Kinase insert domain receptor
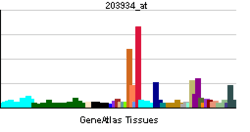
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Kinase insert domain receptor (KDR, a type III receptor tyrosine kinase) also known as vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) is a VEGF receptor. KDR is the human gene encoding it. KDR has also been designated as CD309 (cluster of differentiation 309). KDR is also known as Flk1 (Fetal Liver Kinase 1).
Interactions
Kinase insert domain receptor has been shown to interact with SHC2,[4] Annexin A5[5] and SHC1.[6][7]
See also
Further reading
- Holmes K, Roberts OL, Thomas AM, Cross MJ (October 2007). "Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: structure, function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition.". Cell Signal. 19 (10): 2003–2012. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.05.013. PMID 17658244.
- Petrova TV, Makinen T, Alitalo K (1999). "Signaling via vascular endothelial growth factor receptors.". Exp. Cell Res. 253 (1): 117–30. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4707. PMID 10579917.
- Wang J, Fu X, Jiang C, Yu L, Wang M, Han W, Liu L, Wang J (2014). "Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation promotes therapeutic angiogenesis via upregulation of the VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling pathway in a rat model of vascular dementia.". Behav. Brain Res. 265: 171–180. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2014.02.033. PMC 4000455
 . PMID 24589546.
. PMID 24589546. - Sato Y, Kanno S, Oda N, et al. (2000). "Properties of two VEGF receptors, Flt-1 and KDR, in signal transduction.". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 902 (1): 201–5; discussion 205–7. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06314.x. PMID 10865839.
- Zachary I, Gliki G (2001). "Signaling transduction mechanisms mediating biological actions of the vascular endothelial growth factor family.". Cardiovasc. Res. 49 (3): 568–81. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(00)00268-6. PMID 11166270.
- Vené R, Benelli R, Noonan DM, Albini A (2001). "HIV-Tat dependent chemotaxis and invasion, key aspects of tat mediated pathogenesis.". Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 18 (7): 533–8. doi:10.1023/A:1011991906685. PMID 11688957.
- Lenton K (2003). "VEGFR-2 (KDR/Flk-1).". J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 16 (3): 227–32. PMID 12456025.
- Matsumoto T, Mugishima H (2006). "Signal transduction via vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors and their roles in atherogenesis.". J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 13 (3): 130–5. doi:10.5551/jat.13.130. PMID 16835467.
References
- ↑ "Drugs that physically interact with Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 view/edit references on wikidata".
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Warner, A J; Lopez-Dee J; Knight E L; Feramisco J R; Prigent S A (April 2000). "The Shc-related adaptor protein, Sck, forms a complex with the vascular-endothelial-growth-factor receptor KDR in transfected cells". Biochem. J. England. 347 (Pt 2): 501–9. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3470501. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1220983
 . PMID 10749680.
. PMID 10749680. - ↑ Wen, Y; Edelman J L; Kang T; Sachs G (May 1999). "Lipocortin V may function as a signaling protein for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2/Flk-1". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. UNITED STATES. 258 (3): 713–21. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0678. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 10329451.
- ↑ Zanetti, Adriana; Lampugnani Maria Grazia; Balconi Giovanna; Breviario Ferruccio; Corada Monica; Lanfrancone Luisa; Dejana Elisabetta (April 2002). "Vascular endothelial growth factor induces SHC association with vascular endothelial cadherin: a potential feedback mechanism to control vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 signaling". Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. United States. 22 (4): 617–22. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000012268.84961.AD. PMID 11950700.
- ↑ D'Angelo, G; Martini J F; Iiri T; Fantl W J; Martial J; Weiner R I (May 1999). "16K human prolactin inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced activation of Ras in capillary endothelial cells". Mol. Endocrinol. UNITED STATES. 13 (5): 692–704. doi:10.1210/mend.13.5.0280. ISSN 0888-8809. PMID 10319320.
External links
- Kinase insert domain receptor at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.