Ellsworth Air Force Base
| Ellsworth Air Force Base | |
|---|---|
| Part of Global Strike Command (GSC) | |
| Located near: Box Elder, South Dakota | |
|
A B-1 Lancer from the 28th Bomb Wing practices "touch and go" procedures at Ellsworth Air Force Base | |
| Coordinates | 44°08′47″N 103°04′29″W / 44.14639°N 103.07472°W |
| Site information | |
| Controlled by |
|
| Site history | |
| Built | 1942 |
| In use | 1942–present |
| Garrison information | |
| Garrison |
 28th Bomb Wing |
| Airfield information | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IATA: RCA – ICAO: KRCA – FAA LID: RCA | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 3,280 ft / 1,000 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 44°08′47″N 103°04′29″W / 44.14639°N 103.07472°WCoordinates: 44°08′47″N 103°04′29″W / 44.14639°N 103.07472°W | ||||||||||
| Website | www.ellsworth.af.mil | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
 KRCA Location of Ellsworth Air Force Base | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||



Ellsworth Air Force Base (AFB) (IATA: RCA, ICAO: KRCA, FAA LID: RCA) is a United States Air Force base located approximately 10 miles (16 km) northeast of Rapid City, South Dakota just north of Box Elder, South Dakota.
The host unit at Ellsworth is the 28th Bomb Wing (28 BW) assigned to the Global Strike Command's Eighth Air Force. The 28 BW is one of only two B-1B Lancer strategic bomber wings in the United States Air Force, the other being the 7th Bomb Wing at Dyess AFB, Texas. Since 2015 the 28th Bomb Wing is commanded by Colonel Gentry Boswell[1] and its Command Chief Master Sergeant is Chief Master Sergeant Sonia Lee.[2] A controversial expansion of a bomber training area encompassing the Northern Plains known as the Powder River Training Complex began in 2008.
Overview
Ellsworth AFB is 10 miles east of Rapid City, S.D. The relationship between Ellsworth and Rapid City is exemplified by Ellsworth's main entrance, a gift from the citizens of Rapid City, constructed to symbolize a B-52 Stratofortress, one of the aircraft formerly flown by the 28th Bomb Wing.
The mission of the 28th Bomb Wing is to deliver combat power for global military response. It is divided into the 28th Operations Group, the 28th Maintenance Group, the 28th Mission Support Group and the 28th Medical Group.
Ellsworth's population of approximately 8,000 includes military members, family members and civilian employees. The base's sister city, Rapid City, has a population of just more than 62,500. There are about 3,800 military retirees in Western South Dakota.
Units
Units assigned to Ellsworth are:
- 28th Bomb Wing (Host unit)
- The Wing commander’s staff consists of a vice commander, an executive officer, a secretary, a director of staff, a wing inspector general, a command chief-master sergeant, a historian, information management, protocol, public affairs, legal, chapel, military equal opportunity, wing plans, treaty compliance, safety, honor guard, the 28th Comptroller Contracting Squadron and a Sexual Assault Response Coordinator.
- Provides combat-ready B-1 aircraft and crews to support Joint Chiefs of Staff taskings, including conventional theater operations and power projection. It plans and executes training missions essential to attain versatile power projection and global reach, and provides the aviation infrastructure necessary to conduct safe flight operations for the 34th and 37th Bomb Squadrons. The 28th Operations Group has three squadrons under its command to assist in accomplishing its mission—the 28th Operations Support Squadron, the 34th Bomb Squadron and the 37th Bomb Squadron.
- 28th Maintenance Group
- Responsible for formulating policies and implementing procedures to ensure availability of the 29 B-1 aircraft and associated support equipment and munitions in support of Joint Chief of Staff-tasked and other contingency missions. The 28th Maintenance Group manages the production of a 1,500- member workforce comprising four squadrons, an annual organizational maintenance and reparable support division budget exceeding $42.5 million, aircraft and weapons valued at more than $9 billion and real property worth $168 million. Additionally, the group directs the implementation of plans supporting pre-planned and contingency mobility taskings in support of national objectives.
- 28th Mission Support Group
- Provides mission essential “city” services at home and combat support services while deployed. Nearly 40 percent of military members and civilians stationed at Ellsworth are part of the 28 MSG team which maintains the base infrastructure by providing essential services to military members, Department of Defense civilians, retirees and their family members. Support operations range from base administration, personnel management, security, mobility readiness, vehicle maintenance, supply, educational services, phone and computer support to civil engineering and food services. Additionally, the group supports the base community through fire protection, disaster preparedness, family support. Recreational opportunities are also provided in the form of clubs, fitness facilities, the base library and other sport-related activities.
