Saint Helena
| Saint Helena |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "Loyal and Unshakeable" | ||||||
| Anthem: "God Save the Queen" "My Saint Helena Island" (unofficial) |
||||||
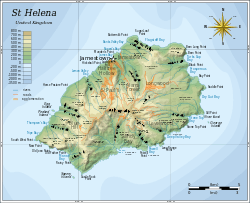 Map of Saint Helena
|
||||||
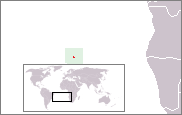 Location of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean.
|
||||||
| Capital | Jamestown 15°56′S 005°43′W / 15.933°S 5.717°W | |||||
| Largest settlement | Half Tree Hollow 15°56′0″S 5°43′12″W / 15.93333°S 5.72000°W | |||||
| Official languages | English | |||||
| Demonym | Saint Heleniana | |||||
| Part of | Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha | |||||
| Government | Non-partisan democracy | |||||
| • | Monarch | Elizabeth II | ||||
| • | Governor | Lisa Phillips | ||||
| Establishment | ||||||
| • | Charter granted | 1657 | ||||
| • | Colonised by the East India Company |
1659 |
||||
| • | Crown colony (Company rule ends) |
22 April 1834[1] |
||||
| • | Current constitution | 1 September 2009 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| • | Total | 121 km2 47 sq mi |
||||
| Population | ||||||
| • | 2016 (Feb) census | 4,534[2] | ||||
| • | Density | 37.5/km2 97.1/sq mi |
||||
| Currency | Saint Helena pound (SHP) | |||||
| Time zone | GMT (UTC) | |||||
| Drives on the | left | |||||
| Calling code | +290 | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | SH-HL | |||||
| Internet TLD | .sh | |||||
| a. | Or simply "Helenian". Informally, the islanders are also referred to as "Saints". UK Postcode: STHL 1ZZ |
|||||
Saint Helena (/ˌseɪnt həˈliːnə/ SAYNT-hə-LEE-nə) is a volcanic tropical island in the South Atlantic Ocean, 4,000 kilometres (2,500 mi) east of Rio de Janeiro and 1,950 kilometres (1,210 mi) west of the Cunene River, which marks the border between Namibia and Angola in southwestern Africa. It is part of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha.[3] Saint Helena measures about 16 by 8 kilometres (10 by 5 mi) and has a population of 4,534 (2016 census).[2] It was named after Saint Helena of Constantinople.
The island, one of the most remote islands in the world, was uninhabited when discovered by the Portuguese in 1502. It was an important stopover for ships sailing to Europe from Asia and South Africa for centuries. Napoleon was imprisoned there in exile by the British, as were Dinuzulu kaCetshwayo (for leading a Zulu army against British rule) and more than 5,000 Boers taken prisoner during the second Boer War.
Between 1791 and 1833, Saint Helena became the site of a series of experiments in conservation, reforestation and attempts to boost rainfall artificially.[4] This environmental intervention was closely linked to the conceptualisation of the processes of environmental change and helped establish the roots of environmentalism.[4]
Saint Helena is Britain's second-oldest remaining overseas territory after Bermuda.
History
Early history (1502–1658)
Most historical accounts state that the island was discovered on 21 May 1502 by Galician navigator João da Nova sailing at the service of Portugal, and that he named it "Santa Helena" after Helena of Constantinople. Another theory holds that the island found by da Nova was actually Tristan da Cunha, 2,430 kilometres (1,510 mi) to the south,[5] and that Saint Helena was discovered by some of the ships attached to the squadron of the Estêvão da Gama expedition on 30 July 1503 (as reported in the account of clerk Thomé Lopes).[6][7][8] However, a paper published in 2015 reviewed the discovery date and dismissed the 18 August as too late for da Nova to make a discovery and then return to Lisbon by 11 September 1502, whether he sailed from Saint Helena or Tristan da Cunha.[9] It demonstrates that 21 May is probably a Protestant rather than Catholic or Orthodox feast-day, first quoted in 1596 by Jan Huyghen van Linschoten, who was probably mistaken because the island was discovered several decades before the Reformation and start of Protestantism.[10][11] The alternative discovery date of 3 May is suggested as being historically more credible; it is the Catholic feast-day for the finding of the True Cross by Saint Helena in Jerusalem, and cited by Odoardo Duarte Lopes[12] and Sir Thomas Herbert.[13]
The Portuguese found the island uninhabited, with an abundance of trees and fresh water. They imported livestock, fruit trees and vegetables, and built a chapel and one or two houses. They formed no permanent settlement, but the island was an important rendezvous point and source of food for ships travelling from Asia to Europe, and frequently sick mariners were left on the island to recover before taking passage on the next ship to call on the island.[14]
Englishman Sir Francis Drake probably located the island on the final leg of his circumnavigation of the world (1577–1580).[15] Further visits by other English explorers followed and, once Saint Helena’s location was more widely known, English ships of war began to lie in wait in the area to attack Portuguese India carracks on their way home. In developing their Far East trade, the Dutch also began to frequent the island. The Portuguese and Spanish soon gave up regularly calling at the island, partly because they used ports along the West African coast, but also because of attacks on their shipping, the desecration of their chapel and religious icons, destruction of their livestock, and destruction of plantations by Dutch and English sailors.
The Dutch Republic formally made claim to Saint Helena in 1633, although there is no evidence that they ever occupied, colonized, or fortified it. By 1651, the Dutch had mainly abandoned the island in favour of their colony at the Cape of Good Hope.
East India Company (1658–1815)

In 1657, Oliver Cromwell[16] granted the English East India Company a charter to govern Saint Helena and, the following year, the company decided to fortify the island and colonise it with planters. The first governor Captain John Dutton arrived in 1659, making Saint Helena one of Britain's oldest colonies outside North America and the Caribbean. A fort and houses were built. After the Restoration of the English monarchy in 1660, the East India Company received a royal charter giving it the sole right to fortify and colonise the island. The fort was renamed James Fort and the town Jamestown, in honour of the Duke of York, later James II of England.
Between January and May 1673, the Dutch East India Company forcibly took the island, before English reinforcements restored English East India Company control. The company experienced difficulty attracting new immigrants, and sentiments of unrest and rebellion fomented among the inhabitants. Ecological problems of deforestation, soil erosion, vermin and drought led Governor Isaac Pyke in 1715 to suggest that the population be moved to Mauritius, but this was not acted upon and the company continued to subsidise the community because of the island's strategic location. A census in 1723 recorded 1,110 people, including 610 slaves.
