Oxycodone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | many |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682132 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Dependence liability | High |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, sublingual, intramuscular, intravenous, intranasal, subcutaneous, transdermal, rectal, epidural[1] |
| ATC code |
N02AA05 (WHO) N02AA55 (WHO) (in combinations) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60–87%[2][3] |
| Protein binding | 45%[2] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic: mainly CYP3A, and, to a much lesser extent, CYP2D6 to oxymorphone (~5%);[2] 95% metabolized (i.e., 5% excreted unchanged)[4] |
| Onset of action |
10–30 minutes (IR)[3][4] 1 hour (CR)[5] |
| Biological half-life |
2–3 hours (IR) (variable) (same t1/2 for all ROAs)[3][4] 4.5 hours (CR)[6] |
| Duration of action |
3–6 hours (IR) (variable)[4] 12 hours (CR)[5] |
| Excretion | Urine (83%)[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | Eukodal, eucodal; dihydrohydroxycodeinone, 7,8-dihydro-14-hydroxycodeinone, 6-deoxy-7,8-dihydro-14-hydroxy-3-O-methyl-6-oxomorphine[7] |
| CAS Number |
76-42-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5284603 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7093 |
| DrugBank |
DB00497 |
| ChemSpider |
4447649 |
| UNII |
CD35PMG570 |
| KEGG |
D05312 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:7852 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL656 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 315.364 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Solubility in water | HCl: 166 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Oxycodone is a semisynthetic opioid synthesized from thebaine, an opioid alkaloid found in the Persian poppy, and one of the many alkaloids found in the opium poppy. It is a moderately potent opioid analgesic, generally indicated for relief of moderate to severe pain.[8] Oxycodone was developed in 1917 in Germany[9][10] as one of several semi-synthetic opioids in an attempt to improve on the existing opioids.[1]
Oxycodone is available as single-ingredient medication in immediate release and controlled release. Parenteral formulations of 10 mg/mL and 50 mg/mL are available in the UK for IV/IM administration.[11] Combination products are also available as immediate-release formulations, with non-narcotic analgesic ingredients such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including aspirin and ibuprofen. An abuse-deterrent combination with naloxone is available in managed-release tablets. If injected, the naloxone precipitates opioid withdrawal symptoms and blocks the effect of the medication. It was originally developed in Germany where it is known as dihydroxycodeinone or eukodal.
Medical uses
Oxycodone has been in clinical use since 1916,[1] and it is used for managing moderate to moderately severe acute or chronic pain.[12] It has been found to improve quality of life for those with many types of pain.[13] Experts are divided regarding use for non cancer-related chronic pain, as most opioids have great potential for dependence and may also create paradoxical pain sensitivity.
Oxycodone is available as controlled-release tablet, intended to be taken every 12 hours.[14] A 2006 review found that controlled-release oxycodone is comparable to instant-release oxycodone, morphine, and hydromorphone in management of moderate to severe cancer pain, with fewer side effects than morphine. The author concluded that the controlled release form is a valid alternative to morphine and a first-line treatment for cancer pain.[15] In 2014, the European Association for Palliative Care recommended oral oxycodone as a second-line alternative to oral morphine for cancer pain.[16]
In the US, extended-release oxycodone is approved for use in children as young as 11 years old. The approved indication is for relief of cancer pain, trauma pain, or pain due to major surgery, in children already treated with opioids, who can tolerate at least 20 mg per day of oxycodone; this provides an alternative to Duragesic (fentanyl) the only other extended-release opioid analgesic approved for children.[17]
Administration
In the United States, oxycodone is only approved for oral use, available as tablets and oral solutions. In the United Kingdom, oxycodone is also approved for intravenous (IV) and intramuscular (IM) use. When first introduced in Germany during World War I, IV and IM oxycodone was commonly used for post-operative pain management of Central Powers soldiers.[1]
Available forms
Oxycodone is available in a variety of formulations for oral or sublingual administration:[3][18][19][20]
- Immediate-release oxycodone (OxyFast, OxyIR, OxyNorm, Roxicodone)
- Controlled-release oxycodone (OxyContin) – 12-hour duration[5]
- Immediate-release oxycodone with paracetamol (acetaminophen) (Oxycocet, Percocet, Roxicet, Tylox)
- Immediate-release oxycodone with aspirin (Endodan, Oxycodan, Percodan, Roxiprin)
- Immediate-release oxycodone with ibuprofen (Combunox)[21]
- Controlled-release oxycodone with naloxone (Targin, Targiniq, Targinact)[22] – 12-hour duration
- Controlled-release oxycodone with naltrexone (Troxyca) – 12-hour duration – pending regulatory approval[23]
Parenteral formulations of oxycodone (brand name OxyNorm) are also avaialable, and are widely used in Europe.[24][25][26]
Adverse effects
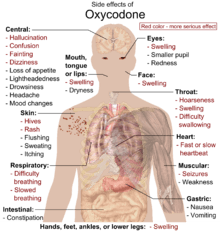
The effects of oxycodone include pain relief, euphoria, anxiolysis, feelings of relaxation, and respiratory depression.[28] Common side effects of oxycodone include constipation (23%), nausea (23%), vomiting (12%), somnolence (23%), dizziness (13%), itching (13%), dry mouth (6%), and sweating (5%).[28][29] Less common side effects (experienced by less than 5% of patients) include loss of appetite, nervousness, abdominal pain, diarrhea, urine retention, dyspnea, and hiccups.[30] In high doses, overdoses, or in some persons not tolerant to opioids, oxycodone can cause shallow breathing, bradycardia, cold/clammy skin, apnea, hypotension, miosis, circulatory collapse, respiratory arrest, and death.[30]
Oxycodone in combination with naloxone in managed-release tablets, has been formulated to both deter abuse and reduce "opioid-induced constipation".[31]
Dependence, addiction and withdrawal
The risk of experiencing severe withdrawal symptoms is high if a patient has become physically dependent and discontinues oxycodone abruptly. Medically, when the drug has been taken regularly over an extended period, it is withdrawn gradually rather than abruptly. People who regularly use oxycodone recreationally or at higher than prescribed doses are at even higher risk of severe withdrawal symptoms. The symptoms of oxycodone withdrawal, as with other opioids, may include "anxiety, panic attack, nausea, insomnia, muscle pain, muscle weakness, fevers, and other flu-like symptoms".[32]
Withdrawal symptoms have also been reported in newborns whose mothers had been either injecting or orally taking oxycodone during pregnancy.[33]
Hormone imbalance
As with other opioids, chronic use of oxycodone (particularly with higher doses) often causes concurrent hypogonadism or hormone imbalance.[34]
Interactions
Oxycodone is metabolized by the enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, and its clearance therefore can be altered by inhibitors and inducers of these enzymes.[25] Natural genetic variation in these enzymes can also influence the clearance of oxycodone, which may be related to the wide inter-individual variability in its half-life and potency.[25]
Ritonavir or lopinavir/ritonavir greatly increase plasma concentrations of oxycodone in healthy human volunteers due to inhibition of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6.[35] Rifampicin greatly reduces plasma concentrations of oxycodone due to strong induction of CYP3A4.[36] There is also a case report of fosphenytoin, a CYP3A4 inducer, dramatically reducing the analgesic effects of oxycodone in a chronic pain patient.[37] Dosage or medication adjustments may be necessary in each case.[35][36][37]
(For lists of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 inhibitors and inducers, see here and here, respectively.)
