Maxthon
 | |||||||||||||
|
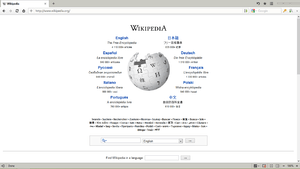
Screenshot of Maxthon Cloud Browser (Version 4) taken on Windows 8 | |||||||||||||
| Developer(s) | Maxthon International Ltd (北京傲游天下科技有限公司) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial release | 2005 | ||||||||||||
| Stable release(s) [±] | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Preview release(s) [±] | |||||||||||||
| None | |||||||||||||
| Development status | Active | ||||||||||||
| Operating system | Windows, Android, macOS, IOS, Windows Phone, Linux | ||||||||||||
| Engines | Trident and WebKit | ||||||||||||
| Size | ~39 MB | ||||||||||||
| Available in | 53 languages[7] | ||||||||||||
| Type | Web browser | ||||||||||||
| License | Freeware | ||||||||||||
| Website |
www | ||||||||||||
Maxthon (Chinese: 傲游浏览器, originally known as MyIE2) is a freeware web browser for Windows, OS X and Linux, developed by Chinese company Maxthon Ltd based in Beijing. It is also available on Windows Phone 8,[8] iOS[9] and Android[10] platforms as Maxthon Mobile. Since the release of version 3, Maxthon supports both the Trident and the WebKit rendering engines.[11]
Maxthon won CNET WebWare 100 Awards in 2008[12] and 2009,[13] and was #97 in PCWorld's list of the 100 Best Products of 2011.[14] In July 2016, concerns were raised regarding the browser's security weakness, when it was found out by cybersecurity experts that it sends "ad blocker status, homepage URL, websites visited by the user (including online searches), and installed applications to a server in Beijing, China" via HTTP, leaving the user information "valuable for a malicious actor looking to conduct a targeted attack."[15]
Overview
Maxthon is a Chinese company known mainly for producing Windows web browsers.[16] It is headquartered in Beijing, with offices in Shanghai, Hong Kong and San Francisco, US. Most of Maxthon's engineers are based in the corporate headquarters in Beijing, which develop and maintain versions of the Maxthon web browser for Windows, macOS, iOS, Windows Phone and Android.[17]
Maxthon has also created other products that include a Chinese language news and information portal i.maxthon.cn, a Chinese language casual gaming portal and humor website, a ‘Kid Safe’ web browser for Android and iOS, a free online account system called Maxthon Passport, and an English language news and information web portal i.maxthon.com.[18]
Corporate history
In 1999, current CEO Ming Jie "Jeff" Chen (Chinese: 陈明杰; pinyin: Chén Míngjié) founded Hong Kong-based Mysoft International Limited to distribute the MyIE browser.[19] In 2005 the company received seed funding from venture capital firm WI Harper Group and Morten Lund, the first Skype investor, and Chen moved the company to Beijing.[20][21] In 2006, Maxthon received further investment from the US-based venture capital firm Charles River Ventures.[22]
On April 10, 2007, TechCrunch reported that Google had invested at least US$1 million in Maxthon;[23] this was denied the following day by Chen.[24] However, in an interview with the Chinese portal Sina.com, Chen did not rule out future "co-operation" between the two businesses.[25]
Maxthon won CNET WebWare 100 Awards in 2008[12] and 2009,[13] and was #97 in PCWorld's list of the 100 Best Products of 2011.[14]
Maxthon was one of the twelve browsers Microsoft presented in 2010 at BrowserChoice.eu, a website that allows users of Windows residing in the European Economic Area to choose which default web browser they would like to use on their computer.[26] In late 2010 Maxthon began releasing new compatibilities, including browsers for Android[10] Mac,[27] iPhone[28] and iPad.[29] As of August 2012, Maxthon is still in the first tier of browsers in BrowserChoice.eu after the removal of Apple Safari.[30] The Maxthon Cloud Browser was released on December 10, 2012.[31]
Software
Development philosophy
According to Maxthon VP and Assistant CEO Karl Mattson, Maxthon develops its web browsers with three goals:
- High performance and standards support.
- An 'out of the box' experience with more integrated features than other browsers.