18th century governors tried to tackle the island's problems by implementing tree plantation, improving fortifications, eliminating corruption, building a hospital, tackling the neglect of crops and livestock, controlling the consumption of alcohol and introducing legal reforms. The island enjoyed a lengthy period of prosperity from about 1770. Captain James Cook visited the island in 1775 on the final leg of his second circumnavigation of the world. St. James' Church was erected in Jamestown in 1774, and Plantation House was built in 1791–92 and has since been the official residence of the Governor.
Edmond Halley visited Saint Helena on leaving the University of Oxford in 1676 and set up an astronomical observatory with a 7.3-metre-long (24 ft) aerial telescope, with the intention of studying stars from the Southern Hemisphere.[17] The site of this telescope is near Saint Mathew's Church in Hutt's Gate in the Longwood district. The 680-metre (2,230 ft) high hill there is named for him and is called Halley's Mount.
Throughout this period, Saint Helena was an important port of call of the East India Company. East Indiamen would stop there on the return leg of their voyages to British India and China. At Saint Helena, ships could replenish supplies of water and provisions and, during wartime, form convoys that would sail under the protection of vessels of the Royal Navy. Captain James Cook's vessel HMS Endeavour anchored and resupplied off the coast of Saint Helena in May 1771 on its return from the European discovery of the east coast of Australia and rediscovery of New Zealand.[18]
The importation of slaves was made illegal in 1792. Governor Robert Patton (1802–1807) recommended that the company import Chinese labour to supplement the rural workforce. The coolie labourers arrived in 1810, and their numbers reached 600 by 1818. Many were allowed to stay, and their descendents became integrated into the population. An 1814 census recorded 3,507 people on the island.
British rule (1815–1821) and Napoleon's exile


In 1815, the British government selected Saint Helena as the place of detention for Napoleon Bonaparte. He was taken to the island in October 1815. Napoleon stayed at the Briars pavilion on the grounds of the Balcombe family's home until his permanent residence at Longwood House was completed in December 1815. Napoleon died there on 5 May 1821.[19]
British East India Company (1821–1834)
After Napoleon's death, the thousands of temporary visitors were withdrawn and the East India Company resumed full control of Saint Helena. Between 1815 and 1830, the EIC made the packet schooner St Helena available to the government of the island, which made multiple trips per year between the island and the Cape, carrying passengers both ways and supplies of wine and provisions back to the island.
Napoleon praised Saint Helena’s coffee during his exile on the island, and the product enjoyed a brief popularity in Paris in the years after his death.
The importation of slaves to Saint Helena was banned in 1792, but the phased emancipation of over 800 resident slaves did not take place until 1827, which was still some six years before the British Parliament passed legislation to ban slavery in the colonies.[20]
Crown colony (1834–1981)
Under the provisions of the 1833 India Act, control of Saint Helena was passed from the East India Company to the British Crown, and it became a crown colony.[1] Subsequent administrative cost cutting triggered the start of a long-term population decline whereby those who could afford to do so tended to leave the island for better opportunities elsewhere. The latter half of the 19th century saw the advent of steam ships not reliant on trade winds, as well as the diversion of Far East trade away from the traditional South Atlantic shipping lanes to a route via the Red Sea (which, prior to the building of the Suez Canal, involved a short overland section). These factors contributed to a decline in the number of ships calling at the island from 1,100 in 1855 to only 288 in 1889.
In 1840, a British naval station established to suppress the African slave trade was based on the island, and between 1840 and 1849 over 15,000 freed slaves, known as "Liberated Africans", were landed there.
In 1858, the French emperor Napoleon III successfully gained the possession, in the name of the French government, of Longwood House and the lands around it, last residence of Napoleon I (who died there in 1821). It is still French property, administered by a French representative and under the authority of the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
On 11 April 1898 American Joshua Slocum, on his famous and epic solo round-the-world voyage, arrived at Jamestown. He departed on 20 April 1898 for the final leg of his circumnavigation having been extended hospitality from the governor, his Excellency Sir R A Standale, presented two lectures on his voyage, and been invited to Longwood by the French Consular agent.
In 1900 and 1901, over 6,000 Boer prisoners were held on the island, and the population reached its all-time high of 9,850 in 1901.
A local industry manufacturing fibre from New Zealand flax was successfully reestablished in 1907 and generated considerable income during the First World War. Ascension Island was made a dependency of Saint Helena in 1922, and Tristan da Cunha followed in 1938. During the Second World War, the United States built Wideawake airport on Ascension in 1942, but no military use was made of Saint Helena.
During this period, the island enjoyed increased revenues through the sale of flax, with prices peaking in 1951. However, the industry declined because of transportation costs and competition from synthetic fibres. The decision by the British Post Office to use synthetic fibres for its mailbags was a further blow, contributing to the closure of the island's flax mills in 1965.
From 1958, the Union Castle shipping line gradually reduced its service calls to the island. Curnow Shipping, based in Avonmouth, replaced the Union-Castle Line mailship service in 1977, using the RMS (Royal Mail Ship) St Helena.
1981 to present

The British Nationality Act 1981 reclassified Saint Helena and the other Crown colonies as British Dependent Territories. The islanders lost their right of abode in Britain. For the next 20 years, many could find only low-paid work with the island government, and the only available employment outside Saint Helena was on the Falkland Islands and Ascension Island. The Development and Economic Planning Department (which still operates) was formed in 1988 to contribute to raising the living standards of the people of Saint Helena.
In 1989, Prince Andrew launched the replacement RMS St Helena to serve the island; the vessel was specially built for the Cardiff–Cape Town route and features a mixed cargo/passenger layout.
The Saint Helena Constitution took effect in 1989 and provided that the island would be governed by a Governor, Commander-in-Chief, and an elected Executive and Legislative Council. In 2002, the British Overseas Territories Act 2002 granted full British citizenship to the islanders, and renamed the Dependent Territories (including Saint Helena) the British Overseas Territories. In 2009, Saint Helena and its two territories received equal status under a new constitution, and the British Overseas Territory was renamed Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha.
The UK government has spent £250 million in the construction of the island's airport. This is aimed at helping the island become more self-sufficient, encouraging economic development while reducing dependence on British government aid. It is also expected to kick-start the tourism industry, with up to 30,000 visitors expected annually.[21] As of August 2015, ticketing was postponed until an airline could be firmly designated.[22] The first plane landed on 15 September 2015, with the first large passenger jet landing on 18 April of the following year, although the airport is not yet officially open due to concerns about wind shear.[23]
Geography
Located in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) from the nearest major landmass, Saint Helena is one of the most remote places in the world. The nearest port on the continent is Namibe in southern Angola, and the nearest international airport the Quatro de Fevereiro Airport of Angola's capital Luanda; connections to Cape Town in South Africa are used for most shipping needs, such as the mail boat that serves the island, the RMS St Helena. The island is associated with two other isolated islands in the southern Atlantic, also British territories: Ascension Island about 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) due northwest in more equatorial waters and Tristan da Cunha, which is well outside the tropics 2,430 kilometres (1,510 mi) to the south. The island is situated in the Western Hemisphere and has the same longitude as Cornwall in the United Kingdom. Despite its remote location, it is classified as being in West Africa by the United Nations.