Pharmacodynamics
Oxycodone is a highly selective full agonist of the μ-opioid receptor (MOR), with low affinity for the δ-opioid receptor (DOR) and κ-opioid receptor (KOR).[24][25] After oxycodone binds to the MOR, a G protein-complex is released, which inhibits the release of neurotransmitters by the cell by reducing the amount of cAMP produced, closing calcium channels, and opening potassium channels.[38]
| Compound[39] | MOR (Ki) | DOR (Ki) | KOR (Ki) | δ/μ (ratio) | κ/μ (ratio) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxycodone | 18 nM nM | 958 nM | 677 nM | 53 | 38 |
Similarly to most other opioids, oxycodone increases prolactin secretion, but its influence on testosterone levels is unknown.[24] Unlike morphine, oxycodone lacks immunosuppressive activity (measured by natural killer cell activity and interleukin 2 production in vitro); the clinical relevance of this has not been clarified.[24]
Controversy
In 1997, a group of Australian researchers proposed (based on a study in rats) that oxycodone acts on KORs, unlike morphine, which acts upon MORs.[40] Further research by this group indicated the drug appears to be a κ2b-opioid agonist.[41] However, this conclusion has been disputed, primarily on the basis that oxycodone produces effects that are typical of μ-opioid agonists.[42]
In 2006, research by a Japanese group suggested the effect of oxycodone is mediated by different receptors in different situations. Specifically in diabetic mice, the κ-opioid receptor appears to be involved in the antinociceptive effects of oxycodone,[43] while in nondiabetic mice, the μ1-opioid receptor seems to be primarily responsible for these effects.[44]
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After a dose of conventional (instant-release) oral oxycodone, the onset of action is 10–30 minutes,[3][4] and peak plasma levels of the drug are attained within roughly 30–60 minutes;[3][4][45] in contrast, after a dose of OxyContin (an oral controlled-release formulation), peak plasma levels of oxycodone occur in about three hours.[30] The duration of instant-release oxycodone is 3 to 6 hours, although this can be variable depending on the individual.[4]
Distribution
Oxycodone in the blood is distributed to skeletal muscle, liver, intestinal tract, lungs, spleen, and brain.[30] Conventional oral preparations start to reduce pain within 10–15 minutes on an empty stomach; in contrast, OxyContin starts to reduce pain within one hour.[12]
Metabolism
The metabolism of oxycodone in humans is extensive (about 95%) and complex, with many minor pathways and resulting metabolites.[4][46] Around 10% (range 8–14%) of a dose of oxycodone is excreted essentially unchanged (unconjugated or conjugated) in the urine.[4] The major metabolites of oxycodone are noroxycodone (70%), noroxymorphone ("relatively high concentrations"),[28] and oxymorphone (5%).[45][47] The immediate metabolism of oxycodone in humans is as follows:[4][6][48]
- N-Demethylation to noroxycodone predominantly via CYP3A4
- O-Demethylation to oxymorphone predominantly via CYP2D6
- 6-Ketoreduction to 6α- and 6β-oxycodol
- N-Oxidation to oxycodone-N-oxide
In humans, N-demethylation of oxycodone to noroxycodone by CYP3A4 is the major metabolic pathway, accounting for 45% ± 21% of a dose of oxycodone, while O-demethylation of oxycodone into oxymorphone by CYP2D6 and 6-ketoreduction of oxycodone into 6-oxycodols represent relatively minor metabolic pathways, accounting for 11% ± 6% and 8% ± 6% of a dose of oxycodone, respectively.[4][24]
Several of the immediate metabolites of oxycodone are subsequently conjugated with glucuronic acid and excreted in the urine.[4] 6α-Oxycodol and 6β-oxycodol are further metabolized by N-demethylation to nor-6α-oxycodol and nor-6β-oxycodol, respectively, and by N-oxidation to 6α-oxycodol-N-oxide and 6β-oxycodol-N-oxide (which can subsequently be glucuronidated as well), respectivelyrespectively.[4][6] Oxymorphone is also further metabolized, as follows:[4][6][48]
- 3-Glucuronidation to oxymorphone-3-glucuronide predominantly via UGT2B7
- 6-Ketoreduction to 6α-oxymorphol and 6β-oxymorphol
- N-Demethylation to noroxymorphone
The first pathway of the above three accounts for 40% of the metabolism of oxymorphone, making oxymorphone-3-glucuronide the main metabolite of oxymorphone, while the latter two pathways account for less than 10% of the metabolism of oxymorphone.[48] After N-demethylation of oxymorphone, noroxymorphone is further glucuronidated to noroxymorphone-3-glucuronide.[48]
Activity contribution of metabolites
A few of the metabolites of oxycodone have also been found to be active as MOR agonists, some of which notably have much higher affinity for (as well as higher efficacy at) the MOR in comparison.[45][49][50] Oxymorphone possesses 3- to 5-fold higher affinity for the MOR than does oxycodone,[4] while noroxycodone and noroxymorphone possess one-third of and 3-fold higher affinity for the MOR, respectively,[4][50] and MOR activation is 5- to 10-fold less with noroxycodone but 2-fold higher with noroxymorphone relative to oxycodone.[47] Noroxycodone, noroxymorphone, and oxymorphone also have longer half-lives than oxycodone.[45][51]
| Compound[28][47] | Ki ([3H]diprenorphine displacement) | EC50 (hMOR1 GTPyS binding) | Cmax (20 mg CR) | AUC (20 mg CR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxycodone | 16.0 nM | 343 nM | 23.2 ± 8.6 ng/mL | 236 ± 102 ng/h/mL |
| Oxymorphone | 0.36 nM | 42.8 nM | 0.82 ± 0.85 ng/mL | 12.3 ± 12 ng/h/mL |