- 'Seamless browsing.' Sometimes referred to as 'portability' by the company, this is a commitment to offering users the ability to 'pick up where they left off' by having parts of their web browsing synced to an encrypted, free cloud account and then pushed to other platforms.[17]
Development history
According to Maxthon International CEO Ming Jie "Jeff" Chen, Maxthon was based on MyIE, a popular modification created by Chinese programmer Changyou to customize Internet Explorer web browser.[32][33] Changyou posted most of the source code[34] for MyIE on his Bulletin board system before leaving the project in 2000. Chen then continued independently developing MyIE and in 2002 released a new version, MyIE2.[35] Users around the world were quite active in contributing to MyIE2's development, adding many plugins, skins and assisting with debugging. MyIE2 was renamed Maxthon in 2003.[22][32]
Maxthon 2 was introduced in July 2007,[36] and Maxthon 3 was released in October 2010. Later that year Maxthon began introducing browsers for portable devices; in December Maxthon for Android[10] was released.[37] On July 7, 2012, Maxthon for Mac[27] was released,[38] with Maxthon for iPhone[28] and iPad released in August 2012.[29] On December 10, 2012, Maxthon Cloud Browser, also dubbed Maxthon 4, hit the market.[31]
Features
The following are accumulated features of the Maxthon browser, culminating in Maxthon 4.
- Split screen option: divides open tabs into left and right of screen when this option is chosen; Sides operate independently. This feature is unavailable since version 4.9.
- Tabbed document interface
- Saves open tabs in case of program shutdown or system crash
- Undo for any tabs accidentally closed
- AD Hunter - an ad blocking utility that blocks pop-up ads, Web banner and floating ads in webpages
- Adobe Flash, Java applet and ActiveX blocker
- Support for custom skins
- Customizable tabs and user interface
- Programmable mouse gestures and mouse chording
- External utility bar – a toolbar that allows you to open third-party programs
- RSS reader
- Supports many Internet Explorer plugins as well as plugins of its own
- Partial Gecko engine support with the use of a third-party program
- A user extensible search toolbar with 8 default search engines
- Automatic updates
- Groups – the ability to bookmark & open multiple pages simultaneously
- URL aliases – open URLs by just typing a word in the address bar
- Simple collector – a small notepad-like utility, used to collect text from web pages. Scripts and macros can be run in the current web page
- Integrated web services – user extensible, including by default translators, Google's cached version of pages, Whois, and anonymous web proxies
Data privacy issues
In 2016 computer security researchers from Fidelis Cybersecurity and Exatel discovered the browser surreptitiously sending sensitive browsing and system data—such as ad blocker status, websites visited, searches conducted and applications installed with their version numbers—to remote servers located in Beijing, China. According to Maxthon, the data is sent as part of the company's 'User Experience Improvement Program' and that it is "voluntary and totally anonymous." However, researchers found the data still being collected and transmitted to remote servers even after users explicitly opted-out of the program. The researchers further found the data being transmitted over an unencrypted connection (HTTP), leaving users vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks. Fidelis' Chief Security Officer, Justin Harvey, noted the data "...contains almost everything you would want in conducting a reconnaissance operation to know exactly where to attack. Knowing the exact operating system and installed applications, and browsing habits it would be trivial to send a perfectly crafted spearphish to the victim or perhaps set up a watering hole attack on one of their most frequented websites."[39]
Browser versions
Version 1.x
Maxthon version 1, which continued version 0 of MyIE2, was an Internet Explorer shell that implemented a tabbed browser using the Trident layout engine which Microsoft introduced with Internet Explorer 4.[40] As such, version 1 was compatible with every version of Windows from Windows 95 to Windows 7.[41] Development of version 1 stopped in 2010 with the so-called Maxthon (Classic), version 1.6.7.35;[41] earlier releases are available from Maxthon,[42] and version 1.6.7.35, which fixed a bug in selecting the default search engine, is still available at other download sites.[43][44]
There are a number of add-ons available for Maxthon Classic,[45] and more are available through discussion forums.[46] Specific threads may provide direct download links as well.[47] Some add-ons are build-specific, but in that case, a clear indication of compatibility can often be found.
Maxthon 1.3.1 have brought cloud-based service for online syncing bookmarks (favorites) in 2005.
