Dunkirk
| Dunkirk Dunkerque | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dunkirk Town Hall | |||
| |||
 Dunkirk | |||
|
Location within Hauts-de-France region  Dunkirk | |||
| Coordinates: 51°02′18″N 2°22′39″E / 51.0383°N 2.377500°ECoordinates: 51°02′18″N 2°22′39″E / 51.0383°N 2.377500°E | |||
| Country | France | ||
| Region | Hauts-de-France | ||
| Department | Nord | ||
| Arrondissement | Dunkirk | ||
| Intercommunality | Dunkerque grand littoral | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor (2014-2020) | Patrice Vergriete | ||
| Area1 | 43.89 km2 (16.95 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2012)2 | 90,995 | ||
| • Density | 2,100/km2 (5,400/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| INSEE/Postal code | 59183 / 59140, 59240, 59640 | ||
| Elevation |
0–17 m (0–56 ft) (avg. 4 m or 13 ft) | ||
|
1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km² (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. 2 Population without double counting: residents of multiple communes (e.g., students and military personnel) only counted once. | |||
Dunkirk (French: Dunkerque, pronounced: [dœ̃kɛʁk]; Dutch: Duinkerke(n) pronounced [ˈdœynkɛrkə(n)]) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. It lies 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) from the Belgian border. The population of the city (commune) at the 2012 census was 90,995 inhabitants.
Etymology and language use
The name of Dunkirk derives from West Flemish "dun(e)" (dune or dun) and "kerke" (church), which together means "church in the dunes".[1] Until the middle of the 20th century the city was situated in the French Flemish area; today the local Flemish variety of the Dutch language can still be heard, but has largely been supplanted by French.
Nowadays, Dunkirk is the world's northernmost Francophone city (not counting minor Canadian settlements such as Fermont, which does have French as a majority language, but is not classified as a city).
History

Middle Ages
A fishing village in the originally flooded coastal area of the English Channel south of the Western Scheldt arose late in the tenth century, when the area was held by the Counts of Flanders, vassals of the French Crown. About 960AD Count Baldwin III had a town wall erected, in order to protect the settlement against Viking raids. The surrounding wetlands were drained and cultivated by the monks of nearby Bergues Abbey. The name Dunkirk (Dutch for 'Church in the dunes') was first mentioned in a tithe privilege of 27 May 1067, issued by Count Baldwin V of Flanders. Count Philip I (1157–1191) brought further large tracts of marshland under cultivation, laid out first plans to build a Canal from Dunkirk to Bergues and vested the Dunkirkers with market rights.
When in the late 13th century the Dampierre count Guy of Flanders entered into the Franco-Flemish War with his suzerain King Philippe IV of France, the Dunkirk citizens sided with the French against their count, who first was defeated at the 1297 Battle of Furnes, but reached de facto autonomy upon the victorious Battle of the Golden Spurs five years later and exacted vengeance. Guy's son Count Robert III (1305–1322) nevertheless granted further city rights to Dunkirk; his successor Count Louis I (1322–1346) had to face the Peasant revolt of 1323–1328, which was crushed by King Philippe VI of France at the 1328 Battle of Cassel, whereafter the Dunkirkers again were affected by the repressive measures of their lord-paramount.
Count Louis remained a loyal liensmen of the French king upon the outbreak of the Hundred Years' War with England in 1337, and prohibited the maritime trade, which led to another revolt by the Dunkirk citizens. After the count had been killed in the 1346 Battle of Crécy, his son and successor Count Louis II of Flanders (1346 – 1384) signed a truce with the English; the trade again flourished and the port was significantly enlarged. However, in the course of the Western Schism from 1378, English supporters of Pope Urban VI (the Roman claimant) disembarked at Dunkirk, captured the city and flooded the surrounding estates. They were ejected by King Charles VI of France, but left great devastations in and around the town.
Upon the extinction of the Counts of Flanders with the death of Louis II in 1384, Flanders was acquired by the Burgundian, Duke Philip the Bold. The fortifications were again enlarged, including the construction of a belfry daymark. As a strategic point, Dunkirk has always been exposed to political covetousness, by Duke Robert I of Bar in 1395, by Louis de Luxembourg in 1435 and finally by the Austrian archduke Maximilian I of Habsburg, who in 1477 married Mary of Burgundy, sole heiress of late Duke Charles the Bold. As Maximilian was the son of Emperor Frederick III, all Flanders was immediately seized by King Louis XI of France. However, the archduke defeated the French troops at the 1479 Battle of Guinegate, and when Mary died in 1482 Maximilian retained Flanders according to the 1482 Treaty of Arras. Dunkirk with Flanders was incorporated into the Habsburg Netherlands and upon the 1581 secession of the Seven United Netherlands, remained part of the Southern Netherlands, which were held by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands) as Imperial fiefs.