| Noroxycodone | 57.1 nM | 1930 nM | 15.2 ± 4.5 ng/mL | 233 ± 102 ng/h/mL |
| Noroxymorphone | 5.69 nM | 167 nM | ? | ? |
However, in spite of the greater in vitro activity of some of its metabolites, it has been determined that oxycodone itself is responsible for 83.0% and 94.8% of its analgesic effect following oral and intravenous administration, respectively.[49] Oxymorphone plays only a minor role, being responsible for 15.8% and 4.5% of the analgesic effect of oxycodone after oral and intravenous administration, respectively.[49] Although the CYP2D6 genotype and the route of administration result in differential rates of oxymorphone formation, the unchanged parent compound remains the major contributor to the overall analgesic effect of oxycodone.[49] In contrast to oxycodone and oxymorphone, noroxycodone and noroxymorphone, while also potent MOR agonists, poorly cross the blood-brain-barrier into the central nervous system, and for this reason, are only minimally analgesic in comparison.[45][47][49][50] In accordance, while higher CYP2D6 activity increases the effects of oxycodone (due to increased conversion into oxymorphone), higher CYP3A4 activity has the opposite effect, and decreases the effects of oxycodone (due to increased metabolism into noroxycodone and noroxymorphone).[52]
Variation
Oxycodone is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system in the liver, making it vulnerable to drug interactions.[30] Some people are fast metabolizers, resulting in reduced analgesic effect, but increased adverse effects, while others are slow metabolisers, resulting in increased toxicity without improved analgesia.[53][54] The dose of oxycodone must be reduced in patients with reduced hepatic function.[12]
Elimination
Oxycodone and its metabolites are mainly excreted in the urine and sweat; therefore, it accumulates in patients with renal impairment.[12]
Bioavailability
Oxycodone can be administered orally, intranasally, via intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous injection, or rectally. The bioavailability of oral administration of oxycodone averages 60–87%, with rectal administration yielding the same results; intranasal varies between individuals with a mean of 46%.[55]
Morphine equivalency
Taken orally, 20 mg of immediate release oxycodone is equivalent to 30 mg of morphine.[56][57] Extended release oxycodone is considered to be twice as potent as oral morphine.[58]
Chemistry
Oxycodone's chemical name is derived from codeine. The chemical structures are very similar, differing only in that
- Oxycodone has a hydroxyl group at carbon-14 (codeine has just a hydrogen in its place)
- Oxycodone has a 7,8-dihydro feature. Codeine has a double bond between those two carbons; and
- Oxycodone has a carbonyl group (as in ketones) in place of the hydroxyl group of codeine.
It is also similar to hydrocodone, differing only in that it has a hydroxyl group at carbon-14.[12]
Oxycodone is marketed as various salts, most commonly as the hydrochloride salt. The free base conversion ratios of different salts are: hydrochloride (0.896), bitartrate (0.667), tartrate (0.750), camphosulphonate (0.576), pectinate (0.588), phenylpriopionate (0.678), sulphate (0.887), phosphate (0.763), and terephthalate (0.792). The hydrochloride salt is the basis of most American oxycodone products whilst bitartrate, tartrate, pectinate, terephthalate and phosphate salts are also available in European products. Methyiodide and hydroiodide are mentioned in older European publications.
Biosynthesis
In terms of biosynthesis, oxycodone has been found naturally in nectar extracts from the orchid family Epipactis helleborine; together along with another opioid: 3-{2-{3-{3-benzyloxypropyl}-3-indol, 7,8-didehydro- 4,5-epoxy-3,6-d-morphinan.[59]
Detection in biological fluids
Oxycodone and/or its major metabolites may be measured in blood or urine to monitor for clearance, abuse, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning, or assist in a medicolegal death investigation. Many commercial opiate screening tests cross-react appreciably with oxycodone and its metabolites, but chromatographic techniques can easily distinguish oxycodone from other opiates.[60]
History
Freund and Speyer of the University of Frankfurt in Germany first synthesized oxycodone from thebaine in 1916,[10] a few years after the German pharmaceutical company Bayer had stopped the mass production of heroin due to hazardous use, harmful use, and dependence. It was hoped that a thebaine-derived drug would retain the analgesic effects of morphine and heroin with less dependence. Unfortunately, this was ultimately not found to be the case.
The first clinical use of the drug was documented in 1917, the year after it was first developed.[10][61] It was first introduced to the US market in May 1939. In early 1928, Merck introduced a combination product containing scopolamine, oxycodone, and ephedrine under the German initials for the ingredients SEE, which was later renamed Scophedal (SCOpolamine ePHEDrine and eukodAL). This combination is essentially an oxycodone analogue of the morphine-based Twilight Sleep, with ephedrine added to reduce circulatory and respiratory effects.
The personal notes of Adolf Hitler's physician, Dr. Theodor Morell, indicate Hitler received repeated injections of "eukodal" (oxycodone).[62]
In the early 1960s, the United States government classified oxycodone as a schedule II drug.