The island of Saint Helena has a total area of 122 km2 (47 sq mi), and is composed largely of rugged terrain of volcanic origin (the last volcanic eruptions occurred about 7 million years ago).[24] Coastal areas are covered in volcanic rock and warmer and drier than the centre. The highest point of the island is Diana's Peak at 818 m (2,684 ft). In 1996 it became the island's first national park. Much of the island is covered by New Zealand flax, a legacy of former industry, but there are some original trees augmented by plantations, including those of the Millennium Forest project, which was established in 2002 to replant part of the lost Great Wood and is now managed by the Saint Helena National Trust. The Millennium Forest is being planted with indigenous gumwood trees. When the island was discovered, it was covered with unique indigenous vegetation, including a remarkable cabbage tree species. The island's hinterland must have been a dense tropical forest but the coastal areas were probably also quite green. The modern landscape is very different, with widespread bare rock in the lower areas, although inland it is green, mainly due to introduced vegetation. There are no native land mammals, but cattle, cats, dogs, donkeys, goats, mice, rabbits, rats and sheep have been introduced, and native species have been adversely affected as a result. The dramatic change in landscape must be attributed to these introductions. As a result, the string tree (Acalypha rubrinervis) and the Saint Helena olive (Nesiota elliptica) are now extinct, and many of the other endemic plants are threatened with extinction.
There are several rocks and islets off the coast, including: Castle Rock, Speery Island, the Needle, Lower Black Rock, Upper Black Rock (South), Bird Island (Southwest), Black Rock, Thompson's Valley Island, Peaked Island, Egg Island, Lady's Chair, Lighter Rock (West), Long Ledge (Northwest), Shore Island, George Island, Rough Rock Island, Flat Rock (East), the Buoys, Sandy Bay Island, the Chimney, White Bird Island and Frightus Rock (Southeast), all of which are within one kilometre (0.62 miles) of the shore.
The national bird of Saint Helena is the Saint Helena plover, known locally as the wirebird, on account of its wire-like legs. It appears on the coat of arms of Saint Helena and on the flag.[25][26]
Climate
The climate of Saint Helena is tropical, marine and mild, tempered by the Benguela Current and trade winds that blow almost continuously.[27][28] The climate varies noticeably across the island. Temperatures in Jamestown, on the north leeward shore, range between 21–28 °C (70–82 °F) in the summer (January to April) and 17–24 °C (63–75 °F) during the remainder of the year. The temperatures in the central areas are, on average, 5–6 °C (9.0–10.8 °F) lower.[28] Jamestown also has a very low annual rainfall, while 750–1,000 mm (30–39 in) falls per year on the higher ground and the south coast, where it is also noticeably cloudier.[29] There are weather recording stations in the Longwood and Blue Hill districts.
Administrative divisions

Saint Helena is divided into eight districts,[30] with the majority housing a community Centre. The districts also serve as statistical divisions. The island is a single electoral area and elects 12 representatives to the Legislative Council[31] of 15.
| District balance |
Area[32] km2 |
Area sq mi | Pop. 1998 | Pop. 2008[33] | Pop. 2016[2] | Pop./km2 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarm Forest | 5.4 | 2.1 | 289 | 276 | 383 | 70.4 |
| Blue Hill | 36.8 | 14.2 | 177 | 153 | 158 | 4.3 |
| Half Tree Hollow | 1.6 | 0.6 | 1,140 | 901 | 984 | 633.2 |
| Jamestown | 3.9 | 1.5 | 884 | 716 | 629 | 161.9 |
| Levelwood | 14.8 | 5.7 | 376 | 316 | 369 | 25.0 |
| Longwood | 33.4 | 12.9 | 960 | 715 | 790 | 23.6 |
| Sandy Bay | 16.1 | 6.2 | 254 | 205 | 193 | 12.0 |
| Saint Paul's | 11.4 | 4.4 | 908 | 795 | 843 | 74.0 |
| Royal Mail Ship St. Helena |
– | – | 149 | 171 | 183 | – |
| Jamestown Harbour |
– | – | 20 | 9 | 13 | – |
| Total | 123.3 | 47.6 | 5,157 | 4,257 | 4,349 | 35.3 |
Population
Demographics


Saint Helena was first settled by the English in 1659, and the island has a population of about 4,250 inhabitants, mainly descended from people from Britain – settlers ("planters") and soldiers – and slaves who were brought there from the beginning of settlement – initially from Africa (the Cape Verde Islands, Gold Coast and west coast of Africa are mentioned in early records), then India and Madagascar. The importation of slaves was made illegal in 1792, thus preventing any further increase in their numbers.
In 1840, Saint Helena became a provisioning station for the British West Africa Squadron,[27] preventing slavery to Brazil (mainly), and many thousands of slaves were freed on the island. These were all African, and about 500 stayed while the rest were sent on to the West Indies and Cape Town, and eventually to Sierra Leone.
Imported Chinese labourers arrived in 1810, reaching a peak of 618 in 1818, after which numbers were reduced. Only a few older men remained after the British Crown took over the government of the island from the East India Company in 1834. The majority were sent back to China, although records in the Cape suggest that they never got any farther than Cape Town. There were also a very few Indian lascars who worked under the harbour master.
The citizens of Saint Helena hold British Overseas Territories citizenship. On 21 May 2002, full British citizenship was restored by the British Overseas Territories Act 2002.[34] See also British nationality law.
During periods of unemployment, there has been a long pattern of emigration from the island since the post-Napoleonic period. The majority of "Saints" emigrated to Britain, South Africa and in the early years, Australia. The population had been steadily declining since the late 1980s and dropped from 5,157 at the 1998 census to 4,257 in 2008.[33] However, as of the 2016 census, the population has risen to 4,534.[2] In the past emigration was characterised by young unaccompanied persons leaving to work on long-term contracts on Ascension and the Falkland Islands, but since "Saints" were re-awarded British citizenship in 2002, emigration to Britain by a wider range of wage-earners has accelerated due to the prospect of higher wages and better progression prospects.
Religion
Most residents belong to the Anglican Communion and are members of the Diocese of St Helena, which has its own bishop and includes Ascension Island. The 150th anniversary of the diocese was celebrated in June 2009.
