Nagpur district
| Nagpur district नागपूर जिल्हा | |
|---|---|
| District of Maharashtra | |
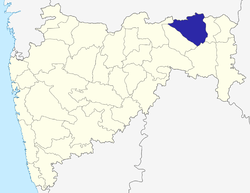 Location of Nagpur district in Maharashtra | |
| Country | India |
| State | Maharashtra |
| Administrative division | Nagpur Division |
| Headquarters | Nagpur |
| Tehsils | 1. Ramtek, 2. Umred, 3. Kalameshwar, 4. Katol, 5. Kamthi, 6. Kuhi, 7. Narkhed, 8. Nagpur, 9. Nagpur (Rural), 10. Parseoni, 11. Bhiwapur, 12. Mouda, 13. Savner, 14. Hingna |
| Government | |
| • Lok Sabha constituencies | 1. Nagpur, 2. Ramtek (SC) (Based on Election Commission website) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9,897 km2 (3,821 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 4,653,171 |
| • Density | 470/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 64.26% |
| Demographics | |
| • Literacy | 89.5% |
| • Sex ratio | 948 |
| Major highways | NH-6, NH-7 |
| Average annual precipitation | 1205 mm |
| Website | Official website |
Nagpur district is a district in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra state in central India. The city of Nagpur is the district headquarters. The district is part of Nagpur Division.
Nagpur district is bounded by Bhandara district on the east, Chandrapur district on the southeast, Wardha district on the southwest, Amravati district on the northwest and Chhindwara district of Madhya Pradesh state on the north.
History
In 1853, after the death of Raghoji III, the princely state of Nagpur was annexed by the British and the territory occupied by the present district became part of Nagpur Province. In 1861, it was merged with the Central Provinces and Nagpur district became a part of one of its divisions, Nagpur division. In 1903, it became part of the Central Provinces and Berar. In 1950, Nagpur district became part of the newly formed Madhya Pradesh state and Nagpur became its capital. In 1956, after the reorganisation of states, Nagpur district was incorporated in Bombay state. On 1 May 1960, it became a district of Maharashtra state and
Geography

Climate
| Nagpur | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Climate data for Nagpur | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 33 (91) |
37 (99) |
41 (106) |
47 (117) |
48 (118) |
45 (113) |
38 (100) |
40 (104) |
39 (102) |
37 (99) |
35 (95) |
32 (90) |
48 (118) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28.6 (83.5) |
32.1 (89.8) |
36.3 (97.3) |
40.2 (104.4) |
42.6 (108.7) |
37.8 (100) |
31.5 (88.7) |
30.4 (86.7) |
31.8 (89.2) |
32.6 (90.7) |
30.4 (86.7) |
28.2 (82.8) |
33.5 (92.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 12.4 (54.3) |
15.0 (59) |
19.0 (66.2) |
23.9 (75) |
27.9 (82.2) |
26.3 (79.3) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.6 (74.5) |
22.9 (73.2) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.9 (58.8) |
12.1 (53.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 7 (45) |
8 (46) |
12 (54) |
17 (63) |
18 (64) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
19 (66) |
11 (52) |
5 (41) |
5.5 (41.9) |
5.9 (42.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10.2 (0.402) |
12.3 (0.484) |
17.8 (0.701) |
13.2 (0.52) |
16.3 (0.642) |
172.2 (6.78) |
304.3 (11.98) |
291.6 (11.48) |
194.4 (7.654) |
51.4 (2.024) |
11.8 (0.465) |
17.2 (0.677) |
1,112.7 (43.807) |
| Source: [1] | |||||||||||||
Divisions
Nagpur district is divided into 14 talukas: Ramtek, Umred, Kalameshwar, Katol, Kamthi, Kuhi, Narkhed, Nagpur, Nagpur (Rural), Parseoni, Bhiwapur, Mouda, Savner and Hingna.
Nagpur district has 12 Vidhan Sabha constituencies: Nagpur South West, Nagpur South, Nagpur East, Nagpur Central, Nagpur West, Nagpur North, Katol, Savner, Hingna, Umred, Kamthi and Ramtek. The first six constituencies are part of Nagpur Lok Sabha constituency and rest are part of Ramtek Lok Sabha constituency.[2]
Demographics
According to the 2011 census Nagpur district has a population of 4,653,171,[3] roughly equal to the nation of Ireland[4] or the US state of South Carolina.[5] This gives it a ranking of 29th in India (out of a total of 640).[3] The district has a population density of 470 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,200/sq mi) .[3] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 14.39%.[3] Nagpur has a sex ratio of 948 females for every 1000 males,[3] and a literacy rate of 89.52%.[3]
The district had a population of 4,653,171 of which 64.26% were urban as of 2011.[6] The current District Collector is Abhishek Krishna. Nagpur district has following administrative bodies which have jurisdiction over different areas[7] -
- Nagpur Municipal Corporation
- Nagpur Improvement Trust
- Narkhed Municipal Council
- Katol Municipal Council
- Saoner Municipal Council
- Ramtek Municipal Council
- Mowad Municipal Council
- Khapa Municipal Council
- Umred Municipal Council
- Narkhed Municipal Council
- Kalmeshwar Municipal Council
Transport
Due to its central location in India, the Nagpur Railway Station is an important railway junction and a transit terminal for trains that connect the country lengthwise and breadthwise, especially trains connecting India's major metropolises, Mumbai to Howrah-Kolkata, Delhi and Jammu to Chennai, Hydrabad, Bangalore and Kanyakumari in the South, as well as western cities such as Pune and Ahemedabad.[8]

Also, Nagpur is a major junction for roadways as India's two major national highways, Kanyakumari-Varanasi (NH 7) and Hajira-Kolkata (NH-6), passing through the city.[8] One more highway number 69 connect Nagpur to Obaidullaganj near Bhopal. Nagpur is at the junction of two Asian Highways namely AH43 Agra to Matara, Sri Lanka and AH46 connecting Kharagpur, India to Dhule, India.
The MSRTC buses run a cheaper transport service in and around the district, reaching out to even the most remote areas of the district.
Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar International Airport in Sonegaon, Nagpur is a domestic and international airport in this district, which connects Nagpur to Mumbai, Delhi, Sharjah, Dubai and muscat via doha .
References
- ↑ "Nagpur, India". Whetherbase. Retrieved 2010-07-01.
- ↑ "District wise List of Assembly and Parliamentary Constituencies". Chief Electoral Officer, Maharashtra website. Retrieved 1 November 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ↑ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". Retrieved 2011-10-01.
Ireland 4,670,976 July 2011 est.
- ↑ "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
South Carolina 4,625,364
- ↑ Census of India
- ↑ "Planning Authority of Nagpur district". Government of Maharashtra. Retrieved 2009-01-08.
- 1 2 Deshpande, Vivek (4 May 2006). "Nagpur stakes claim to lead boomtown pack". The Indian Express. India. Retrieved 22 June 2006.
External links
 |
Chhindwara district, Madhya Pradesh | Seoni district, Madhya Pradesh | Balaghat district, Madhya Pradesh |  |
| Amravati district | |
Bhandara district | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Wardha district | Chandrapur district |
Coordinates: 21°00′N 79°00′E / 21.000°N 79.000°E