Privateer base
The area remained much disputed between Spain, the United Netherlands, England and France. At the beginning of the Eighty Years' War, Dunkirk was briefly in the hands of the Dutch rebels, from 1577. Spanish forces under Duke Alexander Farnese of Parma re-established Spanish rule in 1583 and it became a base for the notorious Dunkirkers. The Dunkirkers briefly lost their home port when the city was conquered by the French in 1646 but Spanish forces recaptured the city in 1652. In 1658, as a result of the long war between France and Spain, it was captured after a siege by Franco-English forces following the battle of the Dunes. The city along with Fort-Mardyck was awarded to England in the peace the following year as agreed in the Franco-English alliance against Spain.
It came under French rule when Charles II of England sold it to France for £320,000[2] on 17 October 1662. The French government developed the town as a fortified port. The town's existing defences were adapted to create ten bastions. The port was expanded in the 1670s by the construction of a basin that could hold up to thirty warships with a double lock system to maintain water levels at low tide. The basin was linked to the sea by a channel dug through coastal sandbanks secured by two jetties. This work was completed by 1678. The jetties were defended a few years later by the construction of five forts, Château d'Espérance, Château Vert, Grand Risban, Château Gaillard, and Fort de Revers. An additional fort was built in 1701 called Fort Blanc. The jetties, their forts, and the port facilities were demolished in 1713 under the terms of the Treaty of Utrecht.[3]
During the reign of Louis XIV, a large number of commerce raiders once again made their base at Dunkirk. Jean Bart was the most famous. The Man in the Iron Mask was arrested at Dunkirk. The 18th century Swedish privateers and pirates Lars Gathenhielm and his wife and partner Ingela Hammar, are known to have sold their ill-gotten gains in Dunkirk. The Treaty of Paris (1763) between France and Great Britain included a clause restricting French rights to fortify Dunkirk, to allay British fears of it being used as an invasion base.
Dunkirk in World War I
The United States Navy established a naval air station on 1 January 1918 to operate seaplanes during the First World War (1914–1918). The base closed shortly after the First Armistice at Compiègne.[4]
In January, 1916, a spy hysteria broke out in Dunkirk. The writer Robert W. Service, then a war correspondent for the Toronto Star, was mistakenly arrested as a spy and narrowly avoided being executed out of hand.
Dunkirk in World War II
During the Second World War (1939–1945), in the May 1940 Battle of France, the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) in France aiding the French, was cut off from the rest of the French Army by the German advance. Encircled by the Germans they retreated to the area around the port of Dunkirk. For years, it was assumed that Adolf Hitler ordered the German Army to stop the attack, favouring bombardment by the Luftwaffe. However, according to the Official War Diary of Army Group A, its commander, Generaloberst Gerd von Rundstedt, ordered the halt. Hitler merely validated the order several hours after the fact. This lull in the action gave the British a few days to evacuate by sea and fortify defences. Winston Churchill, the British Prime Minister, ordered any ship or boat available, large or small, to collect the stranded soldiers. 338,226 men (including 123,000 French soldiers) were evacuated – the miracle of Dunkirk, as Churchill called it. It took over 900 vessels to evacuate the Allied forces and although over two-thirds of those rescued embarked via the harbour, almost 100,000 were taken off the beaches. More than 40,000 vehicles as well as massive amounts of other military equipment and supplies were left behind, their value being less than that of trained fighting men. The British evacuation of Dunkirk through the English Channel was codenamed Operation Dynamo. Forty thousand Allied soldiers (some who carried on fighting after the official evacuation) were captured or forced to make their own way home through a variety of routes including via neutral Spain.
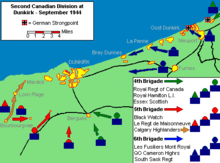
The city was again contested in 1944, with the 2nd Canadian Infantry Division attempting to liberate the city in September, as Allied forces surged northeast after their victory in the Battle of Normandy. However, German forces refused to relinquish their control of the city, which had been converted into a fortress. The German garrison there was "masked" by Allied troops, notably 1st Czechoslovak Armoured Brigade. The fortress under command of German Admiral Friedrich Frisius eventually unconditionally surrendered to the commander of the Czechoslovak forces, Brigade General Alois Liška, on 9 May 1945.[5]
During the German occupation, Dunkirk was largely destroyed by Allied bombings; the artillery siege of Dunkirk was directed on the final day of the war by pilots from No. 652 Squadron RAF, and No. 665 Squadron RCAF.