Other Christian denominations on the island include the Roman Catholic Church (since 1852), the Salvation Army (since 1884), Baptists (since 1845) and, in more recent times, the Seventh-day Adventist Church (since 1949), the New Apostolic Church, and Jehovah's Witnesses (of which one in 35 residents is a member, the highest ratio of any country).[35] The Roman Catholics are pastorally served by the Mission sui iuris of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, whose office of ecclesiastical superior is vested in the Apostolic Prefecture of the Falkland Islands.
The Baha'i Faith has also been represented on the island since 1954.[36]
Politics
Executive authority in Saint Helena is vested in Queen Elizabeth II and is exercised on her behalf by the Governor of Saint Helena. The Governor is appointed by the Queen on the advice of the British government. Defence and Foreign Affairs remain the responsibility of the United Kingdom.
There are fifteen seats in the Legislative Council of Saint Helena, a unicameral legislature, in addition to a Speaker and a Deputy Speaker. Twelve of the fifteen members are elected in elections held every four years. The three ex officio members are the Chief Secretary, Financial Secretary and Attorney General. The Executive Council is presided over by the Governor, and consists of three ex officio officers and five elected members of the Legislative Council appointed by the Governor. There is no elected Chief Minister, and the Governor acts as the head of government. In January 2013 it was proposed that the Executive Council would be led by a "Chief Councillor" who would be elected by the members of the Legislative Council and would nominate the other members of the Executive Council. These proposals were put to a referendum on 23 March 2013 where they were defeated by 158 votes to 42 on a 10% turnout.[37]
Both Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha have an Administrator appointed to represent the Governor of Saint Helena.
One commentator has observed that, notwithstanding the high unemployment resulting from the loss of full passports during 1981–2002, the level of loyalty to the British monarchy by the Saint Helena population is probably not exceeded in any other part of the world.[38] King George VI is the only reigning monarch to have visited the island. This was in 1947 when the King, accompanied by Queen Elizabeth (later the Queen Mother), Princess Elizabeth (later Queen Elizabeth II) and Princess Margaret were travelling to South Africa. Prince Philip arrived at Saint Helena in 1957, followed by his son, Prince Andrew, who visited as a member of the armed forces in 1984, and his daughter, the Princess Royal, in 2002.
Human rights
In 2012, the government of Saint Helena funded the creation of the St. Helena Human Rights Action Plan 2012–2015.[39] Work is being done under this action plan, including publishing awareness-raising articles in local newspapers, providing support for members of the public with human rights queries, and extending several UN Conventions on human rights to St. Helena.[40]
Legislation to set up an Equality & Human Rights Commission was passed by Legislative Council in July 2015. This commenced operation in October 2015.[41]
Child abuse scandal
In 2014 there were reports of child abuse in Saint Helena. Britain’s Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO) has been accused of lying to the United Nations about child abuse in Saint Helena to cover up allegations,[42] including cases of a police officer having raped a four-year-old girl and of a police officer having mutilated a two-year-old.[42][43][44][45]
The British government admits it made an "erroneous" report to the United Nations when it denied that child abuse was rife in Saint Helena.[42]
Sasha Wass QC and her team arrived on Saint Helena on 17 March 2015 to commence the Inquiry and departed on 1 April 2015.[5] Announcements were made in local newspapers in week-ending 13 March 2015 and a website has been set up at www.wassinquiry.org.sh.
The Wass Report was published on 10 December 2015. It found that the lurid headlines in the Daily Mail had come from two social workers who it said were incompetent.
Biodiversity
Saint Helena has long been known for its high proportion of endemic birds and vascular plants. The highland areas contain most of the 400 endemic species recognised to date. Much of the island has been identified by BirdLife International as being important for bird conservation, especially the endemic Saint Helena plover or wirebird, and for seabirds breeding on the offshore islets and stacks, in the north-east and the south-west Important Bird Areas.[46] On the basis of these endemics and an exceptional range of habitats, Saint Helena is on the United Kingdom's tentative list for future UNESCO World Heritage Sites.[47]
Saint Helena's biodiversity, however, also includes marine vertebrates, invertebrates (freshwater, terrestrial and marine), fungi (including lichen-forming species), non-vascular plants, seaweeds and other biological groups. To date, very little is known about these, although more than 200 lichen-forming fungi have been recorded, including 9 endemics,[48] suggesting that many significant discoveries remain to be made.
Economy
- Note: Some of the data in this section have been sourced from the Government of St Helena Sustainable Development Plan.[49]
The island had a monocrop economy until 1966, based on the cultivation and processing of New Zealand flax for rope and string. Saint Helena's economy is now weak, and is almost entirely sustained by aid from the British government. The public sector dominates the economy, accounting for about 50% of gross domestic product. Inflation was running at 4% in 2005. There have been increases in the cost of fuel, power and all imported goods.
The tourist industry is heavily based on the promotion of Napoleon's imprisonment. A golf course also exists and the possibility for sportfishing tourism is great. Three hotels operate on the island but the arrival of tourists is directly linked to the arrival and departure schedule of the RMS St Helena. Some 3,200 short-term visitors arrived on the island in 2013.
Saint Helena produces what is said to be the most expensive coffee in the world. It also produces and exports Tungi Spirit, made from the fruit of the prickly or cactus pears, Opuntia ficus-indica ("Tungi" is the local St Helenian name for the plant). Like Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha, Saint Helena is permitted to issue its own postage stamps, an enterprise that provides a significant income.
Economic statistics
Quoted at constant 2002 prices, GDP fell from £12 million in 1999–2000 to £11 million in 2005–06. Imports are mainly from the UK and South Africa and amounted to £6.4 million in 2004–05 (quoted on an FOB basis). Exports are much smaller, amounting to £0.2 million in 2004–05. Exports are mainly fish and coffee; Philatelic sales were £0.06 million in 2004–05. The limited number of visiting tourists spent about £0.4 million in 2004–05, representing a contribution to GDP of 3%.
Public expenditure rose from £10 million in 2001–02 to £12 million in 2005–06 to £28m in 2012–13. The contribution of UK budgetary aid to total SHG government expenditure rose from £4.6 million in to £6.4 million to £12.1 million over the same period. Wages and salaries represent about 38% of recurrent expenditure.
Unemployment levels are low (31 individuals in 2013, compared to 50 in 2004 and 342 in 1998). Employment is dominated by the public sector, the number of government positions has fallen from 1,142 in 2006 to just over 800 in 2013. Saint Helena’s private sector employs approximately 45% of the employed labour force and is largely dominated by small and micro businesses with 218 private businesses employing 886 in 2004.
Household survey results suggest the percentage of households spending less than £20 per week on a per capita basis fell from 27% to 8% between 2000 and 2004, implying a decline in income poverty. Nevertheless, 22% of the population claimed social security benefit in 2006/7, most of them aged over 60, a sector that represents 20% of the population.
