List of National Historic Landmarks in Texas
Bexar Co.
(top left)
(top left)
Cameron Co. (top left)
Dallas Co. (bottom left)
Galveston Co. (bottom left)
Harris Co. (bottom left)
Travis Co. (bottom left)
Young Co. (bottom left)
Dallas Co. NHLs
Dealey Plaza HD
Fair Park HD
Highland Park Village
Harris Co. NHLs
Apollo Mission Control Center
San Jacinto Battlefield
Space Environment
Simulation Laboratory
USS Texas
Galveston Co. NHLs
East End HD
ELISSA
Strand Historic District
Dealey Plaza HD
Fair Park HD
Highland Park Village
Harris Co. NHLs
Apollo Mission Control Center
San Jacinto Battlefield
Space Environment
Simulation Laboratory
USS Texas
Galveston Co. NHLs
East End HD
ELISSA
Strand Historic District
Travis Co. NHLs
Governor's Mansion
Texas State Capitol
Young Co. NHLs
Ft. Belknap
Harrell Site (restricted)
Governor's Mansion
Texas State Capitol
Young Co. NHLs
Ft. Belknap
Harrell Site (restricted)
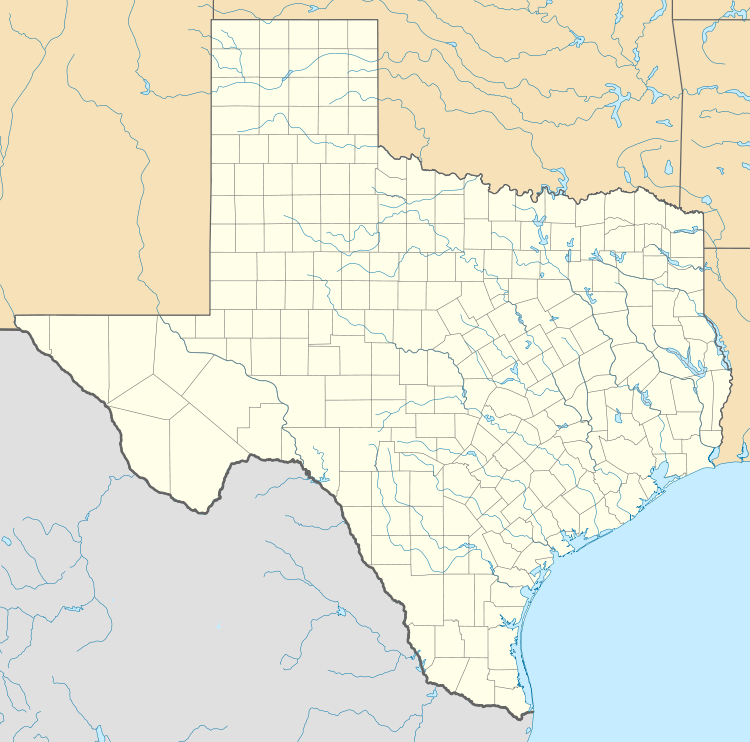
Texas National Historic Landmarks (clickable map)
 Counties with multiple landmarks
Counties with multiple landmarks
 National Historic Landmarks
National Historic Landmarks
 National Historic Landmark Districts
National Historic Landmark Districts
 National Historical Parks
National Historical Parks
 National Historic Site
National Historic Site
 National Historic Landmarks with restricted location (pinned to county, not actual site)
National Historic Landmarks with restricted location (pinned to county, not actual site)
This is a List of National Historic Landmarks in Texas and other landmarks of equivalent landmark status in the state. The United States' National Historic Landmark (NHL) program is operated under the auspices of the National Park Service, and recognizes structures, districts, objects, and similar resources according to a list of criteria of national significance.[1] There are 46 current and one former NHLs in Texas.[2]
Current and former National Historic Landmarks in Texas
The 46 current and one former NHLs in Texas are distributed across 29 of the 254 counties in the state. Eight of the sites are in Bexar County.
