Moorefield, West Virginia
| Moorefield, West Virginia | |
|---|---|
| Town | |
|
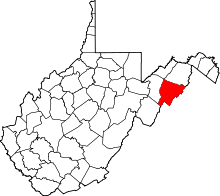
Location of Moorefield, West Virginia | |
| Coordinates: 39°4′N 78°58′W / 39.067°N 78.967°WCoordinates: 39°4′N 78°58′W / 39.067°N 78.967°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | West Virginia |
| County | Hardy |
| Area[1] | |
| • Total | 2.40 sq mi (6.22 km2) |
| • Land | 2.35 sq mi (6.09 km2) |
| • Water | 0.05 sq mi (0.13 km2) |
| Elevation | 810 ft (247 m) |
| Population (2010)[2] | |
| • Total | 2,544 |
| • Estimate (2012[3]) | 2,505 |
| • Density | 1,082.6/sq mi (418.0/km2) |
| Time zone | Eastern (EST) (UTC-5) |
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) |
| ZIP code | 26836 |
| Area code(s) | 304 |
| FIPS code | 54-55588[4] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1543520[5] |


Moorefield is a town in Hardy County, West Virginia, USA. Moorefield is the county seat of Hardy County. It was originally chartered in 1777 and named for Conrad Moore, who owned the land upon which the town was laid out. The population was 2,544 at the 2010 census. Moorefield is located at the confluence of the South Branch Potomac River and the South Fork South Branch Potomac River.
History
Moorefield is situated in the South Branch Valley along the South Branch of the Potomac River. Native Americans populated this area for centuries, farming along the river and hunting in the surrounding mountains. English settlers began arriving in the early 18th century, attracted by the fertile land. This early settlement was centered on the community of Old Fields, which is located about five miles to the north of present-day Moorefield. Conflict between the settlers and Native American populations broke out during the French and Indian War. Two fortifications guarded the South Branch Valley in the vicinity of Moorefield. Fort Buttermilk was erected in 1756 and garrisoned by Captain Thomas Waggoner's Virginia Regiment Company.[6] A second fortress, Fort Pleasant, situated at Henry Van Meter's Farm at Old Fields, guarded the northern side of the valley and was also garrisoned by Captain Thomas Waggoner's Virginia Regiment Company.[7] In the spring of 1756, soldiers from Forts Buttermilk and Pleasant clashed with Shawnee warriors under Bemino (known to the English as Killbuck) at the Battle of the Trough.
The land on which Moorefield was laid out was owned by Conrad Moore. In 1777, the Virginia General Assembly chartered the town of Moorefield in what was then Hampshire County, Virginia (today Hardy County, West Virginia).[8] When Hardy County was separated from Hampshire County by act of the Virginia General Assembly in 1785, Moorefield was chosen as the county seat.[9] Many of the historic houses in Moorefield display vernacular adaptations of Federal and Greek Revival architecture and date to the last quarter of the 18th century and first quart of the 19th century. During the American Civil War, Moorefield was the site of a cavalry engagement between Union Brigadier General William W. Averell and Confederate Brigadier General John McCausland on August 7, 1864.
Geography
Moorefield is located at 39°4′N 78°58′W / 39.067°N 78.967°W (39.063, -78.966).[10]
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 2.40 square miles (6.22 km2), of which, 2.35 square miles (6.09 km2) is land and 0.05 square miles (0.13 km2) is water.[1]
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Moorefield has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[11]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1880 | 554 | — | |
| 1890 | 495 | −10.6% | |
| 1900 | 460 | −7.1% | |
| 1910 | 646 | 40.4% | |
| 1920 | 630 | −2.5% | |
| 1930 | 734 | 16.5% | |
| 1940 | 1,291 | 75.9% | |
| 1950 | 1,405 | 8.8% | |
| 1960 | 1,434 | 2.1% | |
| 1970 | 2,124 | 48.1% | |
| 1980 | 2,257 | 6.3% | |
| 1990 | 2,148 | −4.8% | |
| 2000 | 2,375 | 10.6% | |
| 2010 | 2,544 | 7.1% | |
| Est. 2015 | 2,482 | [12] | −2.4% |
The median income for a household in the town was $24,178, and the median income for a family was $28,919. Males had a median income of $24,423 versus $17,917 for females. The per capita income for the town was $15,704. About 19.8% of families and 21.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 31.2% of those under age 18 and 24.4% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the census[2] of 2010, there were 2,544 people, 1,097 households, and 624 families residing in the town. The population density was 1,082.6 inhabitants per square mile (418.0/km2). There were 1,216 housing units at an average density of 517.4 per square mile (199.8/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 79.0% White, 8.6% African American, 0.4% Native American, 4.7% Asian, 5.4% from other races, and 1.8% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 11.0% of the population.
There were 1,097 households of which 27.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 37.5% were married couples living together, 13.8% had a female householder with no husband present, 5.7% had a male householder with no wife present, and 43.1% were non-families. 34.7% of all households were made up of individuals and 15.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.32 and the average family size was 2.90.
The median age in the town was 40.1 years. 20.1% of residents were under the age of 18; 9.5% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 27.2% were from 25 to 44; 26.7% were from 45 to 64; and 16.4% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the town was 50.9% male and 49.1% female.
References
- 1 2 "US Gazetteer files 2010". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2013-01-24.
- 1 2 "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2013-01-24.
- ↑ "Population Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2013-06-26.
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. 2007-10-25. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ McBride, Stephen; McBride, Kim. "Fort Buttermilk". e-WV. The West Virginia Encyclopedia. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ Adamson, Greg. "Fort Pleasant". e-WV. The West Virginia Encyclopedia. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ Heishman, Phoebe. "Moorefield". e-WV. The West Virginia Encyclopedia. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ Heishman, Phoebe. "Hardy County". e-WV. The West Virginia Encyclopedia. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ↑ Climate Summary for Moorefield, West Virginia
- ↑ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015". Retrieved July 2, 2016.
- ↑ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
External links
-
 Moorefield travel guide from Wikivoyage
Moorefield travel guide from Wikivoyage