Banking and currency
In 1821, Saul Solomon issued a 70,560 copper tokens worth a halfpenny each Payable at St Helena by Solomon, Dickson and Taylor – presumably London partners – that circulated alongside the East India Company's local coinage until the Crown took over the island in 1836. The coin remains readily available to collectors.
Today Saint Helena has its own currency, the Saint Helena pound, which is at parity with the pound sterling. The government of Saint Helena produces its own coinage and banknotes. The Bank of Saint Helena was established on Saint Helena and Ascension Island in 2004. It has branches in Jamestown on Saint Helena, and Georgetown, Ascension Island and it took over the business of the St. Helena government savings bank and Ascension Island Savings Bank.[50]
For more information on currency in the wider region, see the Sterling Currency in the South Atlantic and the Antarctic.
Transport


Saint Helena is one of the most remote islands in the world, and has one commercial airport.[51]
Sea
The ship RMS St Helena runs between Saint Helena and Cape Town on a five-day voyage,[51] also visiting Ascension Island and Walvis Bay, and occasionally voyaging north to Tenerife and Portland, UK. It berths in James Bay, Saint Helena, approximately 30 times per year.[52] The RMS St Helena was due for decommissioning in 2010, but its service life has been extended to July 2017.[53]
Air
.jpg)
After a long period of rumour and consultation, the British government announced plans to construct an airport in Saint Helena in March 2005. The airport was expected to be completed by 2010. However, the approved bidder, the Italian firm Impregilo, was not chosen until 2008, and then the project was put on hold in November 2008, allegedly due to new financial pressures brought on by the financial crisis of 2007–08. By January 2009, construction had not commenced and no final contracts had been signed. Governor Andrew Gurr departed for London in an attempt to speed up the process and solve the problems.
On 22 July 2010, the British government agreed to help pay for the new airport.[54] In November 2011, a new deal was signed between the British government and South African civil engineering company Basil Read, and the airport was scheduled to open in February 2016 with flights to and from South Africa and the UK.[55] In March 2015, South African airline Comair became the preferred bidder to provide weekly air service between the island and Johannesburg, starting from 2016.[56]
The first aircraft landed at the new airport on 15 September 2015, a South African Beechcraft King Air 200, prior to conducting a series of flights to calibrate the airport's radio navigation equipment.[51][57]
The first helicopter landing at the new airfield was conducted by the Wildcat HMA.2 ZZ377 from 825 Squadron 201 Flight, embarked on visiting HMS Lancaster on 23 October 2015.[58]
The airport's opening was due in May 2016, but it was announced in June 2016 that it had been delayed indefinitely due to high winds and wind shear.[59]
Local
A minibus offers a basic service to carry people around Saint Helena, with most services designed to take people into Jamestown for a few hours on weekdays to conduct their business. Car hire is available for visitors.
Media and communications
Radio
Radio St Helena started operations on Christmas Day 1967, and provided a local radio service that had a range of about 100 km (62 mi) from the island, and also broadcast internationally on shortwave radio (11092.5 kHz) on one day a year. The station presented news, features, and music in collaboration with its sister newspaper the St Helena Herald. It closed on 25 December 2012 to make way for a new three-channel FM service, also funded by St. Helena Government and run by the South Atlantic Media Services (formerly St. Helena Broadcasting (Guarantee) Corporation).[60]
Saint FM[61] provided a local radio service for the island which was also available on internet radio[62] and relayed in Ascension Island. The station was not government-funded. It was launched in January 2005 and closed on 21 December 2012. It broadcast news, features, and music in collaboration with its sister newspaper the St Helena Independent (which continues).
Saint FM Community Radio took over the radio channels vacated by Saint FM and launched on 10 March 2013.[63] The station operates as a limited-by-guarantee company owned by its members,[64] and is registered as a fund-raising Association. Membership is open to everyone and grants access to a live audio stream.
Occasional amateur radio operations also occur on the island. The ITU prefix used is ZD7.[65]
Online
St Helena Online[66] is a not-for-profit internet news service run from the UK by a former print and BBC journalist, working in partnership with Saint FM and the St Helena Independent.
St Helena Local [67] offers a news service and online user forum offering information about St Helena. This website is run from overseas but is open to contribution from anyone who has an interest in St Helena.
Saint Helena Island Info [68] is an online resource featuring the history of St. Helena from its discovery to the present day, plus photographs and information about life on St. Helena today.
Saint Helena Government [69] is the official mouthpiece of the island's governing body. It includes news, information for potential visitors and investors, as well as official press releases and pages from the major government departments.
Saint Helena Tourism [70] is a website aimed squarely at the tourist trade with advice on accommodation, transport, food and drink, events and the like. Saint Helena Islands Property Finder - St Helena online accommodation offering self-catering, bed and breakfasts, hotels and property news.
Television
Sure South Atlantic Ltd ("Sure") offers television for the island via 17 analogue terrestrial UHF channels, offering a mix of British, US, and South African programming. The channels are from DSTV and include Mnet, SuperSport, and BBC channels. The feed signal from MultiChoice DStv in South Africa is received by a satellite dish at Bryant's Beacon from Intelsat 7 in the Ku band.[71]
The St Helena Broadcasting Corporation was due to broadcast television in 2014 on channel 1.
Telecommunications
Sure provide the telecommunications service in the territory through a digital copper-based telephone network including ADSL broadband service. In August 2011 the first fibre-optic link was installed on the island, which connects the television reception antennas at Bryant's Beacon to the Cable & Wireless Technical Centre in the Briars.
A satellite ground station with a 7.6-metre (25 ft) satellite dish installed in 1989[72] at The Briars is the only international connection providing satellite links through Intelsat 707 to Ascension island and the United Kingdom.[73] Since all international telephone and internet communications are relying on this single satellite link both internet and telephone service are subject to sun outages.
Saint Helena has the international calling code +290 which, since 2006, Tristan da Cunha shares. Saint Helena telephone numbers changed from 4 to 5 digits on 1 October 2013 by being prefixed with the digit "2", i.e. 2xxxx, with the range 5xxxx being reserved for mobile numbering, and 8xxx being used for Tristan da Cunha numbers (these are still shown as 4 digits).[74]
Mobile telephony was due to start operating on the island by late 2015.[75]
Internet
Saint Helena was granted the use of .sh as its own Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD). This is formally shared with Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha, British Overseas Territories. Registrations of internationalized domain names are also accepted under this TLD so, for example, the German federal state of Schleswig-Holstein uses the .sh domain for some quasi-governmental sites.[76] In practice several sites dedicated to aspects of life on Saint Helena are run from elsewhere in the world so use other TLD's, such as the Saint Helena website[77] which is based in Sweden.