Postwar Dunkirk
On 14 December 2002, the Norwegian auto carrier Tricolor collided with the Bahamian-registered Kariba and sank off Dunkirk Harbour, causing a hazard to navigation in the English Channel.
Climate
Dunkirk has an oceanic climate, with cool winters and warm summers. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Dunkirk has a marine west coast climate, abbreviated "Cfb" on climate maps.[6] Summers are averaging around 21 °C (70 °F), being significantly influenced by the marine currents.
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °C (°F) | 15 (59) |
19 (66) |
24 (75) |
28.4 (83.1) |
34 (93) |
33.4 (92.1) |
38.2 (100.8) |
36.2 (97.2) |
33.5 (92.3) |
30 (86) |
19.5 (67.1) |
16.6 (61.9) |
38.2 (100.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 7 (45) |
7.3 (45.1) |
9.9 (49.8) |
12.4 (54.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
18.4 (65.1) |
20.9 (69.6) |
21.3 (70.3) |
19 (66) |
15.3 (59.5) |
10.8 (51.4) |
7.6 (45.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.1 (41.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
9.7 (49.5) |
12.9 (55.2) |
15.7 (60.3) |
18.1 (64.6) |
18.4 (65.1) |
16.2 (61.2) |
12.8 (55) |
8.7 (47.7) |
5.8 (42.4) |
11.3 (52.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 3.2 (37.8) |
3 (37) |
5.1 (41.2) |
6.9 (44.4) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13 (55) |
15.2 (59.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
13.5 (56.3) |
10.2 (50.4) |
6.7 (44.1) |
3.9 (39) |
8.9 (48) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −13.4 (7.9) |
−18 (0) |
−7 (19) |
−2 (28) |
−1 (30) |
4 (39) |
6.6 (43.9) |
4 (39) |
4 (39) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−8 (18) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−18 (0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 53.5 (2.106) |
42 (1.65) |
46 (1.81) |
42.5 (1.673) |
49.5 (1.949) |
54.5 (2.146) |
58.3 (2.295) |
58.9 (2.319) |
65.7 (2.587) |
75.8 (2.984) |
69.3 (2.728) |
63.7 (2.508) |
679.7 (26.76) |
| Average rainy days | 11.1 | 8.5 | 10 | 8.9 | 9.1 | 9 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 10.1 | 11.4 | 12 | 11.4 | 118.6 |
| Average snowy days | 2.9 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 10.9 |
| Source #1: [7] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: [8] | |||||||||||||
Heraldry
.svg.png) |
The arms of Dunkirk are blazoned: Per fess Or and argent, a lion passant sable armed and langued gules, and a dolphin naiant azure crested, barbed, finned and tailed gules. |
 Full achievement of the arms of Dunkirk |
Administration
The commune has grown substantially by absorbing several neighbouring communes:
- 1970: Merger with Malo-les-Bains (which had been created by being detached from Dunkirk in 1881)
- 1972: Fusion with Petite-Synthe and Rosendaël (the latter had been created by being detached from Téteghem in 1856)
- 1980: Fusion-association with Mardyck (which became an associated commune, with a population of 372 in 1999)
- 1980: A large part of Petite-Synthe is detached from Dunkirk and included into Grande-Synthe
- 2003: Project of fusion with Saint-Pol-sur-Mer (commune created by its territory being detached from Petite-Synthe in 1877). On 19 December 2003, the municipal councils of Dunkirk and Saint-Pol-sur-Mer decided in favour of a fusion-association, which would create a new entity with a population of 94,187. The prefect requested a referendum, although this procedure was not mandatory (it became mandatory on 1 January 2005). The referendum took place on 5 December 2004, actually covering three communes: Dunkerque, Saint-Pol-sur-Mer and Fort-Mardyck. Although the yes won with 54% of the votes, it did not gather 25% of the potential electorate, as required by the law. The prefect rejected the fusion proposal as a consequence.
Economy
Dunkirk has the third-largest harbour in France, after those of Le Havre and Marseille. As an industrial city it depends heavily on the steel, food processing, oil-refining, ship-building and chemical industries.
Cuisine
The cuisine of Dunkirk closely resembles Flemish cuisine; perhaps one of the best known dishes is coq à la bière - chicken in a creamy beer sauce.