- 28th Medical Group
- Tenant Units
- Air Force Financial Services Center
- Area Defense Counsel
- Detachment 226 AFOSI
- Detachment 8, 372 TRS
History
Ellsworth AFB was established in 1941 as Rapid City Army Air Base (AAB). It is named in honor of Brigadier General Richard E. Ellsworth (1911–1953), who was killed when his RB-36 Peacemaker aircraft crashed near Nut Cove, Newfoundland during a training flight. During World War II Ellsworth flew 400 missions in the China Burma India Theater. At the time of his death he commanded the 28th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing.
World War II, 1942-1945
On 2 January 1942, the U.S. War Department established Rapid City Army Air Base as a training location for B-17 Flying Fortress heavy bomber units. Construction proceeded rapidly on the base, with the Control tower opening on 30 Sep 1942; runways, quarters, offices, and facilities completed 1 Oct 1942, and five hangars being completed in late 1942. The airfield had three concrete runways, 7050x300(N/S), 7000x300(E/W), 7872x300(NW/SE). Rapid City AAF was assigned to the 17th Bombardment Training Wing, II Bomber Command. The 88th Bombardment Group was reassigned to the new base in October 1942 to be the base's Operational Training Unit.
In March 1944, heavy bomber operational training ended and the 225th Army Air Force Base Unit began training of replacement personnel for deployed heavy bombardment units in the overseas combat theaters. The field's instructors taught thousands of pilots, navigators, radio operators and gunners from nine heavy bombardment groups and numerous smaller units. All training focused on the Allied drive to overthrow the Axis powers in Europe. On 15 July 1945, the 225th AAFBU was inactivated and Rapid City AAB was placed on standby status as the Army Air Forces began to demobilize.
Postwar era, 1945-1947
Rapid City AAB was reactivated on 11 October 1945 and was assigned to Continental Air Force. It was designated a permanent facility by the Army Air Force. The base briefly trained weather reconnaissance and combat squadrons using P-61 Black Widow, P-38 Lightning, P-51 Mustang, and B-25 Mitchell aircraft.
The airfield was again temporarily shut down from September 1946 – March 1947 and underwent a major construction program to upgrade the temporary wartime facilities to that of a permanent base. The runway was extended to accommodate the B-29 Superfortress, which was completed in the spring of 1948, along with a major overhaul of base facilities.
28th Bombardment Wing, 1948-1958




When operations resumed in 1947 the base was a new United States Air Force asset. The primary unit assigned to Rapid City Air Force Base was the new 28th Bombardment Wing (28 BMW) flying the B-29 Superfortress.
The installation changed names a few more times during its early years. In January 1948, Air Force Chief of Staff Gen Carl A. Spaatz renamed it Weaver Air Force Base in honor of Brig Gen Walter R. Weaver, one of the pioneers in the development of the Air Force. In June of that year, in response to overwhelming public appeals, Secretary of the Air Force Stuart Symington returned the base name to its previous name of Rapid City AFB.
Shortly after additional runway improvements, in July 1949, the 28 BMW began conversion from B-29s to the huge B-36 Peacemaker. In April 1950, the Air Staff reassigned the base from 15th Air Force to 8th Air Force.
The base experienced one of its worst peacetime tragedies in March 1953 when an RB-36 and its entire crew of 23 crashed in Newfoundland while returning from a routine exercise in Europe. On 13 June 1953, President Dwight D. Eisenhower made a personal visit to dedicate the base in memory of Brig Gen Richard E. Ellsworth, commander of the 28th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing, who lost his life in that mishap. The base was subsequently renamed Ellsworth AFB, and unlike the previous local controversy in 1948, there was no community objection to the name change.
Headquarters Strategic Air Command (HQ SAC) reassigned the 28 BMW from 8th Air Force back to 15th Air Force in October 1955. Approximately one year later, SAC set plans in motion to replace the 28th's B-36s with the new all-jet B-52 Stratofortress. The last B-36 left Ellsworth on 29 May 1957 and the first B-52 arrived sixteen days later. In 1958, all base units came under the command of the 821st Strategic Aerospace Division, headquartered at Ellsworth.
Air Defense Command, 1953-1962
Air Defense Command activated the 740th Aircraft Control and Warning Squadron at Rapid City AFB on 1 February 1953 under the ADC 31st Air Division. The site was located on the base, and was given designation "M-97". The site was established as part of the planned deployment by ADC of forty-four Mobile radar stations across the United States to support the permanent Radar network established during the Cold War for air defense of the United States. Prior to its operational use, the squadron was reassigned to the 29th Air Division on 16 February 1953, and Rapid City AFB was re-designated as Ellsworth AFB.