In 1996, Purdue Pharma introduced OxyContin, a controlled release formulation of oxycodone.[63][64] The product has been a commercial success,[63] and since its introduction, Purdue has earned more than $31 billion from OxyContin.[65]
Society and culture
Legal status
General
Oxycodone is subject to international conventions on narcotic drugs. In addition, oxycodone is subject to national laws that differ by country. The 1931 Convention for Limiting the Manufacture and Regulating the Distribution of Narcotic Drugs of the League of Nations included oxycodone.[66] The 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of the United Nations, which replaced the 1931 convention, categorized oxycodone in Schedule I.[67] Global restrictions on Schedule I drugs include "limit[ing] exclusively to medical and scientific purposes the production, manufacture, export, import, distribution of, trade in, use and possession of" these drugs; "requir[ing] medical prescriptions for the supply or dispensation of [these] drugs to individuals"; and "prevent[ing] the accumulation" of quantities of these drugs "in excess of those required for the normal conduct of business".[67]
Australia
Oxycodone is in Schedule I (derived from the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs) of the Commonwealth's Narcotic Drugs Act 1967.[68] In addition, it is in Schedule 8 of the Australian Standard for the Uniform Scheduling of Drugs and Poisons ("Poisons Standard"), meaning it is a "controlled drug... which should be available for use but require[s] restriction of manufacture, supply, distribution, possession and use to reduce abuse, misuse and physical or psychological dependence".[69]
Canada
Oxycodone is a controlled substance under Schedule I of the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act (CDSA).[70]
Canadian legislative changes
In February 2012, Ontario passed legislation to allow the expansion of an already existing drug-tracking system for publicly funded drugs to include those that are privately insured. This database will function to identify and monitor patient’s attempts to seek prescriptions from multiple doctors or retrieve from multiple pharmacies. Other provinces have proposed similar legislation, while some, such as Nova Scotia, have legislation already in effect for monitoring prescription drug use. These changes have coincided with other changes in Ontario’s legislation to target the misuse of painkillers and high addiction rates to drugs such as oxycodone. As of February 29, 2012, Ontario passed legislation delisting oxycodone from the province’s public drug benefit program. This was a first for any province to delist a drug based on addictive properties. The new law prohibits prescriptions for OxyNeo except to certain patients under the Exceptional Access Program including palliative care and in other extenuating circumstances. Patients already prescribed oxycodone will receive coverage for an additional year for OxyNeo, and after that, it will be disallowed unless designated under the exceptional access program.[71]
Much of the legislative activity has stemmed from Purdue Pharma’s decision in 2011 to begin a modification of Oxycontin’s composition to make it more difficult to crush for snorting or injecting. The new formulation, OxyNeo, is intended to be preventative in this regard and retain its effectiveness as a painkiller. Since introducing its Narcotics Safety and Awareness Act, Ontario has committed to focusing on drug addiction, particularly in the monitoring and identification of problem opioid prescriptions, as well as the education of patients, doctors, and pharmacists.[72] This Act, introduced in 2010, commits to the establishment of a unified database to fulfil this intention.[73] Both the public and medical community have received the legislation positively, though concerns about the ramifications of legal changes have been expressed. Because laws are largely provincially regulated, many speculate a national strategy is needed to prevent smuggling across provincial borders from jurisdictions with looser restrictions.[74]
In 2015, Purdue Pharma's abuse-resistant OxyNEO and six generic versions of OxyContin had been on the Canada-wide approved list for prescriptions since 2012. In June 2015, then federal Minister of Health Rona Ambrose announced that within three years all oxycodone products sold in Canada would need to be tamper-resistant. Some experts warned that the generic product manufacturers may not have the technology to achieve that goal, possibly giving Purdue Pharma a monopoly on this opiate.[75]
Canadian lawsuits
Several class action suits across Canada have been launched against the Purdue group of companies and affiliates. Claimants argue the pharmaceutical manufacturers did not meet a standard of care and were negligent in doing so. These lawsuits reference earlier judgments in the United States, which held that Purdue was liable for wrongful marketing practices and misbranding. Since 2007, the Purdue companies have paid over $650 million in settling litigation or facing criminal fines.[76]
Germany
The drug is in Appendix III of the Narcotics Act (Betäubungsmittelgesetz or BtMG).[77] The law allows only physicians, dentists, and veterinarians (Ärzte, Zahnärzte und Tierärzte) to prescribe oxycodone and the federal government to regulate the prescriptions (e.g., by requiring reporting).[77]
Hong Kong
Oxycodone is regulated under Part I of Schedule 1 of Hong Kong's Chapter 134 Dangerous Drugs Ordinance.[78]
Japan
Oxycodone is a restricted drug in Japan. Its import and export is strictly restricted to specially designated organizations having prior permit to import it. In a high-profile case a top Toyota executive, who claimed to be unaware of the law, was arrested for importing oxycodone into Japan.[79][80]
Singapore
Oxycodone is listed as a Class A drug in the Misuse of Drugs Act of Singapore, which means offences in relation to the drug attract the most severe level of punishment. A conviction for unauthorized manufacture of the drug attracts a minimum sentence of 10 years of imprisonment and corporal punishment of 5 strokes of the cane, and a maximum sentence of life imprisonment or 30 years of imprisonment and 15 strokes of the cane.[81] The minimum and maximum penalties for unauthorized trafficking in the drug are respectively 5 years of imprisonment and 5 strokes of the cane, and 20 years of imprisonment and 15 strokes of the cane.[82]
United Kingdom
Oxycodone is a Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act.[83] For Class A drugs, which are "considered to be the most likely to cause harm", possession without a prescription is punishable by up to seven years in prison, an unlimited fine, or both.[84] Dealing of the drug illegally is punishable by up to life imprisonment, an unlimited fine, or both.[84] In addition, oxycodone is a Schedule 2 drug per the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001 which "provide certain exemptions from the provisions of the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971".[85]
United States
Under the Controlled Substances Act, enacted in 1971 by President Richard Nixon,[86] oxycodone is a Schedule II controlled substance whether by itself or part of a multi-ingredient medication. The DEA lists oxycodone both for sale and for use in manufacturing other opioids as ACSCN 9143 and in 2013 approved the following annual aggregate manufacturing quotas: 131.5 metric tons for sale, down from 153.75 in 2012, and 10.25 metric tons for conversion, unchanged from the previous year.[87]
Recreational use
Effects
Oxycodone, like other opioid analgesics, tends to induce feelings of euphoria, relaxation and reduced anxiety in those who are occasional users.[88] These effects make it one of the most commonly abused pharmaceutical drugs in the United States.[89]
Preventive measures
In August 2010, Purdue Pharma reformulated their long-acting oxycodone line, marketed as OxyContin, using a polymer, Intac,[90] to make the pills extremely difficult to crush or dissolve[91] in water to reduce OxyContin abuse.[92] The FDA approved relabeling the reformulated version as abuse-resistant in April 2013.[93]
Pfizer manufactures a preparation of short-acting oxycodone, marketed as OXECTA, which contains inactive ingredients, referred to as tamper-resistant AVERSION® Technology.[94] It does not deter oral abuse. Approved by the FDA in the US in June 2011, the new formulation makes crushing, chewing, snorting, or injecting the opioid impractical because of a change in its chemical properties.[95]
Australia
The non-medical use of oxycodone existed from the early 1970s, but by 2015, 91% of a national sample of injecting drug users in Australia had reported using oxycodone, and 27% had injected it in the last six months.[96]
Canada
Opioid-related deaths in Ontario had increased by 242% from 1969 to 2014.[97] By 2009 in Ontario there were more deaths from oxycodone overdose than from cocaine overdose.[98] Deaths from opioid pain relievers had increased from 13.7 deaths per million residents in 1991 to 27.2 deaths per million residents in 2004.[99] The abuse of oxycodone in Canada became a problem. Areas where oxycodone is most problematic are Atlantic Canada and Ontario, where its abuse is prevalent in rural towns, and in many smaller to medium-sized cities.[100] Oxycodone is also widely available across Western Canada, but methamphetamine and heroin are more serious problems in the larger cities, while oxycodone is more common in rural towns. Oxycodone is diverted through doctor shopping, prescription forgery, pharmacy theft, and overprescribing.[100][101]
The recent formulations of oxycodone, particularly Purdue Pharma's crush-, chew-, injection- and dissolve-resistant OxyNEO[102] which replaced the banned OxyContin product in Canada in early 2012, have led to a decline in the abuse of this opiate but have increased the abuse of the more potent drug fentanyl.[103] According to a Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse study quoted in Maclean's magazine, there were at least 655 fentanyl-related deaths in Canada in a five-year period.[104]
In Alberta, the Blood Tribe police claimed that from the fall of 2014 through January 2015, oxycodone pills or a lethal fake variation referred to as Oxy 80s[105] containing fentanyl made in illegal labs by members of organized crime were responsible for ten deaths on the Blood Reserve, which is located southwest of Lethbridge, Alberta.[106] Province-wide, approximately 120 Albertans died from fentanyl-related overdoses in 2014.[105]
United Kingdom
Abuse and diversion of oxycodone in the UK commenced in the early- to mid-2000s.[107] The first known death due to overdose in the UK occurred in 2002.[108] However, recreational use remains relatively rare.
