List of United States state legislatures
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of the United States of America |
|---|
 |
|
Legislature
|
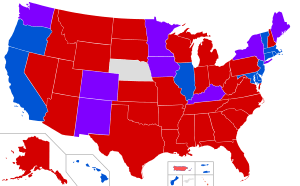
Each state in the United States has a legislature as part of its form of civil government. Most of the fundamental details of the legislature are specified in the state constitution. 49 state legislatures are bicameral bodies, composed of a lower house (Assembly, General Assembly, State Assembly, House of Delegates, or House of Representatives) and an upper house (Senate). The United States also has five non-state territories and one federal district with local legislative branches, which are also listed below. Among the states, the Nebraska Legislature is the lone unicameral body, although 3 other areas (the District of Columbia, Guam and the U.S. Virgin Islands) also have unicameral bodies.
The exact names, dates, term lengths, term limits, electoral systems, electoral districts, and other details are determined by the individual states' laws.
Party summary
The party composition of the legislatures (and party summary of the individual legislative chambers), as of January 2017, is:
| 32 | Republican-controlled legislatures |
| 13 | Democratic -controlled legislatures |
| 5 | Split legislatures |
| 50 | Total |
"Split" means that either the two chambers have different majority parties (e.g., Democratic Senate and Republican House), that one chamber is evenly split between parties, or that a coalition or "hung" chamber has occurred. The Nebraska legislature, though officially nonpartisan is de facto Republican-controlled, and listed as such.
In several states, the political party that controls the legislature is not the one that usually wins the state in Presidential elections. Also note that, due to the workings of politics, a party with a numerical majority in a chamber may be forced to share power with other parties due to informal coalitions or may cede power outright because of divisions.
The table below shows total state government control in 31 states, which means that the Governor and the legislative-chamber majorities are all of the same political party.
| 26 | Republican-controlled governments |
| 6 | Democratic -controlled governments |
| 6 | Democratic governor/Republican-controlled legislature |
| 7 | Republican governor/Democratic -controlled legislature |
| 1 | Independent governor/split legislature |
| 1 | Republican governor/Split legislature |
| 3 | Democratic governor/Split legislature |
| 50 | Total |
Statistics
State legislatures
- As of January 2017[1]
| 4,164 | Republican (R) legislators |
| 3,180 | Democratic (D) legislators |
| 9 | Progressive (P) legislators |
| 4 | Libertarian (L) legislators |
| 1 | Conservative (C) legislator |
| 1 | Independence (Ind.) legislator |
| 1 | Working Families (WF) legislator |
| 23 | Independent and nonpartisan (I) legislators |
| 7383[2] | Total |
Territorial and Federal District Legislatures
| State | Governor | Name | Lower house | Upper house | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Party strength | Term (years) | Name | Party strength | Term (years) | ||||
| American Samoa | Governor | Fono | House of Representatives | Nonpartisan 20 + 1 nonvoting delegate | 2 | Senate | Nonpartisan 18 | 4 | |
| District of Columbia | Mayor | Council | - | - | - | Council (unicameral) | D 11–0, 2 I | 4 | |
| Guam | Governor | Legislature | - | - | - | Legislature (unicameral) | D 9–6 | 2 | |
| Northern Mariana Islands | Governor | Commonwealth Legislature | House of Representatives | R 15-0, 5 I | 2 | Senate | R 7-0, 2 I | 4 | |
| Puerto Rico | Governor | Legislative Assembly | House of Representatives | PNP 34-16, 1 PIP [nb 6] | 4 | Senate | PNP 21-4, 1 PIP, 1 I | 4 | |
| US Virgin Islands | Governor | Legislature | - | - | - | Legislature (unicameral) | D 11-0, 3 I, 1 ICM | 2 | |
| 55 | New Progressive (PNP) legislators |
| 31 | Democratic (D) legislators |
| 28 | Republican (R) legislators |
| 20 | Popular Democratic (PPD) legislators |
| 2 | Puerto Rican Independence (PIP) legislators |
| 1 | Independent Citizens Movement (ICM) legislators |
| 51 | Independent and nonpartisan (I) legislators |
| 1 | Non-voting delegate (Swains Island) |
| 189 | Total |
See also
- Political party strength in U.S. states
- Comparison of U.S. state governments
- State legislature (United States)
- United States state legislatures' partisan trend
- National Conference of State Legislatures
Notes
- ↑ The Constitution of California names it the "California Legislature", but the Legislature brands itself as the "California State Legislature".
- ↑ The Constitution of Louisiana vests legislative authority in "a legislature, consisting of a Senate and a House of Representatives," and refers to it as "the legislature" throughout, without officially designating a term for the two houses together. However, the two bodies do use the term "Louisiana State Legislature" in official references to itself.
- ↑ When Nebraska switched to a unicameral legislature in 1937, the lower house was abolished. All current Nebraskan legislators are referred to as "Senators", as the pre-1937 senate was retained house.
- ↑ The Constitution of Utah names it the "Legislature of the State of Utah", but the Legislature brands itself as the "Utah State Legislature".
- ↑ The Constitution of Washington names it "the legislature of the state of Washington", but the Legislature brands itself as the "Washington State Legislature".
- ↑ The ruling parties of Puerto Rico are separate from the Republican and Democratic parties.
References
- ↑
- ↑ "2014 State and Legislative Partisan Composition" (PDF). National Conference of State Legislatures. January 31, 2014. Retrieved February 10, 2014.