- Key
| National Historic Landmark | |
| National Historic Landmark District | |
| National Historical Park | |
| National Historic Site | |
| * | Delisted Landmark |
| [Note 1] | Landmark name | Image | Date designated[Note 2] | Location | County | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alamo |  |
(#66000808) |
San Antonio 29°25′34″N 98°29′10″W / 29.426058°N 98.486084°W |
Bexar | Former mission and fortress compound; now a museum; built by the Spanish Empire in the 18th century; later used as a fortress in the 19th century; scene of the 1836 Battle of the Alamo |
| 2 | Apollo Mission Control Center |  |
(#85002815) |
Houston 29°33′23″N 95°05′18″W / 29.556471°N 95.088460°W |
Harris | NASA control center |
| 3 |
Bastrop State Park |  |
(#97001242) |
Bastrop 30°06′39″N 97°16′25″W / 30.110833°N 97.273611°W |
Bastrop | This park was designed in the 1930s as a showcase of Civilian Conservation Corps work. Its facilities were designed by CCC architect Herbert Maier. |
| 4* | USS Cabot | .jpg) |
August 7, 2001 (#90000334) |
Brownsville |
Cameron | The Cabot was the last remaining of nine former Independence-class light aircraft carriers built in late 1943. War correspondent Ernie Pyle dubbed her the "Iron Maiden" as she served in nearly every major Pacific battle of WW II during her service without repair stops earning her nine battle stars and a Presidential Unit Citation. She would later be transferred to the Spanish Navy where she would serve from 1967-1989 as the SNS Dédalo. She was later purchased by preservation interests and returned to the U.S. first at New Orleans and then moored at Brownsville in 1997. As fund-raising efforts for her rehabilitation were ultimately unsuccessful, she was scrapped for salvage in 2000.[3] |
| 5 |
Dealey Plaza Historic District |  |
(#93001607) |
Dallas 32°46′43″N 96°48′30″W / 32.778611°N 96.808333°W |
Dallas | Site of Kennedy assassination and surrounding buildings that are rumored to have held additional assassins. |
| 6 |
East End Historic District | .jpg) |
(#75001979) |
Galveston 29°18′16″N 94°46′58″W / 29.304444°N 94.782778°W |
Galveston | Galveston's East End was where the city elite built a number of elaborate mansions. |
| 7 | ELISSA (Bark) |  |
(#78002930) |
Galveston 29°20′00″N 94°46′39″W / 29.333255°N 94.777452°W |
Galveston | Tall ship launched in 1877 |
| 8 | Espada Aqueduct |  |
(#66000809) |
San Antonio 29°19′57″N 98°27′41″W / 29.332523°N 98.461469°W |
Bexar | Built by Franciscan friars in 1731 to supply irrigation water to the lands near Mission San Francisco de la Espada |
| 9 |
Fair Park Texas Centennial Buildings |  |
(#86003488) |
Dallas 32°46′55″N 96°45′56″W / 32.781944°N 96.765556°W |
Dallas | Surviving Art Deco buildings from the 1936 Texas Centennial Exposition. |
| 10 | Fort Belknap |  |
(#66000824) |
Newcastle 33°09′03″N 98°44′28″W / 33.150775°N 98.741211°W |
Young | Key frontier post of the 1850s; now a museum. |
| 11 | Fort Brown |  |
(#66000811) |
Brownsville 25°53′54″N 97°29′32″W / 25.898333°N 97.492222°W |
Cameron | Military post of the United States Army in Texas during the latter half of 19th century and the early part of the 20th century |
| 12 |
Fort Concho |  |
(#66000823) |
San Angelo 31°27′10″N 100°25′45″W / 31.452778°N 100.429167°W |
Tom Green | Established as U.S. Army post in 1867; deactivated 1889; comprises most of the original fort |
| 13 |
Fort Davis | |
(#66000045) |
Fort Davis 30°35′45″N 103°55′33″W / 30.595833°N 103.925833°W |
Jeff Davis | From 1854 to 1891 Fort Davis protected migrants, mail coaches, and freight wagons, and controlled the southern stem of the Great Comanche War Trail and Mescalero Apache war trails. |
| 14 | Fort Richardson | |
(#66000816) |
Jacksboro 33°12′29″N 98°09′53″W / 33.208056°N 98.164722°W |
Jack | This Texas frontier fort was established in 1867 and abandoned in 1878. It was renovated and reopened as a state park in 1973. |
| 15 | Fort Sam Houston |  |
(#75001950) |
San Antonio 29°28′35″N 98°25′51″W / 29.476255°N 98.43083°W |
Bexar | Since the 1870s this facility has served as a major military base for the southern United States. It housed Geronimo following his capture, and has been used as the launching point for a variety of military operations. |
| 16 | John Nance Garner House |  |
(#76002074) |
Uvalde 29°12′44″N 99°47′31″W / 29.212152°N 99.791837°W |
Uvalde | Home of John Nance Garner, Vice President under Franklin Delano Roosevelt |