Saint Helena has a 10/3.6 Mbit/s[73] internet link via Intelsat 707 provided by Sure. Serving a population of more than 4,000, this single satellite link is considered inadequate in terms of bandwidth.
ADSL broadband service is provided with maximum speeds of up to 1,536 KBit/s downstream and 512 KBit/s upstream offered on contract levels from lite at £16 per month to gold+ at £190 per month.[78] There are a few public WiFi hotspots in Jamestown, which are also being operated by Sure (formerly Cable & Wireless).[79]
The South Atlantic Express, a 10,000 km (6,214 mi) submarine communications cable connecting Africa to South America, run by the undersea fibre optic provider eFive, will pass St Helena relatively closely. There were no plans to land the cable and install a landing station ashore, which could supply St Helena's population with sufficient bandwidth to fully leverage the benefits of today's information society. In January 2012, a group of supporters petitioned the UK government to meet the cost of landing the cable at St Helena.[80] On 6 October 2012, eFive agreed to reroute the cable through St. Helena after a successful lobbying campaign by A Human Right, a San Francisco-based NGA working on initiatives to ensure all people are connected to the internet. Islanders have sought the assistance of the UK Department for International Development and Foreign and Commonwealth Office in funding the £10m required to bridge the connection from a local junction box on the cable to the island. The UK government has announced that a review of the island's economy would be required before such funding would be agreed.[81]
Local newspapers
The island has two local newspapers, both of which are available on the internet. The St Helena Independent[82] has been published since November 2005. The Sentinel newspaper was introduced in 2012.[83]
Culture and society
Education
Education is free and compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16 [84] The island has three primary schools for students of age 4 to 11: Harford, Pilling, and St Paul’s. Prince Andrew School provides secondary education for students aged 11 to 18. At the beginning of the academic year 2009–10, 230 students were enrolled in primary school and 286 in secondary school.[85]
The Education and Employment Directorate also offers programmes for students with special needs, vocational training, adult education, evening classes, and distance learning. The island has a public library (the oldest in the Southern Hemisphere[86]) and a mobile library service which operates weekly in rural areas.[87]
The English national curriculum is adapted for local use.[87] A range of qualifications are offered – from GCSE, A/S and A2, to Level 3 Diplomas and VRQ qualifications:[88]
- A/S & A2 and Level 3 Diploma
- Business Studies
- English
- English Literature
- Geography
- ICT
- Psychology
- Maths
- Accountancy
- VRQ
- Building and Construction
- Automotive Studies
Saint Helena has no tertiary education. Scholarships are offered for students to study abroad.[87]
Sport
Sports played on the island include football, cricket, volleyball, tennis, golf, motocross, shooting and sailing. Saint Helena has sent teams to a number of Commonwealth Games. Saint Helena is a member of the International Island Games Association.[89] The Saint Helena cricket team made its debut in international cricket in Division Three of the African region of the World Cricket League in 2011.
The Governor's Cup is a yacht race between Cape Town and Saint Helena island, held every two years in December/January; the most recent event was in December 2010. In Jamestown a timed run takes place up Jacob's Ladder every year, with people coming from all over the world to take part.
Scouting
There are scouting and guiding groups on Saint Helena and Ascension Island. Scouting was established on Saint Helena island in 1912.[90] Lord and Lady Baden-Powell visited the Scouts on Saint Helena on the return from their 1937 tour of Africa. The visit is described in Lord Baden-Powell's book entitled African Adventures.[91]
Namesake
St Helena, the suburb of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia was named after the island.
See also
References
- 1 2 The St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Constitution Order 2009 "...the transfer of rule of the island to His Majesty’s Government on 22 April 1834 under the Government of India Act 1833, now called the Saint Helena Act 1833" (Schedule Preamble)
- 1 2 3 4 "Census 2016 – summary report" (PDF). St Helena Government. Retrieved 21 September 2016.
- ↑ "Constitution of St. Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha". UK Archives. 2009. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- 1 2 Richard Grove, Green Imperialism: Colonial Expansion, Tropical Island Edens and the Origins of Environmentalism, 1600–1860 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995), pp. 309–379
- ↑ article: Tristan da Cunha (distance)
- ↑ A. H. Schulenburg, 'The discovery of St Helena: the search continues'. Wirebird: The Journal of the Friends of St Helena, Issue 24 (Spring 2002), pp. 13–19.
- ↑ Duarte Leite, História dos Descobrimentos, Vol. II (Lisbon: Edições Cosmos, 1960), 206.
- ↑ de Montalbodo, Paesi Nuovamente Retovati & Nuovo Mondo da Alberico Vesputio Fiorentino Intitulato (Venice: 1507)
- ↑ Ian Bruce, ‘St Helena Day’, Wirebird The Journal of the Friends of St Helena, no. 44 (2015): 32–46.
- ↑ Jan Huyghen van Linschoten, Itinerario, voyage ofte schipvaert van Jan Huygen Van Linschoten naer Oost ofte Portugaels Indien, inhoudende een corte beschryvinghe der selver landen ende zee-custen... waer by ghevoecht zijn niet alleen die conterfeytsels van de habyten, drachten ende wesen, so van de Portugesen aldaer residerende als van de ingeboornen Indianen. (C. Claesz, 1596).
- ↑ Jan Huygen van Linschoten, John Huighen Van Linschoten, His Discours of Voyages Into Ye Easte [and] West Indies: Divided Into Foure Bookes (London: John Wolfe, 1598).
- ↑ Duarte Lopes and Filippo Pigafetta, Relatione del Reame di Congo et delle circonvicine contrade tratta dalli scritti & ragionamenti di Odoardo Lope[S] Portoghese / per Filipo Pigafetta con disegni vari di geografiadi pianti, d’habiti d’animali, & altro. (Rome: BGrassi, 1591).
- ↑ Thomas Herbert, Some Yeares Travels into Africa et Asia the Great: Especially Describing the Famous Empires of Persia and Industant as Also Divers Other Kingdoms in the Orientall Indies and I’les Adjacent (Jacob Blome & Richard Bishop, 1638), 353.
- ↑ Knowlson, James R. (1968), "A Note on Bishop Godwin's "Man in the Moone:" The East Indies Trade Route and a 'Language' of Musical Notes", Modern Philology, 65 (4): 357–91, doi:10.1086/390001, JSTOR 435786
- ↑ Drake and St Helena, privately published by Robin Castell in 2005
- ↑ "Historical Chronology". St. Helena Foundation. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ Gazetteer – p. 7. MONUMENTS IN FRANCE – page 338 Archived 16 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Beaglehole, J.C., ed. (1968). The Journals of Captain James Cook on His Voyages of Discovery, vol. I:The Voyage of the Endeavour 1768–1771. Cambridge University Press. p. 468. OCLC 223185477.