Version 2.x
Maxthon Browser 2 is a multi-tab browser released in July 2007.[36] A later modification in 2008 was the first browser on the market to offer cloud-based services for syncing bookmarks and history.[16] Version 2.x also blocks malicious plug-ins to prevent pop-ups and floating ads, and supports a variety of plug-in tools and IE extensions. It also supports a wide variety of skins and is customizable. New features included:[18]
- Maxthon Passport: once the user signs in and registers for free Passport Membership, avatar remains in that space for future visits[48]
- Multi Tab Manager: right-clicking on the 'Tab menu' brings up a function intended to make browsing and other operations more efficient.
- Mouse Gestures: right clicking and performing gestures with the mouse allows users to trigger customizable actions.
- Maxthon Smart Accelerator: the built-in is intended to increase browsing speed (see icon at Maxthon status bar)
- Autofill capability: automatically saves content entered into web forms and fills them automatically in the future.
- Undo list: after closing a webpage accidentally, the Undo button and Undo can restore it. All closed pages and browsing history are recorded in Undo list.
- Online Favorites: registering as a Maxthon Passport member allows instant access to cloud syncing services like online favorites.
- Feed reader: native Web syndication client.
- Super Drag and Drop: users can drag and drop selected text for a web search in their default search engine, or drag and drop a selected link or image to open in a new tab.
- URL alias: through 'tab right click menu,' users can assign a 'special/sticky name' to a webpage, which can be entered in the address bar to open the corresponding webpage. Naming is possible through the 'right click tab menu.'
- Super agent: supports the adoption of HTTP, HTTPS, Socks4, Socks4a, Socks5, and other internet connection proxies, and also supports proxy that require authentication. By setting the Advanced Proxy Rule, the Maxthon Web browser can automatically switch to different proxy servers.
- External Tools: users can add commonly used (i.e. possibly IE compatible only) tools and software shortcuts to their Maxthon browser. The software can be set to start up and shut down with the Maxthon browser.
- Web Toolbar: provides users with a set of commonly used small features. Among them The Maxthon website brings together a number of entertainment and social networking sites.
- AD blocking: through the menu "Webpage Content Block," Ad Hunter can block pop-ups, ads and malicious web harassment. Supports customizable filters.
- URL Key: through settings center, set an URL Key and press a function key to open one or more URLs.
- Web Sniffer: Web sniffer can capture FLV media files from video sites, allowing for download and saving. Users can also customize the type of files to sniff for.
- Screen Capture: users can arbitrarily snap a whole page, a region, a specified window and page content to the clipboard. Users can also configure the saving path and file format of the screenshot through setting options.
- Maxthon Download: without having to call other download programs, using the browser’s built-in Maxthon download can complete numbers of small download tasks. The Maxthon download manager has several features.
- Plug-ins (Extensions): plug-ins can be used or programmed and shared with other users
- Skins: different skins available.
Version 3.x
Maxthon 3 was released in the fall of 2010, after a beta period of 8 months.[49] It has both Trident and Webkit layout engines. New features included:[50]
- Dual Display Engines: Maxthon uses the Ultra Mode, powered by the Webkit rendering engine, by default. It will switch automatically to Retro Mode, powered by the Trident-rendering engine, as needed to display older-style Web pages.
- Mouse Gesture: Maxthon's Mouse Gesture feature lets you navigate through the web by moving the mouse in patterns that tell the browser to go back, forward, refresh, and even hide.
- Super Drag & Drop: allows Drag and Drop to open new pages and images or perform a web search.
- Smart Address Bar: allows searching by typing keywords directly into address bar
- Magic Fill: Maxthon securely saves names and passwords of visited websites, then fills in that information upon return.
- AD Hunter: removes advertisements with one click and automatically blocks pop-up windows.
- Maxthon Passport: once the user sign-ins and registers for free Passport Membership, avatar remains in that space for future visits.[48]
- Online Favorites: registering as a Maxthon Passport member allows instant access to cloud syncing services like online favorites.
- Multi Search: after selecting Maxthon Multi Search, user can input keywords in the address or search bar. Maxthon Multi Search shows what multiple search engines return for the query.
Maxthon Cloud Browser
Also known as Maxthon Cloud, Maxthon 4 was released on December 10, 2012.[31] At the same time it released Passport and its cloud features.[51] Maxthon Passport allowed users to sign-in and register for free Passport Membership, and their avatar remains in that space for future visits. Registering also gives users access to cloud syncing services like online favorites.[48] New features include:[52]
- Cloud Push: supports sending text, images, websites/links and tabs to Mac, Android and Windows operating systems.