United States
In the United States, more than 12 million people use opioid drugs recreationally.[109] In 2010, 16,652 deaths were related to opioid overdose in combination with other drugs such as benzodiazepines and alcohol.[110] In September 2013, the FDA released new labeling guidelines for long acting and extended release opioids requiring manufacturers to remove moderate pain as indication for use, instead stating the drug is for "pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long term opioid treatment."[111] The updated labeling will not restrict physicians from prescribing opioids for moderate, as needed use.[109]
Oxycodone is the most widely recreationally used opioid in America. The US Department of Health and Human Services estimates that about 11 million people in the US consume oxycodone in a non-medical way annually.[112] In 2007, about 42,800 emergency room visits occurred due to "episodes" involving oxycodone.[113] Diverted oxycodone may be taken orally or ingested through insufflation; used intravenously, or the heated vapors inhaled. In 2008, recreational use of oxycodone and hydrocodone were involved in 14,800 deaths. Some of the cases were due to overdoses of the acetaminophen component, resulting in fatal liver damage.[114]
Reformulated OxyContin is causing some recreational users to change to heroin, which is cheaper and easier to obtain.[115]
Economics
The International Narcotics Control Board estimated 11.5 short tons (10.4 t) of oxycodone were manufactured worldwide in 1998;[116] by 2007 this figure had grown to 75.2 short tons (68.2 t).[116] United States accounted for 82% of consumption in 2007 at 51.6 short tons (46.8 t). Canada, Germany, Australia and France combined accounted for 13% of consumption in 2007.[116][117] In 2010, 1.3 short tons (1.2 t) of oxycodone were illegally manufactured using a fake pill imprint. This accounted for 0.8% of consumption. These illicit tablets were later seized by the US Drug Enforcement Administration, according to the International Narcotics Control Board.[118] The board also reported 122.5 short tons (111.1 t) manufactured in 2010. This number had decreased from a record high of 135.9 short tons (123.3 t) in 2009.[119]
Names
Expanded expression for the compound oxycodone in the academic literature include "dihydrohydroxycodeinone",[7][120][121] "Eucodal",[120][121] "Eukodal",[1][61] "14-hydroxydihydrocodeinone",[7][120] and "Nucodan".[120][121] In a UNESCO convention, the translations of "oxycodone" are oxycodon (Dutch), oxycodone (French), oxicodona (Spanish), الأوكسيكودون (Arabic), 羟考酮 (Chinese), and оксикодон (Russian).[122] The word "oxycodone" should not be confused with "oxandrolone", "oxazepam", "oxybutynin", "oxytocin", or "Roxanol".[123]
Research
There are a few case reports that oxycodone may have antidepressant effects in some individuals with severe, treatment-resistant major depressive disorder.[124]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Kalso E (2005). "Oxycodone". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 29 (5S): S47–S56. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2005.01.010. PMID 15907646.
- 1 2 3 4 "Roxicodone, OxyContin (oxycodone) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Retrieved 8 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Jennifer A. Elliott; Howard S. Smith (19 April 2016). Handbook of Acute Pain Management. CRC Press. pp. 82–. ISBN 978-1-4665-9635-1.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Howard Smith; Steven Passik (25 April 2008). Pain and Chemical Dependency. Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 195–. ISBN 978-0-19-530055-0.
- 1 2 3 Connie Henke Yarbro; Debra Wujcik; Barbara Holmes Gobel (15 November 2010). Cancer Nursing: Principles and Practice. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. pp. 695–. ISBN 978-1-4496-1829-2.
- 1 2 3 4 Richard A. McPherson; Matthew R. Pincus (31 March 2016). Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 336–. ISBN 978-0-323-41315-2.
- 1 2 3 O'Neil, Maryadele J., ed. (2006). The Merck index (14 ed.). Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck & Co. ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1.
- ↑ Drewes, Asbjørn M; Jensen, Rasmus D; Nielsen, Lecia M; Droney, Joanne; Christrup, Lona L; Arendt-Nielsen, Lars; Riley, Julia; Dahan, Albert (2013). "Differences between opioids: pharmacological, experimental, clinical and economical perspectives" (PDF). British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 75 (1): 60–78. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04317.x. ISSN 0306-5251. PMC 3555047
 . PMID 22554450.
. PMID 22554450. - ↑ German (DE) Patent 296916
- 1 2 3 Sneader W (2005). Drug discovery: a history. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. p. 119. ISBN 0-471-89980-1.
- ↑ "eMC". eMC. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Oxycodone". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ↑ Riley J, Eisenberg E, Müller-Schwefe G, Drewes AM, Arendt-Nielsen L (2008). "Oxycodone: a review of its use in the management of pain". Curr Med Res Opin. 24 (1): 175–192. doi:10.1185/030079908X253708. PMID 18039433.
- ↑ Biancofiore G (September 2006). "Oxycodone controlled release in cancer pain management". Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2 (3): 229–34. doi:10.2147/tcrm.2006.2.3.229. PMC 1936259
 . PMID 18360598.
. PMID 18360598. - ↑ Biancofiore G (September 2006). "Oxycodone controlled release in cancer pain management.". Therapeutics and clinical risk management. 2 (3): 229–34. doi:10.2147/tcrm.2006.2.3.229. PMC 1936259
 . PMID 18360598.
. PMID 18360598. - ↑ Hanks GW, Conno F, Cherny N, Hanna M, Kalso E, McQuay HJ, Mercadante S, Meynadier J, Poulain P, Ripamonti C, Radbruch L, Casas JR, Sawe J, Twycross RG, Ventafridda V (March 2001). "Morphine and alternative opioids in cancer pain: the EAPC recommendations". Br. J. Cancer. 84 (5): 587–93. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2001.1680. PMC 2363790
 . PMID 11237376.
. PMID 11237376. - ↑ http://www.msn.com/en-us/news/us/fda-approves-oxycontin-for-kids-11-to-16/ar-BBlK3zS?ocid=spartandhp
- ↑ Harry J. Gould, III, MD, PhD (11 December 2006). Understanding Pain: What It Is, Why It Happens, and How It's Managed. Demos Medical Publishing. pp. 71–. ISBN 978-1-934559-82-6.
