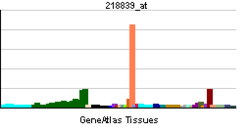
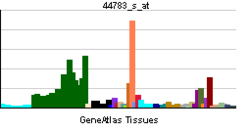
HEY1
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HEY1 gene.[3][4][5]
Function
This gene encodes a nuclear protein belonging to the hairy and enhancer of split-related (HESR) family of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-type transcriptional repressors. Expression of this gene is induced by the Notch and c-Jun signal transduction pathways. Two similar and redundant genes in mouse are required for embryonic cardiovascular development, and are also implicated in neurogenesis and somitogenesis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[5]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Leimeister C, Externbrink A, Klamt B, Gessler M (Jul 1999). "Hey genes: a novel subfamily of hairy- and Enhancer of split related genes specifically expressed during mouse embryogenesis". Mechanisms of Development. 85 (1-2): 173–7. doi:10.1016/S0925-4773(99)00080-5. PMID 10415358.
- ↑ Kokubo H, Lun Y, Johnson RL (Jul 1999). "Identification and expression of a novel family of bHLH cDNAs related to Drosophila hairy and enhancer of split". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 260 (2): 459–65. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0880. PMID 10403790.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: HEY1 hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1".
Further reading
- Iso T, Kedes L, Hamamori Y (Mar 2003). "HES and HERP families: multiple effectors of the Notch signaling pathway". Journal of Cellular Physiology. 194 (3): 237–55. doi:10.1002/jcp.10208. PMID 12548545.
- Kokubo H, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Johnson RL (Jul 2005). "Hesr, a mediator of the Notch signaling, functions in heart and vessel development". Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 15 (5): 190–4. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2005.05.005. PMID 16165016.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (Jan 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1-2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (Oct 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1-2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Chin MT, Maemura K, Fukumoto S, Jain MK, Layne MD, Watanabe M, Hsieh CM, Lee ME (Mar 2000). "Cardiovascular basic helix loop helix factor 1, a novel transcriptional repressor expressed preferentially in the developing and adult cardiovascular system". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (9): 6381–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.9.6381. PMID 10692439.
- Steidl C, Leimeister C, Klamt B, Maier M, Nanda I, Dixon M, Clarke R, Schmid M, Gessler M (Jun 2000). "Characterization of the human and mouse HEY1, HEY2, and HEYL genes: cloning, mapping, and mutation screening of a new bHLH gene family". Genomics. 66 (2): 195–203. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6200. PMID 10860664.
- Maier MM, Gessler M (Aug 2000). "Comparative analysis of the human and mouse Hey1 promoter: Hey genes are new Notch target genes". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 275 (2): 652–60. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3354. PMID 10964718.
- Nakagawa O, McFadden DG, Nakagawa M, Yanagisawa H, Hu T, Srivastava D, Olson EN (Dec 2000). "Members of the HRT family of basic helix-loop-helix proteins act as transcriptional repressors downstream of Notch signaling". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (25): 13655–60. doi:10.1073/pnas.250485597. PMC 17631
 . PMID 11095750.
. PMID 11095750. - Sun J, Kamei CN, Layne MD, Jain MK, Liao JK, Lee ME, Chin MT (May 2001). "Regulation of myogenic terminal differentiation by the hairy-related transcription factor CHF2". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (21): 18591–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101163200. PMID 11279181.
- Iso T, Sartorelli V, Chung G, Shichinohe T, Kedes L, Hamamori Y (Sep 2001). "HERP, a new primary target of Notch regulated by ligand binding". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 21 (17): 6071–9. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.17.6071-6079.2001. PMC 87324
 . PMID 11486044.
. PMID 11486044. - Taylor KL, Henderson AM, Hughes CC (Nov 2002). "Notch activation during endothelial cell network formation in vitro targets the basic HLH transcription factor HESR-1 and downregulates VEGFR-2/KDR expression". Microvascular Research. 64 (3): 372–83. doi:10.1006/mvre.2002.2443. PMID 12453432.
- Elagib KE, Xiao M, Hussaini IM, Delehanty LL, Palmer LA, Racke FK, Birrer MJ, Ganapathy-Kanniappan S, Shanmugasundaram G, McDevitt MA, Goldfarb AN (Sep 2004). "Jun blockade of erythropoiesis: role for repression of GATA-1 by HERP2". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 24 (17): 7779–94. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.17.7779-7794.2004. PMC 506977
 . PMID 15314183.
. PMID 15314183. - Suzuki Y, Yamashita R, Shirota M, Sakakibara Y, Chiba J, Mizushima-Sugano J, Nakai K, Sugano S (Sep 2004). "Sequence comparison of human and mouse genes reveals a homologous block structure in the promoter regions". Genome Research. 14 (9): 1711–8. doi:10.1101/gr.2435604. PMC 515316
 . PMID 15342556.
. PMID 15342556. - Kokubo H, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Nakazawa M, Saga Y, Johnson RL (Feb 2005). "Mouse hesr1 and hesr2 genes are redundantly required to mediate Notch signaling in the developing cardiovascular system". Developmental Biology. 278 (2): 301–9. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.10.025. PMID 15680351.
External links
- HEY1 protein, human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- FactorBook HEY1
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/20/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.