- Cloud Share: supports sharing text, images, websites/links and files online.
- Cloud Download: supports downloading files in various formats and uploading them to My Cloud for backup on any device.
- My Cloud Tabs: lets users remember previous sessions, by automatically syncing tabs to iOS, Windows or Android devices.
- Cloud Sync: Syncs account data (Favorites, Settings and Magic Fill data) to other devices.
- Reader Mode: adjusts font sizes and removes ads on articles for visibility, with a "night mode" option for low light.
- Magic Fill: Maxthon securely saves names and passwords of visited websites, then fills in that information upon return.
- Ad Hunter: removes advertisements with one click, and automatically blocks pop-up windows.
- New Session: users and gamers can simultaneously log into the same website with different accounts.
- Source Sniffer: extract all photos, embedded videos and audio files from a web page and download them.
- SkyNote: save and access text notes anywhere, and sync them across Windows and Android.
- "Do Not Track": privacy from ad networks and beacons.
- Google Safe Browsing: identifies websites and warns if they are not safe and not secure before visiting.
- Privacy mode: disables browsing history.
Maxthon Mobile
For Android
Maxthon Mobile for Android, a version for Android phones, was first released in 2010,[53] followed in 2011 by a version optimized for 10 inch tablets.[35] New features in 2012 included:
- Cloud Push: supports sending text, images, websites/links and tabs to Mac, Android and Windows operating systems.
- Cloud Share: supports sharing text, images, websites/links and files online
- Cloud Download: supports downloading files in various formats and uploading them to 'My Cloud' for backup on any device.
- Cloud Tabs: lets users remember previous sessions, by automatically syncing tabs to iOS, Windows or Android devices.
- Sync Bookmarks/Favorites: sync Favorites across Windows, Mac and iOS devices.
- Full screen browsing
- App Center: function to find and group web apps and content.
- Super Gesture:: allows for the use of gestures to create, close, switch and restore tabs.
- Read-Ahead: preloads pages automatically.
- Reader Mode: adjusts font sizes and removes ads on articles for visibility, with a "night mode" option for low light
For iOS
Maxthon Mobile for iOS was launched in July 2012, for iPhone,[28] iPad, and iOS universal. Maxthon Cloud Browser for iOS saves and syncs key settings, content and features for users across multiple platforms and other devices. Mouse gestures can control the opening and switching between tabs.[29][54] New features include:
- Cloud Push: supports sending text, images, websites/links and tabs to Mac, Android and Windows operating systems.
- Cloud Share: supports sharing text, images, websites/links and files online
- Cloud Download: supports downloading files in various formats and uploading them to 'My Cloud' for backup on any device.
- Cloud Tabs: lets users remember previous sessions, by automatically syncing tabs to iOS, Windows or Android devices.
- Sync Bookmarks/Favorites: works across Windows, Mac and iOS devices.
- Reader Mode: adjusts font sizes and removes ads on articles for visibility, with a "night mode" option for low light
- Brightness Control: adjust screen brightness within the browser.
- Portrait Orientation Lock: supports switching the screen orientation in Maxthon Browser.
- Privacy Protection: allows browsing without tracking
- New User Interface: full-screen browsing mode.
For Mac
In July 2012, Maxthon Cloud Browser for macOS[55] was released.[8] It allows Mac users with a Maxthon Passport account to keep all user data in sync across different devices and operating systems.[8][27] New features include:
- Cloud Push: supports sending text, images, websites/links and tabs to Mac, Android and Windows operating systems.
- Cloud Share: supports sharing text, images, websites/links and files with other people.
- Cloud Download: supports downloading files in various formats and uploading them to 'My Cloud' for backup on any device.
- My Cloud Tabs: lets users remember previous sessions, by automatically syncing tabs to iOS, Windows or Android devices.
- Cloud Sync: allows for syncing of bookmarks, favorites, and other content across Windows, Mac and Android devices.
- Super Drag and Drop: allows user to highlight a URL or webpage text, then drag and drop into the Address Bar to open a new page or execute a web search.