- ↑ Keith Graves (29 September 2015). Drug I.D. & Symptom Guide 6th Edition QWIK-CODE. LawTech Publishing Group. pp. 99–. ISBN 978-1-56325-225-9.
- ↑ Linda Skidmore-Roth (16 July 2015). Mosby's Drug Guide for Nursing Students, with 2016 Update. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 789–. ISBN 978-0-323-17297-4.
- ↑ Raymond S. Sinatra; Oscar A. de Leon-Cassasola (27 April 2009). Acute Pain Management. Cambridge University Press. pp. 198–. ISBN 978-0-521-87491-5.
- ↑ Peter S. Staats; Sanford M. Silverman (28 May 2016). Controlled Substance Management in Chronic Pain: A Balanced Approach. Springer. pp. 172–. ISBN 978-3-319-30964-4.
- ↑ http://www.cnbc.com/2016/06/07/reuters-america-update-2-fda-panel-backs-tevas-abuse-resistant-opioid-painkiller.html
- 1 2 3 4 5 Mellar P. Davis (28 May 2009). Opioids in Cancer Pain. OUP Oxford. pp. 155–158. ISBN 978-0-19-923664-0.
- 1 2 3 4 Karen Forbes (29 November 2007). Opioids in Cancer Pain. OUP Oxford. pp. 64–65. ISBN 978-0-19-921880-6.
- ↑ Helen Bradbury; Barry Strickland Hodge (8 November 2013). Practical Prescribing for Medical Students. SAGE Publications. pp. 93–. ISBN 978-1-4462-9753-7.
- ↑ American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (2009-03-23). "Oxycodone". U.S. National Library of Medicine, MedlinePlus. Retrieved 2009-03-27.
- 1 2 3 4 Dermot R. Fitzgibbon; John D. Loeser (28 March 2012). Cancer Pain. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 198–. ISBN 978-1-4511-5279-1.
- ↑ "Oxycodone Side Effects". Drugs.com. Retrieved 22 May 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 1. Package insert Oxycontin (PDF). Stamford, CT: Purdue Pharma L.P. 2007-11-05. Retrieved 2009-03-23.
- ↑ Simpson K, et al. (December 2008). "Fixed-ratio combination oxycodone/naloxone compared with oxycodone alone for the relief of opioid-induced constipation in moderate-to-severe noncancer pain". Curr Med Res Opin. 24 (12): 3503–3512. doi:10.1185/03007990802584454. PMID 19032132. Retrieved 2009-04-09.
- ↑ "Oxycodone". Center for Substance Abuse Research. 2005-05-02. Retrieved 2009-03-25.
- ↑ Rao R, Desai NS (June 2002). "OxyContin and neonatal abstinence syndrome" (PDF). J Perinatol. 22 (4): 324–5. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7210744. PMID 12032797. Retrieved 2009-03-25.
- ↑ Brennan MJ (2013). "The effect of opioid therapy on endocrine function". The American Journal of Medicine. 126 (3 Suppl 1): S12–8. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2012.12.001. PMID 23414717.
- 1 2 Nieminen, Tuija H.; Hagelberg, Nora M.; Saari, Teijo I.; Neuvonen, Mikko; Neuvonen, Pertti J.; Laine, Kari; Olkkola, Klaus T. (2010). "Oxycodone concentrations are greatly increased by the concomitant use of ritonavir or lopinavir/ritonavir". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 66 (10): 977–985. doi:10.1007/s00228-010-0879-1. ISSN 0031-6970.
- 1 2 Nieminen, Tuija H.; Hagelberg, Nora M.; Saari, Teijo I.; Pertovaara, Antti; Neuvonen, Mikko; Laine, Kari; Neuvonen, Pertti J.; Olkkola, Klaus T. (2009). "Rifampin Greatly Reduces the Plasma Concentrations of Intravenous and Oral Oxycodone". Anesthesiology. 110 (6): 1371–1378. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e31819faa54. ISSN 0003-3022.
- 1 2 Pon, PharmD, Doreen; Hwang, PharmD Candidate, Joon; Lo, PharmD Candidate, Teresa; Van Zyl, MD, FACEP, Carin (2015). "Case study. Decreased responsiveness to oxycodone: A case of a pharmacokinetic drug interaction?". Journal of Opioid Management. 11 (4): 357–361. doi:10.5055/jom.2015.0284. ISSN 1551-7489.
- ↑ Chahl, L. Opioids- mechanism of action. Aust Prescr 1996, 19, 63.
- ↑ Kalso, Eija (2005). "Oxycodone". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 29 (5): 47–56. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2005.01.010. ISSN 0885-3924.
- ↑ Ross FB, Smith MT (1997). "The intrinsic antinociceptive effects of oxycodone appear to be κ-opioid receptor mediated". Pain. 73 (2): 151–157. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(97)00093-6. PMID 9415500.
- ↑ Smith MT (2008). "Differences between and combinations of opioids re-visited". Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 21 (5): 596–601. doi:10.1097/ACO.0b013e32830a4c4a. PMID 18784485.
- ↑ Kalso E (2007). "How different is oxycodone from morphine?". Pain. 132 (3): 227–228. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.09.027. PMID 17961923.
- ↑ Nozaki C, Saitoh A, Kamei J (2006). "Characterization of the antinociceptive effects of oxycodone in diabetic mice". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 535 (1–3): 145–151. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.02.002. PMID 16533506.
- ↑ Nozaki C, Kamei J (2007). "Involvement of mu1-opioid receptor on oxycodone-induced antinociception in diabetic mice". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 560 (2–3): 160–162. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.021. PMID 17292346.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Lalovic, B; Kharasch, E; Hoffer, C; Risler, L; Liuchen, L; Shen, D (2006). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral oxycodone in healthy human subjects: Role of circulating active metabolites". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 79 (5): 461–479. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2006.01.009. ISSN 0009-9236.
- ↑ Moore KA, Ramcharitar V, Levine B, Fowler D (September 2003). "Tentative identification of novel oxycodone metabolites in human urine". J Anal Toxicol. 27 (6): 346–52. doi:10.1093/jat/27.6.346. PMID 14516487.
- 1 2 3 4 Victor R. Preedy (25 April 2016). Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse Volume 3: General Processes and Mechanisms, Prescription Medications, Caffeine and Areca, Polydrug Misuse, Emerging Addictions and Non-Drug Addictions. Elsevier Science. pp. 462–464. ISBN 978-0-12-800677-1.
