Amphetaminil
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
17590-01-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 28615 |
| ChemSpider |
26613 |
| KEGG |
D07446 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2104064 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H18N2 |
| Molar mass | 250.338 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Amphetaminil (brand name Aponeuron; former developmental code name AN-1), also known as N-cyanobenzylamphetamine,[1] is a stimulant drug derived from amphetamine, which was developed in the 1970s and used for the treatment of obesity,[2] ADHD,[3][4] and narcolepsy.[5] It has largely been withdrawn from clinical use following problems with abuse.[6] The drug is a prodrug to amphetamine.[7][8]
Stereochemistry
Amphetaminil is a molecule with two stereogenic centers. Thus, four different stereoisomers exist:
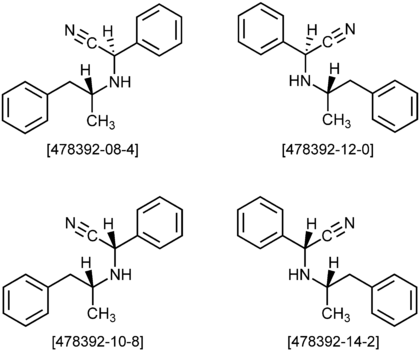
- (R)-2-[(R)-1-Phenylpropan-2-ylamino]-2-phenylacetonitrile (CAS-Nr. 478392-08-4)
- (S)-2-[(S)-1-Phenylpropan-2-ylamino]-2-phenylacetonitrile (CAS-Nr. 478392-12-0)
- (R)-2-[(S)-1-Phenylpropan-2-ylamino]-2-phenylacetonitrile (CAS-Nr. 478392-10-4)
- (S)-2-[(R)-1-Phenylpropan-2-ylamino]-2-phenylacetonitrile (CAS-Nr. 478392-14-2)
References
- ↑ I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 13–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ↑ Harris LS. The stimulants and hallucinogens under consideration: a brief overview of their chemistry and pharmacology. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1986; 17:107.
- ↑ Meyer-Probst B, Vehreschild T. Influencing the lack of concentration in hyperkinetic schoolchildren with Aponeuron. Psychiatrie, Neurologie und Medizinische Psychologie (Leipz) 1976; 28:491.
- ↑ Paclt I, Florian J, Brunclikova J, Ruzickova I. Effect of Aponeuron in the treatment of children with hyperkinetic syndrome. (Czech). Ceska a Slovenska Psychiatrie. 1996 May;92 Suppl 1:41-57.
- ↑ Schlesser JL. Drugs Available Abroad - A Guide to Therapeutic Drugs Approved Outside the US. MEDEX Books, Detroit, 1991.
- ↑ Winter E. Drug abuse and dependence of the amphetamine type with special regard to Amphetaminil (Aponeuron(R)). (German). Psychiatrie, Neurologie und Medizinische Psychologie (Leipzig). 1976 Sep;28(9):513-25.
- ↑ Amitava Dasgupta (2 July 2012). Resolving Erroneous Reports in Toxicology and Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: A Comprehensive Guide. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 96–. ISBN 978-1-118-34785-0.
- ↑ AHC Media, LLC (17 March 2014). Pediatric Trauma Care II: A clinical reference for physicians and nurses caring for the acutely injured child. AHC Media, LLC. pp. 118–. ISBN 978-1-934863-59-6.
| α1 |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α2 |
| ||||||
| β |
| ||||||
| |||||||
| D1-like |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-like |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.