- Mouse Gesture: allows for simple shape creation with the mouse, and trigger commands like Refresh, Close Tab, Page Top/Down and Previous/Next Tab.
- Extension Center: company supported feature for finding browser extensions, compatible with Google Chrome extensions.[18]
- "Do Not Track": privacy from ad networks and beacons.
- Adobe Flash support pre-installed in software.
- All user data encrypted for security.
For Windows Phone
Recently released.
Release history (version 4+)
Windows
The browser for Windows, version 4.0.6.1200 (2013-5-6), introduced Maxthon Skin and various bug fixes. 4.1.0.4000 (2013-7-11), fixed a number of bugs related to closing tabs and launching the browser. It also updated Flash to the latest official version and improved Webkit stability. The Beta release 4.1.2.1200 (2013-8-1) introduced touch zooming and panning in win8, HTML5 online/offline operation, and CSS Filter GPU Acceleration.[56]
Mac
Mac version 4.0.6.2000 (2013-7-25) contained improvements such as better support for PDF and Flash, while 4.0.6.3000 (2013-8-2) improved stability on Mac OS X 10.7.0 and 10.7.2.[57]
Android
Android browser version 4.0.4.1000 (2013-03-28) included new features, such as an automatic UI adjustment for tablets with screens larger than 7 inch, support links invoking native app (i.e., thunder://, ek2://, etc.), and a number of bug fixes. 4.0.5.2000, released less than a week later on April 3, added in features such as Cloud Push in Download Manager and via Lan transfer, with improvements such as adding a favorites button to the tool bar. 4.0.6.2000 (2013-6-09), included new features such as text auto-wrap in Android 4.0 and above, phone contacts supported in Cloud Push, and Search keywords stay in address bar after performing a search. Improvements included the removal of WWW/WAP mode switch.[58]
iOS
Version 4.2 (2013-7-22) for iOS added new languages, URL autofill, related search keywords, browser history matching, and what is dubbed "Lightning-fast Cloud Push" via LAN. Version 4.2.1, released a week later on July 29, included bug fixes for iPhone4.[59]
See also
References
- ↑ "Maxthon for Windows Changelog". Maxthon International. 10 October 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ↑ "Maxthon Web Browser - Android". Google Play Store. 9 May 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ↑ "Maxthon for Mac". Mac App Store. Maxthon Technology Limited. 30 April 2015. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ↑ "Maxthon for iOS". Mac App Store. Maxthon Technology Limited. 27 September 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ↑ "Maxthon for Windows Phone". Microsoft Store. 15 September 2014.
- ↑ "Maxthon for Linux Changelog". Maxthon International. 9 September 2014. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ↑ Translate Maxthon
- 1 2 3 Eswarlu, Venkat (December 10, 2012). "Maxthon Cloud Browser Released". Techdows. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ "Maxthon for iOS". Maxthon. Retrieved 2 January 2013.
- 1 2 3 "Maxthon for Android". Maxthon. Retrieved 2 January 2013.
- ↑ "Maxthon 3". Maxthon. Retrieved 23 November 2012.
- 1 2 Shankland, Stephen (21 April 2008). "Webware 100 winner: Maxthon". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved 8 February 2011.
- 1 2 "Webware 100 winner: Maxthon". CNET. CBS Interactive. 19 May 2009. Retrieved 8 February 2011.
- 1 2 "100 Best Products of 2011". PCWorld Communications, Inc. Retrieved 12 January 2012.
- ↑ http://www.securityweek.com/maxthon-browser-sends-sensitive-data-china
- 1 2 "About". Maxthon. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- 1 2 "Cloud Browser with Muscle & Security, Startup Maxthon Caters to HTML5 Users". RightStartups. July 13, 2013. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- 1 2 3 "Maxthon 2". Maxthon International Limited. Retrieved 2012-01-12.
- ↑ "MyIE Tabbed Browser". Mysoft International Limited. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ "Angle Subscriber Exclusive: WI Harper & Skype Co-Founder To Invest In Chinese Browser/Search Play". Pacific Epoch. 2005-05-30. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ Schonfeld, Erick; Yen, Yi-Wyn. "It's a Web, Web, Web 2.0 world". CNNMoney.com. Cable News Network. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- 1 2 Lu, Gang (31 December 2006). "Maxthon Goes to Global Market - A New Way to Surf The World in 2007". Mobinode. Retrieved 1 January 2008.