- 1 2 3 4 Pavel Anzenbacher; Ulrich M. Zanger (29 May 2012). Metabolism of Drugs and Other Xenobiotics. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 420–. ISBN 978-3-527-32903-8.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Klimas, Romina; Witticke, Diana; El Fallah, Sarah; Mikus, Gerd (2013). "Contribution of oxycodone and its metabolites to the overall analgesic effect after oxycodone administration". Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 9 (5): 517–528. doi:10.1517/17425255.2013.779669. ISSN 1742-5255.
- 1 2 3 Lemberg, Kim K.; Siiskonen, Antti O.; Kontinen, Vesa K.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, Jari T.; Kalso, Eija A. (2008). "Pharmacological Characterization of Noroxymorphone as a New Opioid for Spinal Analgesia". Anesthesia & Analgesia. 106 (2): 463–470. doi:10.1213/ane.0b013e3181605a15. ISSN 0003-2999.
- ↑ Firestein, Gary S.; Budd, Ralph C.; Gabriel, Sherine E.; McInnes, Iain B.; O'Dell, James R. (21 June 2016). Kelley and Firestein's Textbook of Rheumatology. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 1080–. ISBN 978-0-323-31696-5. LCCN 2016009254.
- ↑ Samer, CF; Daali, Y; Wagner, M; Hopfgartner, G; Eap, CB; Rebsamen, MC; Rossier, MF; Hochstrasser, D; Dayer, P; Desmeules, JA (2010). "Genetic polymorphisms and drug interactions modulating CYP2D6 and CYP3A activities have a major effect on oxycodone analgesic efficacy and safety". British Journal of Pharmacology. 160 (4): 919–930. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00709.x. ISSN 0007-1188.
- ↑ Gasche Y, Daali Y, Fathi M, Chiappe A, Cottini S, Dayer P, Desmeules J (December 2004). "Codeine intoxication associated with ultrarapid CYP2D6 metabolism". N. Engl. J. Med. 351 (27): 2827–31. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa041888. PMID 15625333.
- ↑ Otton SV, Wu D, Joffe RT, Cheung SW, Sellers EM (April 1993). "Inhibition by fluoxetine of cytochrome P450 2D6 activity". Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 53 (4): 401–9. doi:10.1038/clpt.1993.43. PMID 8477556.
- ↑ Analgesic Expert Group. Therapeutic Guidelines: Analgesic. Version 4. Melbourne: Therapeutic Guidelines Ltd, 2007.
- ↑ "Treatment of Pain". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ Ferrell, Betty Rolling; Pasero, Chris; McCaffery, Margo (2010). "Table 16-1 Equianalgesic Dose Chart". Pain Assessment and Pharmacologic Management. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 0323082637.
- ↑ Levy, Enno Freye; in collaboration with Joseph Victor (2007). Opioids in medicine a comprehensive review on the mode of action and the use of analgesics in different clinical pain states. New York: Springer Science+Business Media B.V. p. 371. ISBN 1402059477.
- ↑ "Why do pollinators become 'sluggish'? Nectar chemical constituents from Epipactis helleborine L. Crantz Orchidaceae". Applied Ecology & Environmental Research. 2005;3(2):29-38. Jakubska A, Przado D, Steininger M, Aniol-Kwiatkowska A, Kadej M.
- ↑ Baselt, R. (2011) Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 9th edition, Biomedical Publications, Foster City, CA, pp. 1259–1262.
- 1 2 Sunshine A, Olson NZ, Colon A, Rivera J, Kaiko RF, Fitzmartin RD, Reder RF, Goldenheim PD (July 1996). "Analgesic efficacy of controlled-release oxycodone in postoperative pain". J Clin Pharmacol. 36 (7): 595–603. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1996.tb04223.x. PMID 8844441.
- ↑ Breitenbach, Dagmar (9 September 2015). "A fresh light on the Nazis' wartime drug addiction". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- 1 2 Art Van Zee (2009). "The Promotion and Marketing of OxyContin: Commercial Triumph, Public Health Tragedy". American Journal of Public Health. 99 (2): 221–227. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2007.131714. PMC 2622774
 . PMID 18799767.
. PMID 18799767. - ↑ "Oxycodone". Cesar.umd.edu. Retrieved June 15, 2014.
- ↑ "More than 1 million OxyContin pills ended up in the hands of criminals and addicts. What the drugmaker knew". Los Angeles Times. July 10, 2016.
- ↑ League of Nations (1931). "Convention for limiting the manufacture and regulating the distribution of narcotic drugs" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- 1 2 "United Nations conference for the adoption of a single convention on narcotic drugs. Final act" (PDF). 1961. Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- ↑ Commonwealth of Australia. "Narcotic Drugs Act 1967 – first schedule". Australasian Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Australian Government. Department of Health and Aging. Therapeutic Goods Administration (June 2008). Standard for the uniform scheduling of drugs and poisons no. 23 (PDF). Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia. ISBN 1-74186-596-4. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Canada Department of Justice (2009-02-27). "Controlled Drugs and Substances Act (1996, c. 19)". Retrieved 2009-03-23.
- ↑ Olgilvie, Megan. "Ontario delisting OxyContin and its substitute from drug benefit program" Toronto Star (2012-02-17)
- ↑ Narcotics Safety and Awareness Act. 2010. Ministry of Health and Long Term Care.
- ↑ Dhalla, Irfan and Born, Karen (2012-02-22) Opioids. healthydebate.ca Archived March 21, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Ontario OxyContin Rules: New Restrictions Applauded But National Rules Needed. Huffington Post. Canadian Press (2012-02-20)
- ↑ Weeks, Carly; Howlett, Karen (August 4, 2015). "New oxycodone rules would give drug maker a monopoly in Canada, experts warn". Globe and Mail. Toronto, Ontario. Retrieved December 15, 2015.
- ↑ Martin, Kevin. Lawsuit attacks OxyContin use. C-Health. Sun Media (2008-08-08)
- 1 2 German Federal Ministry of Justice (2009-01-19). "Act on the circulation of narcotics (Narcotics Act – BtMG)" (in German). Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, People's Republic of China. "Dangerous drugs ordinance – chapter 134". Hong Kong Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- ↑ Toyota's American PR chief arrested for suspected drug violation
- ↑ Toyota: American exec did not intend to break Japan law
- ↑ Misuse of Drugs Act (Cap. 185, 2008 Rev. Ed.) (Singapore), section 6(1).
- ↑ Misuse of Drugs Act (Singapore), section 5(1).
- ↑ "List of drugs currently controlled under the Misuse of Drugs legislation" (PDF). UK. Home Office. 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- 1 2 "Class A, B and C drugs". UK. Home Office. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- ↑ "Statutory instrument 2001 No. 3998. The Misuse of Drugs regulations 2001". UK. Office of Public Sector Information. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- ↑ DEA. "Controlled substance scheduling". Drug information and scheduling. Drug Enforcerment Administration. Retrieved 23 November 2015.
