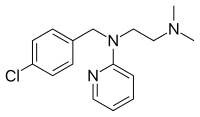
Chloropyramine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets), IM, IV, topical |
| ATC code | D04AA09 (WHO) R06AC03 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~100%[1] |
| Metabolism | Extensive hepatic |
| Onset of action | 15–30 min (oral) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
59-32-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 25295 |
| DrugBank |
DB08800 |
| ChemSpider |
23628 |
| UNII |
2K3L8O9SOV |
| KEGG |
D07195 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1194287 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.383 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H20ClN3 |
| Molar mass | 289.803 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Chloropyramine is a classical ("old" or first generation) antihistamine drug approved in some Eastern European countries (like Russia) for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, and other atopic (allergic) conditions. Related indications for clinical use include angioedema (Quincke's edema), allergic reactions to insect bites, food and drug allergies, and anaphylactic shock.
Chloropyramine is known as a competitive reversible H1 receptor antagonist (also known as an H1 inverse agonist), meaning that it exerts its pharmacological action by competing with histamine for the H1 subtype histamine receptor. By blocking the effects of histamine, the drug inhibits the vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and tissue edema associated with histamine release in the tissue. The H1 antagonistic properties of chloropyramine can be used by researchers for the purposes of blocking the effects of histamine on cells and tissues. In addition, chloropyramine has some anticholinergic properties.[1]
Chloropyramine's anticholinergic properties and the fact that it can pass through the blood–brain barrier are linked to its clinical side effects: drowsiness, weakness, vertigo, fatigue, dryness in the mouth, constipation, and rarely — visual disturbances and increase of intraocular pressure.
Clinical dosage and administration
In cases of severe allergic reactions, chloropyramine can be injected intramuscularly or intravenously. Oral administration: In adults, 25 mg can be taken 3 to 4 times daily (up to 150 mg); in children over 5 years old, 25 mg can be taken 2 to 3 times daily. For external application, the skin or the eye conjunctiva can be treated up to several times a day by applying a thin layer of cream or ointment containing 1% chloropyramine hydrochloride.
Contraindications
Contraindications for parenteral or oral administration include benign prostatic hyperplasia, peptic ulcer, pyloric and duodenal stenosis, uncontrolled glaucoma, pregnancy and breast-feeding. It is not intended for the management of acute bronchospasm.[1]
Special warnings and precautions
Chloropyramine should not be used internally with alcohol, sedative drugs and hypnotics because of the potentiation of the effects. It should be used with caution in patients suffering from hyperthyroidism, cardiovascular diseases and asthma. In children, it can induce agitation, and in many adult patients dizziness may be observed. Because of the pronounced sedative effect the preparation should be prescribed cautiously in drivers and people working with machines.
Drug interactions
Chloropyramine should not be used internally with MAO inhibitors. Because of its anticholinergic activity, concurrent administration with cholinomimetics is not advisable. General anesthetics, analgesic agents and psycholeptics potentiate the sedative effect of chloropyramine.
Trade names
- Allergosan, Sopharma AD (BG, GE, LV)
- Suprastin, Egis Pharmaceuticals PLC (GE, HU, LT, LV, RU)
- Supralgon, Biopharm JSC (GE)
- Supranorm-Tsiteli A, Rompharm Co. (GE)
- Synopen, Pliva d.o.o. (BA, HR, RS)
Synthesis
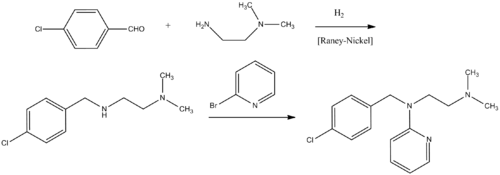
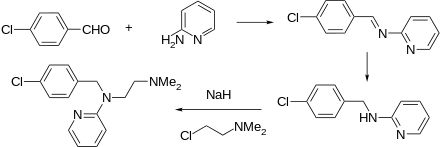
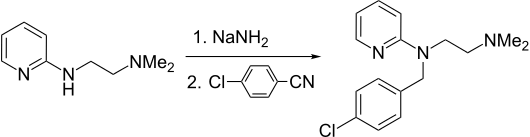
The preparation begins with the condensation of 4-chlorobenzaldehyde with 1,1-dimethy[ethylenediamine. The resulting Schiff base is reduced. The resulting amine is then further reacts with 2-bromopyridine in the presence of sodamide.
See also
- Mepyramine (4-methoxy analog)
- Methapyrilene
- Chlorothen
References
- 1 2 3 "Chloropyramine Tablets for Oral Use. Prescribing Information". State Register of Medicines (in Russian). Ozon OOO. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ↑ Vaughan, J. R.; Anderson, G. W.; Clapp, R. C.; Clark, J. H.; English, J. P.; Howard, K. L.; Marson, H. W.; Sutherland, L. H.; Denton, J. J. (1949). "Antihistamine agents; halogenated N,N-dimethyl-N-benzyl-N-(2-pyridyl)-ethylenediamines". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 14 (2): 228–234. doi:10.1021/jo01154a006. PMID 18117722.
- ↑ H.L. Kenneth, U.S. Patent 2,569,314 (1951).
- ↑ E.M. Cates, R.F. Phillips, U.S. Patent 2,607,778 (1952).
- ↑ J.R. Geigy AG., CH 264754 (1950).
- ↑ J.R. Geigy AG., CH 266234 (1950).
- ↑ J. R. Geigy AG., CH 266235 (1950).
- ↑ J.R. Geigy AG., GB 651596 (1951).