- ↑ Arrington, Michael (10 April 2007). "Google Takes Partial Ownership Of Maxthon Browser". TechCrunch. Retrieved 1 January 2008.
- ↑ Luis, J. (25 February 2014). "Maxthon Expands Into Russia". GAMbIT Magazine. Retrieved 1 February 2014.
- ↑ "Maxthon浏览器创始人否认谷歌入股传言". Sina.com. 10 May 2007. Retrieved 1 January 2008.
- ↑ BBC, Microsoft offers browser choices to Europeans, 1 March 2010
- 1 2 3 "Maxthon for Mac". Maxthon International Limited. beta
- 1 2 3 "Maxthon Web Browser Now Available for iPhone -- Offers Cross-Platform Syncing and Exclusive Features". Maxthon. 2012-08-20. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- 1 2 3 Knight, Shawn (2012-08-21). "Maxthon mobile browser now available for ios devices". TechSpot. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ "Select your web browser(s)". BrowserChoice.eu. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- 1 2 3 Williams, Mike (2012-12-10). "Maxthon Browser 4 released and renamed: "Maxthon Cloud Browser"". Software Crew. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- 1 2 Lipskas, Vygantas (2011-10-24). "Interview With Jeff Chen, The CEO Of Maxthon Ltd.". FavBrowser.com. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ "General FAQs - Maxthon Wiki". Maxthon International Limited. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ "MyIE Original Visual C++ Source Code Download...". Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- 1 2 "About Maxthon". Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- 1 2 Linder, Brad (July 23, 2007). "Maxthon 2 web browser released". Switched. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ Matthews, Lee (2010-12-16). "Maxthon browser for Android now available -- and it's good". Switched. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ "Maxthon Web Browser Now Available for Mac Computers". Maxthon. July 30, 2012. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑
- Kovacs, Eduard (14 July 2016). "Maxthon Browser Sends Sensitive Data to China". SecurityWeek. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- Abel, Robert (14 July 2016). "Maxthon browser vulnerable to Chinese cyberespionage and MitM attacks". SC Magazine. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- Koliba, Ján (16 July 2016). "Vážna hrozba: Webový prehliadač Maxthon špehuje, všetko posiela". www.zive.sk (in Slovak). Ringier / Axel Springer. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- Weisensee, Jan (15 July 2016). "Maxthon-Browser sendet kritische Daten nach China". Golem.de (in German). Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- Soeteman, Krijn (15 July 2016). "Maxthon-browser stuurt zonder toestemming gegevens door naar server in China". Tweakers.net (in Dutch). Persgroep Online Services. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- ↑ Spanbauer, Scott; Bass, Steve (2005-01-03). "The New Web Challengers". PCWorld. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- 1 2 "Maxthon (Classic) specifications". CNET.com. CBS Interactive. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ "Maxthon Browser 1.x Series". Maxthon International Limited. Archived from the original on November 8, 2011. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ "Download Free Maxthon, Maxthon 1.6.7.35". Brothersoft. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ "Maxthon (Classic) 1.6.7.35 (Windows)". ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ Addons for Maxthon 1.x and 2.x
- ↑ Maxthon Forum
- ↑ More Options 1.6.x on Maxthon forum Archived February 13, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- 1 2 3 "Maxthon Passport". Maxthon International Limited. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ THEORACLE (2010-09-06). "Maxthon 3.0 Released". Locker Gnome. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ "Maxthon 3". Maxthon International Limited. Retrieved 2012-01-12.
- ↑ "Maxthon Launches New 'Cloud Browser'". INfiniGeek. December 2010. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ↑ "Maxthon 4". Maxthon International Limited. Retrieved 2012-01-25.
- ↑ Lu, Gang (2010-12-14). "Maxthon Released Its Mobile Version for Android". TechNode.com. Retrieved 2012-01-12.
- ↑ Maxthon Cloud Browser on iTunes
- ↑ Maxthon for Mac Changelog
- ↑ "Changelog: Windows". Maxthon. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ "Changelog: Mac". Maxthon. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ "Changelog: Android". Maxthon. Retrieved 2013-08-27.
- ↑ "Changelog: IOS". Maxthon. Retrieved 2013-08-27.