- ↑ "DEA Diversion Control CSA". US Dept of Justice – DEA. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/features/oxycontin-pain-relief-vs-abuse
- ↑ http://newlifehouse.com/top-10-commonly-abused-prescription-medications/
- ↑ Staff (2010). "New Abuse Deterrent Formulation Technology for Immediate-Release Opiods" (PDF). Grünenthal Group. Grünenthal Group Worldwide. Retrieved December 15, 2015.
- ↑ Diep, Francie (May 13, 2013). "How Do You Make a Painkiller Addiction-Proof". Popular Science. Bonnier Corporation.
- ↑ Coplan, Paul (2012). Findings from Purdue’s Post-Marketing Epidemiology Studies of Reformulated OxyContin’s Effects (PDF). NASCSA 2012 Conference. Scottsdale, Arizona. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 14, 2013.
- ↑ "Press Announcements > FDA approves abuse-deterrent labeling for reformulated OxyContin:". US Government – FDA. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ no byline.-->. "Pfizer and Acura Announce FDA Approval of Oxectatm (Oxycodone HCL, USP) CII". Pfizer News and Media. Pfizer Inc. Retrieved December 15, 2015.
- ↑ Fiore, Kristina (June 20, 2011). "FDA Okays New Abuse-Resistant Opioid". MedPage Today. MedPage Today. Retrieved December 15, 2015.
- ↑ Black E (2008). Australian drug trends 2007. Findings from the Illicit Drug Reporting System (IDRS) (PDF). Sydney: National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, University of New South Wales. ISBN 978-0-7334-2625-4.
- ↑ Boyle, Theresa (7 July 2014), "Opioid deaths soaring, study finds Opioid-related deaths in Ontario jumped by a whopping 242 per cent over two decades, according to a study by ICES and St. Mike's", The Star, Toronto, Ontario, retrieved 23 January 2015
- ↑ Donovan, Kevin (10 February 2009), "Oxycodone found to be more deadly than heroin", The Star, Toronto, Ontario, retrieved 23 January 2015
- ↑ "Study finds huge rise in oxycodone deaths". CTV News. Retrieved 2009-12-07.
- 1 2 OxyContin Fact Sheet. (PDF). ccsa.ca. Retrieved on 2012-05-10.
- ↑ Health Canada – Misuse and Abuse of Oxycodone-based Prescription Drugs. Hc-sc.gc.ca (2010-01-11). Retrieved on 2012-05-10.
- ↑ Kirkey, Sharon (May 23, 2012). "OxyNEO another prescription for disaster?". Globe and Mail. Toronto, Ontario.
- ↑ Criger, Erin (August 17, 2015). "Death of OxyContin behind rise of fentanyl?". CityNews. Rogers Digital Media.
- ↑ Gatehouse, Jonathon; Macdonald, Nancy (June 22, 2015). "Fentanyl: The King of all Opiates, and a Killer Drug Crisis". Macleans. Rogers Media. Retrieved December 15, 2015.
- 1 2 Southwick, Reid (December 2, 2015). "Fentanyl brings tragedy to Blood Tribe". Calgary Herald. Calgary, Alberta. Retrieved December 15, 2015.
- ↑ Police believe organized crime is flooding the Blood Tribe reserve with an illegal drug that has been linked to 10 deaths, Alberta, 23 January 2015, retrieved 23 January 2015
- ↑ Gordon T (2008-03-30). "Scots' use of 'hillbilly heroin' rises by 430%". Sunday Times (London).
- ↑ Thompson T (2002-03-24). "Epidemic fear as 'hillbilly heroin' hits the streets". Society Guardian. Retrieved 2009-04-16.
- 1 2 Girioin, Lisa; Haely, Melissa (11 September 2013). "FDA to require stricter labeling for pain drugs". Los Angeles Times. pp. A1 and A9.
- ↑ "Drug Overdose in the United States: Fact Sheet". Centers for Disease Control. Retrieved 12 September 2013.
- ↑ "ER/LA Opioid Analgesic Class Labeling Changes and Postmarket Requirements" (PDF). FDA. Retrieved 12 September 2013.
- ↑ Now a counselor, she went from stoned to straight, San Francisco Chronicle, November 2. 2015.
- ↑ "Oxycontin and Addiction". consumer.healthday.com. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ Policy Impact: Prescription Pain Killer Overdoses Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ↑ Reformulated OxyContin reduces abuse but many addicts have switched to heroin, The Pharmaceutical Journal, 16 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 International Narcotics Control Board (2009). Narcotic drugs: estimated world requirements for 2009; statistics for 2007. Report E/INCB/2008/2 (PDF). New York: United Nations. ISBN 978-92-1-048124-3.
- ↑ "Availability of Opioid Analgesics in the World and Asia, With a special focus on: Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand" (PDF). University of Wisconsin Pain & Policy Studies Group/World Health Organization (WHO) Collaborating Center for Policy and Communications in Cancer Care. United Nations. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
- ↑ Narcotic Drugs: Estimated World Requirements for 2012 and Statistics for 2010. International Narcotics Control Board (2011).
- ↑ Narcotic Drugs: Estimated World Requirements for 2012 and Statistics for 2010. International Narcotics Control Board (2011).
- 1 2 3 4 Eddy NB (1973). The National Research Council involvement in the opiate problem, 1928–1971. Washington: National Academy of Sciences.
- 1 2 3 May EL, Jacobson AE (1989). "The Committee on Problems of Drug Dependence: a legacy of the National Academy of Sciences. A historical account". Drug Alcohol Depend. 23 (3): 183–218. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(89)90083-5. PMID 2666074.
- ↑ United Nations Educational, Scientific; Cultural Organization (2005). "International convention against doping in sport" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- ↑ Hicks RW, Becker SC, Cousins DD, eds. (2008). MEDMARX data report. A report on the relationship of drug names and medication errors in response to the Institute of Medicine’s call for action (PDF). Rockville, MD: Center for the Advancement of Patient Safety, US Pharmacopeia. Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- ↑ Stoll, A. L.; Rueter, S. (1999-12-01). "Treatment augmentation with opiates in severe and refractory major depression". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 156 (12): 2017. doi:10.1176/ajp.156.12.2017. ISSN 0002-953X. PMID 10588427.
Further reading
- Coluzzi, F. & Mattia, C. (July–August 2005). "Oxycodone. Pharmacological profile and clinical data in chronic pain management" (PDF). Minerva Anestesiol. 71 (7–8): 451–60. PMID 16012419. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 9, 2006.