- ↑ Roberts, Andrew (2014). Napoleon : A Life. New York: Viking. pp. 778, 781–82, 784, 801. ISBN 978-0-670-02532-9.
- ↑ New research published on http://sthelena.uk.net; shortened extract published in the Saint Helena Independent on 3 June 2011.
- ↑ England's St Helena exiles welcome island airport project, BBC News Online, 21 April 2012, retrieved 21 February 2012
- ↑ "Building an airport at the end of the Earth – Remote Atlantic runway to open up Napoleon's hidden island". cnn.com. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "The vet, the tortoise and the airport".
- ↑ Natural History of Saint Helena Archived 13 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Bird Watching, St Helena Tourism, archived from the original on 17 September 2010, retrieved 17 January 2011
- ↑ Our Flag, Moonbeams Limited, retrieved 11 November 2014
- 1 2 "St. Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha", CIA World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, retrieved 21 July 2012
- 1 2 About St Helena, St Helena News Media Services Archived 20 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ BBC Weather Centre Archived 9 February 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ St Helena Independent, 3 October 2008 page 2
- ↑ "Constitution". St Helena.
- ↑ "Census 2016- Summary Data". St Helena Government. Retrieved 21 September 2016.
- 1 2 "2008 Population Census of St Helena" (PDF). St Helena Government. Retrieved 21 September 2016.
- ↑ St Helena celebrates the restoration of full citizenship, Telegraph, 22 May 2002
- ↑ 2014 Yearbook of Jehovah's Witnesses. Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society of Pennsylvania. p. 184.
- ↑ "Please click the link below". sthelenabahai.org. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "CONSTITUTIONAL POLL – RESULTS". The Islander. 25 March 2013. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- ↑ Smallman, David L., Quincentenary, a Story of St Helena, 1502–2002; Jackson, E. L. St Helena: The Historic Island, Ward, Lock & Co, London, 1903
- ↑ "index.htm redirecting to http://humanrightssthelena.org/index.htm" (PDF). External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ "The Equality & Human Rights Commission • Introduction". humanrightssthelena.org. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "The Equality & Human Rights Commission • Introduction". humanrightssthelena.org. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 "'Violent and brutal': UK Foreign Office admits cover-up in St Helena child abuse scandal". rt.com. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ↑ "St Helena child abuse: Foreign Office 'was warned British island couldn't cope 12 years ago'". Telegraph. 2015. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ↑ "St Helena child abuse: 'a lot of dark things do happen on this island'". Telegraph. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ↑ "St Helena child abuse: how did sex abusers get away with it for so long?". Telegraph. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ↑ "Important Bird Areas", BirdLife data zone, BirdLife International, 2012, retrieved 9 November 2012
- ↑ "Tentative Lists: St. Helena". UNESCO. 27 January 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ Aptroot, A. "Lichens of St Helena and Ascension Island". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 158: 147–171, 2008
- ↑ News.co.sh Archived 18 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ About Us: History of the Bank of St. Helena, Bank of St. Helena, archived from the original on 7 February 2012, retrieved 21 July 2012
- 1 2 3 Rosenberg, Zach. "Tiny, Remote St. Helena Gets Its First Airport" Air & Space/Smithsonian, 18 September 2015. Accessed: 26 September 2015.
- ↑ "RMS St. Helena Schedule & Fares". RMS St. Helena. Archived from the original on 26 April 2010. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ August Graham (2016-07-14). "RMS Extended to July" (PDF). The Sentinel. p. 2. Retrieved 2016-08-06.
- ↑ Daniel McElroy & Christopher Hope (22 July 2012). "Britain to pay for St. Helena airstrip backed by Lord Ashcroft". The Telegraph. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ "Remote UK island colony of St Helena to get airport". BBC News. 3 November 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ "St Helena Air Services to be Provided by Comair Aviation Only" (PDF). Saint Helena Government. 27 March 2015.
- ↑ "HISTORY MADE AS FIRST EVER PLANE LANDS AT ST HELENA". Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ↑ "Wildcat becomes first helicopter to land at St Helena Airport". Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- ↑ "St Helena airport too windy to open". BBC News. 9 June 2016.
- ↑ Simon Pipe (14 June 2012). "Media saga takes new twist as Mike plans more radio stations". St. Helena Online. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ "Saint FM Homepage". Saint FM. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ "Saint FM Live Stream". Saint FM. Archived from the original on 7 June 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ "About Saint FM". Saint FM. Saint FM Community Radio. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ↑ Moonbeams Limited. "Saint Helena Island Info: All about St. Helena • Saint FM Community Radio". sainthelenaisland.info.
- ↑ "Saint Helena Island Info: All about St. Helena, in the South Atlantic Ocean • Amateur (“Ham”) Radio". sainthelenaisland.info. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "Saint Helena Online". Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ "St Helena Local". St Helena Local. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ "Saint Helena Island Info". Saint Helena Island Info. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ "Saint Helena Government". Saint Helena Government. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ "Saint Helena Tourism". Saint Helena Tourism. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- ↑ "Public Information on the Television Delivery on the KU-BAND" (PDF). Cable and Wireless. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 December 2011. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ↑ "Cable & Wireless Carries out Major Mechanical Maintenance" The St Helena Independent Volume 1, Issue 37 Friday 21 July 2006, p. 8 Archived 10 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 "Telecommunications network". cwi.sh. Archived from the original on 14 February 2012.
- ↑ www.itu.int
- ↑ "RMS St Helena to make last voyage". Independent Online.
- ↑ .SH IDN Policy, NIC, Saint Helena.
- ↑ "St Helena". The St Helena Foundation. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ http://www.sure.co.sh/downloads/BroadbandPackages.pdf
- ↑ "WiFi". Web.archive.org. 30 June 2010. Archived from the original on 30 June 2010. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ↑ Christian von der Ropp. "Connect St Helena". Connectsthelena.org. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ↑ Dave Lee (3 January 2013). "Island community St Helena renews plea for internet cash from UK". BBC News Online. Retrieved 2 January 2013.
- ↑ "St Helena Independent". Saint.fm. 17 April 2015. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ↑ "SHBC The Sentinel". St Helena Broadcasting (Guarantee) Corporation, LTD. Retrieved 18 August 2013.