| 17 | Governor's Mansion | .jpg) |
(#70000896) |
Austin 30°16′20″N 97°44′34″W / 30.272318°N 97.742708°W |
Travis | First designated Texas historic landmark, damaged by arson June 8, 2008 |
| 18 | HA. 19 (Midget Submarine) |  |
(#89001428) |
Fredericksburg 30°16′20″N 98°52′06″W / 30.272222°N 98.868333°W |
Gillespie | Historic I.J.N. Ko-hyoteki class midget submarine; part of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941; grounded and captured |
| 19 | Hangar 9, Brooks Air Force Base |  |
(#70000895) |
San Antonio 29°20′32″N 98°26′37″W / 29.342129°N 98.443645°W |
Bexar | Only surviving hangar of 16 builtin at Brooks Air Force Base in 1918. It is now a museum. |
| 20 | Harrell Site | |
(#66000825) |
South Bend Address Restricted |
Young | A late prehistoric Plains Indian archeological site. |
| 21 | Highland Park Shopping Village |  |
(#97001393) |
Highland Park 32°50′09″N 96°48′20″W / 32.835833°N 96.805556°W |
Dallas | Second shopping mall constructed in the U.S.; opened in 1931, and still in operation |
| 22 |
J A Ranch | |
(#66000807) |
Amarillo 34°49′00″N 101°11′17″W / 34.816667°N 101.188056°W |
Armstrong | Founded by John George Adair and Charles Goodnight, this is still one of the largest ranches in the Texas Panhandle, and remains in the hands of Adair descendants. |
| 23 |
Lyndon Baines Johnson Boyhood Home |  |
(#69000202) |
Johnson City 30°14′27″N 98°37′27″W / 30.240833°N 98.624167°W |
Blanco | Boyhood home of President Lyndon B. Johnson. Johnson lived here from the age of five until his high school graduation in 1924. |
| 24 |
King Ranch |  |
(#66000820) |
Kingsville 27°31′07″N 97°55′01″W / 27.518611°N 97.916944°W |
Kenedy, Kleberg, Nueces, and Willacy | Founded in 1853, this is the largest ranch in the United States; it is larger than Rhode Island. |
| 25 | Landergin Mesa | |
(#66000821) |
Vega Address Restricted |
Oldham | This is a major Panhandle culture archeological site. |
| 26 | USS Lexington |  |
(#03001043) |
Corpus Christi 27°48′54″N 97°23′19″W / 27.815°N 97.388611°W |
Nueces | This Essex-class aircraft carrier, known as "The Blue Ghost", was the fifth United States Naval ship named in honor of the Revolutionary War Battle of Lexington. After service in the Second World War and the Cold War, it is now a museum ship. |
| 27 | Lubbock Lake Site |  |
(#71000948) |
Lubbock 33°37′19″N 101°53′23″W / 33.621944°N 101.889722°W |
Lubbock | This major archeological site includes evidence from as far back as 10,000BC. The public can view ongoing archeological work at the site. |
| 28 | Lucas Gusher, Spindletop Oil Field |  |
(#66000818) |
Beaumont 30°01′09″N 94°04′26″W / 30.019167°N 94.073889°W 30°01′09″N 94°04′26″W / 30.019167°N 94.073889°W |
Jefferson | The Spindletop Oil Field was in 1901 where the first major oil gusher of the Texas Oil Boom was discovered. |
| 29 | Majestic Theatre | |
(#75001952) |
San Antonio 29°25′35″N 98°29′27″W / 29.426460°N 98.490713°W |
Bexar | This 1929 theater is the largest in Texas and the second largest in the United States. |
| 30 | Mission Concepcion | .jpg) |
(#70000740) |
San Antonio 29°23′27″N 98°29′34″W / 29.390888°N 98.492760°W |
Bexar | Part of San Antonio Missions National Historical Park, this 1731 Spanish mission was also the site of the 1831 Battle of Concepción, and early action in the Texas Revolution. |
| 31 | Palmito Ranch Battlefield | |
(#93000266) |
Brownsville 25°56′48″N 97°17′07″W / 25.946667°N 97.285278°W |
Cameron | Site of the 1865 Battle of Palmito Ranch, the last major engagement of the American Civil War. |
| 32 |
Palo Alto Battlefield | |
(#66000812) |
Brownsville 26°01′17″N 97°28′50″W / 26.021389°N 97.480556°W |
Cameron | Site of the 1846 Battle of Palo Alto, a precipitating event of the Mexican-American War. |
| 33 | Plainview Site | |
(#66000814) |
Plainview Address Restricted |
Hale | A major archeological site known for Plainview point spear tips. |
| 34 | Walter C. Porter Farm |  |
(#66000819) |
Terrell 32°46′40″N 96°16′28″W / 32.777778°N 96.274444°W |
Kaufman | Part of this farm was used as an experimental agricultural farm in the early 20th century. Successful experiments here led to the establishment of the United States Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Extension Service. |
| 35 | Presidio Nuestra Senora De Loreto De La Bahia |  |
(#67000024) |
Goliad 28°38′48″N 97°22′54″W / 28.646667°N 97.381667°W |