Prototype metre
In June 1792 the French astronomers Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre and Pierre François André Méchain set out to measure the meridian arc distance from Dunkirk to Barcelona, two cities lying on approximately the same longitude as each other and also the longitude through Paris. The belfry was chosen as the reference point in Dunkirk.
Using this measurement and the latitudes of the two cities they could calculate the distance between the North Pole and the Equator in classical French units of length and hence produce the first prototype metre which was defined as being one ten millionth of that distance.[9] The definitive metre bar, manufactured from platinum, was presented to the French legislative assembly on 22 June 1799.
Dunkirk was the most easterly cross-channel measuring point for the Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790), which used trigonometry to calculate the precise distance between the Paris Observatory and the Royal Greenwich Observatory. Sightings were made of signal lights at Dover Castle from the Dunkirk Belfry, and vice versa.
Tourist attractions
- The Musée Portuaire displays exhibits of images about the history and presence of the port.
- The Musée des Beaux-Arts has a large collection of Flemish, Italian and French paintings and sculptures.
- The Carnival of Dunkirk
 The Tour du Leughenaer (the Liar's Tower)
The Tour du Leughenaer (the Liar's Tower) The church Saint Eloi
The church Saint Eloi Dunkirk Town Hall
Dunkirk Town Hall Carnival in Dunkirk
Carnival in Dunkirk Malo-les-Bains beach front
Malo-les-Bains beach front
Transport
Dunkirk has a ferry connection which does not accept foot passengers with Dover, England. The Gare de Dunkerque railway station offers connections to Gare de Calais-Ville, Gare de Lille Flandres, Arras and Paris, and several regional destinations in France. The railway line from Dunkirk to De Panne and Adinkerke, Belgium, shown on major on-line maps, is not used by passenger trains.
Foot passengers have to go to Gare de Calais-Ville for a connection on P&O Ferries to reach Dover.
Sports
- USL Dunkerque, French football club, currently playing in the National.
- The Four Days of Dunkirk (or Quatre Jours de Dunkerque) is an important elite professional road bicycle racing event.
- Stage 2 of the 2007 Tour de France departed from Dunkirk.
Notable residents
- Jean Bart, naval commander and privateer
- Marvin Gakpa, footballer
- Robert Malm, footballer
- Jean-Paul Rouve, actor
- François Rozenthal, ice hockey player
- Maurice Rozenthal, ice hockey player
- Djoumin Sangaré, footballer
- Tancrède Vallerey, writer
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities

|
|
Friendship links
Dunkirk has co-operation agreements with:
 Dartford, Kent, England, United Kingdom since March 1988[10]
Dartford, Kent, England, United Kingdom since March 1988[10] Thanet, Kent, England, United Kingdom since 18 June 1993[10]
Thanet, Kent, England, United Kingdom since 18 June 1993[10]
See also
References
- ↑ Pul, Paul Van (2007). In Flanders Flooded Fields: Before Ypres There Was Yser. Pen and Sword. p. 89. ISBN 978-1473814318.
The French name of Dunkerque in fact is derived from the Flemish Duinkerke, which means 'church in the dunes'!
- ↑ "Correspondence and papers of the first Duke of Ormonde, chiefly on Irish and English public affairs: ref. MS. Carte 218, fol(s). 5 – date: 26 December 1662" (Description of contents of carte papers). Oxford University, Bodleian Library, Special Collections and Western Manuscripts: Carte Papers. 2006. Retrieved 17 October 2007.
- ↑ "> 3D > Dunkirk Sea Forts". Fortified Places. Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ↑ Van Wyen, Adrian O. (1969). Naval Aviation in World War I. Washington, D.C.: Chief of Naval Operations. p. 60.
- ↑ (Czech) Czech army page
- ↑ "Dunkerque, France Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)". Weatherbase. Retrieved 6 September 2015.
- ↑ "Meteo 59-62". Retrieved April 18, 2013.
- ↑ "La Meteo". Retrieved April 18, 2013.
- ↑ Adler, Ken (2002). The measure of all things: The seven year odyssey that transformed the world. Abacus. ISBN 0-349-11507-9.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Dunkirk International" (in French). Archived from the original on November 9, 2007. Retrieved December 17, 2007.
- ↑ "British towns twinned with French towns". Archant Community Media Ltd. Retrieved 2013-07-11.
- ↑ "Town Twinning". Middlesbrough Council. Retrieved 4 March 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dunkerque. |
| Look up Dunkirk in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikinews has related news: French fishermen blockade Channel ports |