- ↑ "Education Ordinance 2009" (PDF). Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- ↑ Government of St Helena. "Number of schools, enrolment and teachers:by category of school" (PDF). Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- ↑ "Community". Saint Connect. Archived from the original on 26 September 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- 1 2 3 Government of St Helena. "Education and Employment Directorate". St Helena Government. Archived from the original on 30 December 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- ↑ Prince Andrew School. "Sixth Form". Prince Andrew School. Archived from the original on 28 October 2013. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- ↑ Island Games St Helena profile
- ↑ ScoutBaseUK A Scouting Timeline Archived 14 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "A Baden-Powell Bibliography". July 2007. Archived from the original on 13 August 2012. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
Further reading
- Aptroot, Andre. Lichens of St Helena, Pisces Publications, Newbury, UK, 2012, ISBN 9781874357537
- Brooke, T. H., A History of the Island of St Helena from its Discovery by the Portuguese to the Year 1806, Printed for Black, Parry and Kingsbury, London, 1808
- Bruce, I. T., Thomas Buce: St Helena Postmaster and Stamp Designer, Thirty years of St Helena, Ascension and Tristan Philately, pp 7–10, 2006, ISBN 1-890454-37-0
- Cannan, Edward Churches of the South Atlantic Islands 1502–1991 ISBN 0-904614-48-4
- Chaplin, Arnold, A St Helena's Who's Who or a Directory of the Island During the Captivity of Napoleon, published by the author in 1914. This has recently been republished under the title Napoleon’s Captivity on St Helena 1815–1821, Savannah Paperback Classics, 2002, ISBN 1-902366-12-3
- Clements, B.; "St Helena:South Atlantic Fortress"; Fort, (Fortress Study Group), 2007 (35), pp. 75–90
- Crallan, Hugh, Island of St Helena, Listing and Preservation of Buildings of Architectural and Historic Interest, 1974
- Cross, Tony St Helena including Ascension Island and Tristan Da Cunha ISBN 0-7153-8075-3
- Dampier, William, Piracy, Turtles & Flying Foxes, 2007, Penguin Books, 2007, pp 99–104, ISBN 0-14-102541-7
- Darwin, Charles, Geological Observations on the Volcanic Islands, Chapter 4, Smith, Elder & Co., London, 1844.
- Denholm, Ken, South Atlantic Haven, a Maritime History for the Island of St Helena, published and printed by the Education Department of the Government of St Helena
- Duncan, Francis, A Description of the Island Of St Helena Containing Observations on its Singular Structure and Formation and an Account of its Climate, Natural History, and Inhabitants, London, Printed For R Phillips, 6 Bridge Street, Blackfriars, 1805
- Eriksen, Ronnie, St Helena Lifeline, Mallet & Bell Publications, Norfolk, 1994, ISBN 0-620-15055-6
- Evans, Dorothy, Schooling in the South Atlantic Islands 1661–1992, Anthony Nelson, 1994, ISBN 0-904614-51-4
- George, Barbara B. St Helena — the Chinese Connection (2002) ISBN 0189948922
- Gosse, Philip Saint Helena, 1502–1938 ISBN 0-904614-39-5
- Hakluyt, The Principal Navigations Voyages Traffiques & Discoveries of the English Nation, from the Prosperous Voyage of M. Thomas Candish esquire into the South Sea, and so around about the circumference of the whole earth, begun in the yere 1586, and finished 1588, 1598–1600, Volume XI.
- Hibbert, Edward, St Helena Postal History and Stamps, Robson Lowe Limited, London, 1979
- Hearl, Trevor W., St Helena Britannica: Studies in South Atlantic Island History (ed. A.H. Schulenburg), Friends of St Helena, London, 2013
- Holmes, Rachel, Scanty Particulars: The Scandalous Life and Astonishing Secret of James Barry, Queen Victoria's Most Eminent Military Doctor, Viking Press, 2002, ISBN 0-375-5055-63
- Jackson, E. L. St Helena: The Historic Island, Ward, Lock & Co, London, 1903
- Janisch, Hudson Ralph, Extracts from the St Helena Records, Printed and Published at the "Guardian" Office by Benjamin Grant, St Helena, 1885
- Keneally, Tom, Napoleon's Last Island, ISBN 978 0 85798 460 9, Penguin Random House Australia, 2015
- Kitching, G. C., A Handbook of St Helena Including a short History of the island Under the Crown
- Lambdon, Phil. Flowering plants and ferns of St Helena, Pisces Publications, Newbury, UK, 2012, ISBN 9781874357520
- Melliss, John C. M., St Helena: A Physical, Historical and Topographical Description of the Island Including Geology, Fauna, Flora and Meteorology, L. Reeve & Co, London, 1875
- Schulenburg, A. H., 'St Helena Historiography, Philately, and the "Castella" Controversy', South Atlantic Chronicle: The Journal of the St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Philatelic Society, Vol. XXIII, No.3, pp. 3–6, 1999
- Schulenburg, A.H., '"Island of the Blessed": Eden, Arcadia and the Picturesque in the Textualizing of St Helena', Journal of Historical Geography, Vol.29, No.4 (2003), pp. 535–53
- Schulenburg, A.H., 'St Helena: British Local History in the Context of Empire', The Local Historian, Vol.28, No.2 (1998), pp. 108–122
- Shine, Ian, Serendipity in St Helena, a Genetical and Medical Study of an isolated Community, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1970 ISBN 0-08-012794-0
- Smallman, David L., Quincentenary, a Story of St Helena, 1502–2002 ISBN 1-872229-47-6
- Van Linschoten, Iohn Huighen, His Discours of Voyages into ye Easte & West Indies, Wolfe, London, 1598
- Weider, Ben & Hapgood, David The Murder of Napoleon (1999) ISBN 1-58348-150-8
- Wigginton, Martin. Mosses and liverworts of St Helena, Pisces Publications, Newbury, UK, 2012, ISBN 9781874357-51-3
External links
- The Official Government Website of Saint Helena
- Radio Saint FM (live broadcasting from Saint Helena)
- Friends of St Helena – supporting St Helena and providing information about the island since 1988
- The Saint Helena Virtual Library and Archive
- Saint Helena Island Information website
 Wikimedia Atlas of Saint Helena
Wikimedia Atlas of Saint Helena- Saint Helena Travel Guide from Travellerspoint.
- The Official Website for St Helena Tourism
- The first website on St Helena — since 1995
- The St Helena Institute – Dedicated to St Helena and Dependencies research since 1997
- BBC News: Life on one of the world's most remote islands
- St Helena Association (UK)
- Saint Helena at DMOZ
- Main sites, habitations and occupants of the island during Napoleon's captivity
- South Atlantic news, in association with the Saint Helena Independent
- St Helenas online rental accommodation and property finder
- Seale, Robert F. (1834) The geognosy of the island St. Helena, illustrated in a series of views, plans and sections. London: Achermann and Co. – digital facsimile from the Linda Hall Library
- Isolated Islands: St. Helena (2014), Globe Trekker (Travel Documentory)
Coordinates: 15°57′S 005°43′W / 15.950°S 5.717°W


Countries.png)