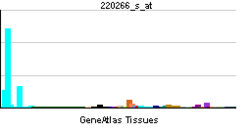
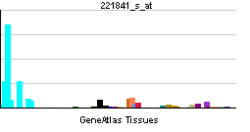
KLF4
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a member of the KLF family of transcription factors and regulates proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and somatic cell reprogramming. Evidence also suggests that KLF4 is a tumor suppressor in certain cancers, including Colorectal cancer.[3]
In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), KLF4 has been demonstrated to be a good indicator of stem-like capacity. It is suggested that the same is true in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
In humans, the protein is encoded by the KLF4 gene.[4] The KLF4 gene is conserved in chimpanzee, rhesus monkey, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, and frog.[5]
Interactions
KLF4 has been shown to interact with CREB-binding protein.[6]
It was found that the transcription factor Klf4 present at the promoter of an enzymatic subunit of telomerase (TERT), where it formed a complex with β-catenin. Klf4 was required for accumulation of β-catenin at the Tert promoter but was unable to stimulate Tert expression in the absence of β-catenin.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ El-Karim; et al. (2013). "Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates genetic stability in mouse embryonic fibroblasts". Molecular Cancer. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-12-89.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: KLF4 Kruppel-like factor 4 (gut)".
- ↑ "Kruppel-like factor 4".
- ↑ Geiman DE, Ton-That H, Johnson JM, Yang VW (March 2000). "Transactivation and growth suppression by the gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor (Krüppel-like factor 4) are dependent on acidic amino acid residues and protein-protein interaction". Nucleic Acids Res. 28 (5): 1106–13. doi:10.1093/nar/28.5.1106. PMC 102607
 . PMID 10666450.
. PMID 10666450. - ↑ Hoffmeyer K, Raggioli A, Rudloff S, Anton R, Hierholzer A, Del Valle I, Hein K, Vogt R, Kemler R (June 2012). "Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates telomerase in stem cells and cancer cells". Science. 336 (6088): 1549–54. doi:10.1126/science.1218370. PMID 22723415.
Further reading
- Rowland BD, Peeper DS (2006). "KLF4, p21 and context-dependent opposing forces in cancer.". Nat. Rev. Cancer. 6 (1): 11–23. doi:10.1038/nrc1780. PMID 16372018.
- Shields JM, Christy RJ, Yang VW (1996). "Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor expressed during growth arrest.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (33): 20009–17. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.33.20009. PMC 2330254
 . PMID 8702718.
. PMID 8702718. - Garrett-Sinha LA, Eberspaecher H, Seldin MF, de Crombrugghe B (1997). "A gene for a novel zinc-finger protein expressed in differentiated epithelial cells and transiently in certain mesenchymal cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (49): 31384–90. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.49.31384. PMID 8940147.
- Yet SF, McA'Nulty MM, Folta SC, et al. (1998). "Human EZF, a Krüppel-like zinc finger protein, is expressed in vascular endothelial cells and contains transcriptional activation and repression domains.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (2): 1026–31. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.2.1026. PMID 9422764.
- Zhang W, Shields JM, Sogawa K, et al. (1998). "The gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor suppresses the activity of the CYP1A1 promoter in an Sp1-dependent fashion.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (28): 17917–25. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.28.17917. PMC 2275057
 . PMID 9651398.
. PMID 9651398. - Foster KW, Ren S, Louro ID, et al. (1999). "Oncogene expression cloning by retroviral transduction of adenovirus E1A-immortalized rat kidney RK3E cells: transformation of a host with epithelial features by c-MYC and the zinc finger protein GKLF.". Cell Growth Differ. 10 (6): 423–34. PMID 10392904.
- Segre JA, Bauer C, Fuchs E (1999). "Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin.". Nat. Genet. 22 (4): 356–60. doi:10.1038/11926. PMID 10431239.
- Geiman DE, Ton-That H, Johnson JM, Yang VW (2000). "Transactivation and growth suppression by the gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor (Krüppel-like factor 4) are dependent on acidic amino acid residues and protein-protein interaction.". Nucleic Acids Res. 28 (5): 1106–13. doi:10.1093/nar/28.5.1106. PMC 102607
 . PMID 10666450.
. PMID 10666450. - Zhang W, Geiman DE, Shields JM, et al. (2000). "The gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor (Kruppel-like factor 4) mediates the transactivating effect of p53 on the p21WAF1/Cip1 promoter.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (24): 18391–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000062200. PMC 2231805
 . PMID 10749849.
. PMID 10749849. - Okano J, Opitz OG, Nakagawa H, et al. (2000). "The Krüppel-like transcriptional factors Zf9 and GKLF coactivate the human keratin 4 promoter and physically interact.". FEBS Lett. 473 (1): 95–100. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01468-X. PMID 10802067.
- Higaki Y, Schullery D, Kawata Y, et al. (2002). "Synergistic activation of the rat laminin gamma1 chain promoter by the gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor (GKLF/KLF4) and Sp1.". Nucleic Acids Res. 30 (11): 2270–9. doi:10.1093/nar/30.11.2270. PMC 117209
 . PMID 12034813.
. PMID 12034813. - Chen ZY, Shie JL, Tseng CC (2003). "Gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor represses ornithine decarboxylase gene expression and functions as checkpoint regulator in colonic cancer cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (48): 46831–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204816200. PMID 12297499.
- Yoon HS, Chen X, Yang VW (2003). "Kruppel-like factor 4 mediates p53-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (4): 2101–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211027200. PMC 2229830
 . PMID 12427745.
. PMID 12427745. - Wang N, Liu ZH, Ding F, et al. (2003). "Down-regulation of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expression in esophageal cancer.". World J. Gastroenterol. 8 (6): 966–70. PMID 12439907.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Chen X, Whitney EM, Gao SY, Yang VW (2003). "Transcriptional profiling of Krüppel-like factor 4 reveals a function in cell cycle regulation and epithelial differentiation.". J. Mol. Biol. 326 (3): 665–77. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(02)01449-3. PMC 2693487
 . PMID 12581631.
. PMID 12581631. - Dang DT, Chen X, Feng J, et al. (2003). "Overexpression of Krüppel-like factor 4 in the human colon cancer cell line RKO leads to reduced tumorigenecity.". Oncogene. 22 (22): 3424–30. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206413. PMC 2275074
 . PMID 12776194.
. PMID 12776194. - Mao Z, Song S, Zhu Y, et al. (2003). "Transcriptional regulation of A33 antigen expression by gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor.". Oncogene. 22 (28): 4434–43. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206508. PMID 12853980.
- Ohnishi S, Ohnami S, Laub F, et al. (2003). "Downregulation and growth inhibitory effect of epithelial-type Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF4, but not KLF5, in bladder cancer.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 308 (2): 251–6. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01356-1. PMID 12901861.
- Hinnebusch BF, Siddique A, Henderson JW, et al. (2004). "Enterocyte differentiation marker intestinal alkaline phosphatase is a target gene of the gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor.". Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 286 (1): G23–30. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00203.2003. PMID 12919939.
External links
- KLF4 protein, human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- KLF4 microarray expression results and literature
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.