3 | - | 1 | 26 | 53 | 2,117 | 323 | 121,486 | 1,375,817 |
| Kharagpur | 2 | 8 | 2 | 27 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 54 | 98 | 1841 | 197 | 93,110 | 1,814,309 |
| Ghatal | 1 | 4 | 1 | 15 | - | - | - | 46 | 67 | 988 | 66 | 46,006 | 742,984 |
| Paschim Medinipur district | 6 | 23 | 26 | 82 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 133 | 259 | 5,784 | 673* | 334,298 | 4,966,520 |
- Excluding Nursing Homes
NGOs
- Anjali Human Development and Research Organisation Jhargram PIN 721507
- Science Centre, Midnapore, Pin-721101, functioning since 1987 in the field of science popularisation, building scientific temper among people especially among children, development of science teaching through innovative low cost experiments and have receive Jawahalal Nehru Prize in 2000-01 from ISCA and Meghnad Puraskar from Department of Science and Technology, Government of West Bengal for Science Popularization.
- Belda Federation of Traders Organisation, Subhas Pally,Post- Belda- 721424,Secretary- Lakshman Ch. Sahoo.
- Ghatal Nabadoy Welfare Society, Ghatal, Paschim Medinipur, Pin - 721212
- Public Profit Policy Trust of India(P.P.P.T.I.),Kalkali,Sarishakhola,Keshpur,Midnapore.
- Sarada Kalyan Bhandar
- Vidyasagar Vidyapith
- Sri Sri Nitya Gopal Vision Care Foundation
- Midnapore.in - Legacy of Midnapore
- C.F.Andrews .Memorial.Society-Jhargram
- Barnali Sarangi Foundation - Rohini
- Society for Positive Atmosphere and Related Support to HIV/AIDS (SPARSHA)-Medinipur Town, Goura,
- Paschim Khirai Society for Rural & Child Development, Paschim Khirai, Pingla, Midnapore West- 721140
- Bhelampur Saibaba Sechyasebi seba Sangha,Bhelampur, Gansarisha, Keshiary, Paschim Medinipur, Pin-721133
- Lowada Cactus Welfare Association, Lowada, Debra, Paschim Medinipur, Pin-721136
- Gopali Youth welfare Society, Gopali, Kharagpur
- Gandhi Mission Trust
- Sarbik Palli Kalyan Kendra (estb 1986),Kiageria,Chandrakona Block-II, Pin-721201
- Dantan Science Club Dantan Paschim Medinipur pin-721426
- Pindrui Sonali Sangha.(Estd. 1985) Pindrui. Pingla. Paschim Medinipur. 721131
References
- 1 2 3 4 "District Human Development Report: Paschim Medinipur" (PDF). Chapter I Introduction and Human Development Indices for Paschim Mednipur. Development and Planning Department, Government of West Bengal, 2011. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- 1 2 Ministry of Panchayati Raj (8 September 2009). "A Note on the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme" (PDF). National Institute of Rural Development. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ↑ Singh, Vijayita. "Red Corridor to be redrawn". The Hindu, 25 July 2016. Retrieved 1 August 2016.
- ↑ "District Human Development Report: Paschim Medinipur" (PDF). May 2011. Page 271. Development & Planning Department, Government of West Bengal. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ↑ "District Statistical Handbook 2014 Paschim Medinipur". Table 2.2, 2.4(a). Department of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of West Bengal. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- 1 2 "Directory of District, Sub division, Panchayat Samiti/ Block and Gram Panchayats in West Bengal, March 2008". West Bengal. National Informatics Centre, India. 19 March 2008. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- 1 2 "Administration Setup". Official website of Purba Medinipur district. Archived from the original on 25 April 2008. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
- ↑ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". Retrieved 1 October 2011.
Eritrea 5,939,484 July 2011 est.
- ↑ "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
Missouri 5,988,927
- ↑ http://www.naachgaana.com/2012/04/16/shah-rukh-khan-inaugurates-the-prayag-film-city-in-chandrakona/
- ↑ http://www.ambigeriagovtcollege.org
- ↑ "District Statistical Handbook 2014 Paschim Medinipur". Table 3.1, 3.3. Department of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of West Bengal. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
Annyaman Samaj kalyan Samity. Tulip Model School. Khakurda.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Paschim Medinipur district. |
- Official website of Paschim Midnapore
- Map of old Medinipur district (district has now been split)
-
 Midnapore travel guide from Wikivoyage
Midnapore travel guide from Wikivoyage -
 Kharagpur travel guide from Wikivoyage
Kharagpur travel guide from Wikivoyage -
 Jhargram travel guide from Wikivoyage
Jhargram travel guide from Wikivoyage - Jhargram Holidays (Official Website)
 |
Bankura district | Hooghly district |  | |
| East Singhbhum district, Jharkhand | |
Howrah district | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Mayurbhanj district, Orissa | Balasore district, Orissa | East Midnapore district |