Goliad | Chapel and former fortress compound; now a museum; built by the Spanish Empire in the 18th century; also used as a fortress in the 19th century; scene of the 1836 Battle of Goliad and Goliad Massacre |
| 36 |
Randolph Field Historic District |  |
(#96000753) |
San Antonio 29°31′56″N 98°16′48″W / 29.532222°N 98.28°W |
Bexar | The historic core of Randolph Air Force Base, this area was established in the 1920s as a training field for military aviators. |
| 37 | Samuel T. Rayburn House |  |
(#72001361) |
Bonham 33°34′05″N 96°12′26″W / 33.567967°N 96.207174°W |
Fannin | Longtime home of United States Speaker of the House Samuel T. Rayburn |
| 38 | Resaca De La Palma Battlefield | .jpg) |
(#66000813) |
Brownsville 25°56′15″N 97°29′10″W / 25.9375°N 97.486111°W |
Cameron | Site of the 1846 Battle of Resaca de La Palma, fought early in the Mexican-American War. |
| 39 |
Roma Historic District | .jpg) |
(#72001371) |
Roma 26°24′22″N 99°01′05″W / 26.406111°N 99.018056°W |
Starr | A well-preserved 19th century Rio Grande border town. |
| 40 | San Jacinto Battlefield |  |
(#66000815) |
Houston 29°44′56″N 95°04′49″W / 29.748889°N 95.080278°W |
Harris | Site of the decisive Battle of San Jacinto, securing the independence of Texas from Mexico. |
| 41 | Space Environment Simulation Laboratory, Chambers A and B | .jpg) |
(#85002810) |
Houston 29°33′32″N 95°05′17″W / 29.559003°N 95.0881°W |
Harris | This laboratory for testing equipment in space-like environments has been in use since 1965. |
| 42 | Spanish Governor's Palace |  |
(#70000741) |
San Antonio 29°25′30″N 98°29′40″W / 29.425082°N 98.494570°W |
Bexar | This early Spanish colonial house was home to aristocratic leaders of the Spanish Texas, and is now a city museum. |
| 43 |
Strand Historic District |  |
(#70000748) |
Galveston 29°18′23″N 94°47′37″W / 29.306389°N 94.793611°W |
Galveston | The Victorian downtown of Galveston. |
| 44 | USS TEXAS |  |
(#76002039) |
Houston 29°45′15″N 95°05′22″W / 29.754217°N 95.089499°W |
Harris | After seeing action in the First and Second World Wars, this ship was the first United States Navy battleship to become a museum, and the first to be named a National Historic Landmark. |
| 45 | Texas State Capitol |  |
(#70000770) |
Austin 30°16′22″N 97°44′28″W / 30.272734°N 97.741078°W |
Travis | The seat of Texas government, construction on this Italian Renaissance Revival building began in the 1870s. |
| 46 | Trevino-Uribe Rancho |  |
(#73002342) |
San Ygnacio 27°02′42″N 99°26′36″W / 27.045°N 99.443333°W |
Zapata | Fortified house built c. 1830, shortly after San Ygnacio's founding. |
| 47 | Woodland | |
(#74002097) |
Huntsville 30°42′53″N 95°33′10″W / 30.714722°N 95.552778°W |
Walker | This modest house was the home of Texas leader Sam Houston in the 1840s and 1850s. |
- Notes
- ↑ Numbers represent an ordering by significant words. Various colorings, defined here, differentiate National Historic Landmarks and historic districts from other NRHP buildings, structures, sites or objects.
- ↑ The eight-digit number below each date is the number assigned to each location in the National Register Information System database, which can be viewed by clicking the number.
See also
- List of National Historic Landmarks by state
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Texas
- History of Texas
- List of areas in the United States National Park System
- List of National Natural Landmarks in Texas
References
- ↑ Staff (April 15, 2015). "Learn about the National Historic Landmarks Program". National Park Service. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- ↑ Staff (June 2011). "National Historic Landmarks Survey: List of National Historic Landmarks by State (Texas)" (PDF). National Park Service. Retrieved October 24, 2016..
- ↑ Staff (September 5, 2014). "U.S.S. Cabot (CVL-28)". National Historic Landmarks Program, National Park Service. Retrieved October 22, 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to National Historic Landmarks in Texas. |
- "National Historic Landmarks Survey: List of National Historic Landmarks by State" (PDF). U.S. Department of the Interior. November 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-11-30. Retrieved 2008-01-25.
- National Historic Landmarks Program at the National Park Service
- National Park Service listings of National Historic Landmarks
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.