The 740th AC&W Squadron began operations in 1955 with AN/MPS-7 search radar, and initially the station functioned as a Ground-Control Intercept (GCI) and warning station. As a GCI station, the squadron's role was to guide interceptor aircraft toward unidentified intruders picked up on the unit's radar scopes.
An AN/MPS-14 height-finder radar was added in 1956. In 1959 an AN/FPS-20A search radar replaced the AN/MPS-7 set. The squadron was reassigned to the Minot Air Defense Sector on 1 January 1961.
Air Defense Command deactivated the Ellsworth radar site on 15 August 1962 and the 740th was discontinued. After M-97 closed, coverage was assumed by Sundance AFS, Wyoming (TM-201/Z-201).[3][4]
Nike missiles, 1957-1962
To provide air defense of the base, the United States Army established the Ellsworth AFB Defense Area in 1957 and constructed Nike-Ajax Surface-to-air missile sites for air defense. Sites were located near Ellsworth AFB E-01 was north 44°12′09″N 103°05′50″W / 44.20250°N 103.09722°W, E-20 was east-northeast 44°09′02″N 103°00′10″W / 44.15056°N 103.00278°W, E-40 was south-southeast 44°06′14″N 103°05′54″W / 44.10389°N 103.09833°W, and E-70 was west-southwest 44°09′12″N 103°12′59″W / 44.15333°N 103.21639°W. Headquarters facilities were located at Ellsworth. In 1958, batteries E-20, E-40, and E-70 were removed from service and E-01 was converted to fire Nike Hercules missiles. This battery remained in service until 1961. as part of the reduction of the air defenses in the United States against aircraft.
An Army Air-Defense Command Post (AADCP) was established at Ellsworth in 1960 for Nike missile command-and-control functions. The site was equipped with the AN/GSG-5(V) BIRDIE solid-state computer system. The AADCP was integrated with the Air Defense Command General Surveillance radar facilities. The AADCP ceased all operations when the ADC radar site shut down in 1962.
After the Army closed their facilities, the military housing at the Nike Integrated Fire Control sites was transferred to control of Ellsworth, and was used as Air Force military family housing until about 1990.
HGM-25A Titan I Missile, 1960-1965
In October 1960, Ellsworth entered the "Space Age," with the activation of the 850th Strategic Missile Squadron, initially assigned to the 28 BMW. For more than a year this squadron prepared for the emplacement of HGM-25A Titan I intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM), which finally arrived in 1962, shortly after the activation of the 44th Strategic Missile Wing (44 SMW) in January. Headquarters SAC named the 44th SMW 'host wing' at Ellsworth. The Titan I Missile retired in 1965.
LGM-30 Minuteman Missile, 1962-1980's
In July 1962, SAC activated the 66th Missile Squadron, the first of three such units slated to operate 150 LGM-30B Minuteman I ICBMs under the 44 SMW. The 67th Missile Squadron joined the 44th in August, followed by the 68th Missile Squadron in September 1962. The older Titan I's were inactivated in March 1965.
On 1 June 1971, SAC inactivated the 821st Strategic Aerospace Division and by October of that year, an upgraded LGM-30F Minuteman II also replaced the Minuteman I missiles.
Ellsworth soon became known as one of "The Showplaces of SAC" along with Minot AFB and Grand Forks AFB in North Dakota as it continued to fight the Cold War by maintaining two legs of America's strategic triad: strategic bombardment and ICBMs. It carried out these missions for more than 15 years with relatively little change. Then, the 1980s brought many new challenges.
B-1B Lancer, 1987-present
In 1986, the base and the 28 BMW made extensive preparations to phase out the B-52 fleet and become the second home for the advanced B-1B Lancer. Contractors completed new unaccompanied enlisted dormitories in March, a new security police squadron headquarters in October, and gave Ellsworth's 13,497-foot (4,114 m) runway a much-needed facelift. In addition, they completed new aircraft maintenance facilities for the complex new aircraft. The last of the 28 BMW's B-52Hs left in early 1986 and in January 1987, the wing received the first of 35 B-1B bombers.
The 12th Air Division moved to Ellsworth on 15 July 1988. This organization was responsible for training B-1B, B-52, and KC-135 Stratotanker aircrews at Ellsworth and other SAC bases in the region. Headquarters SAC activated a third wing, the 99th Strategic Weapons Wing, at Ellsworth on 10 August 1989. This wing assumed primary responsibility for B-1B advanced aircrew training.
Modern era 1990-present
Internationally, the destruction of the Berlin Wall in October 1989 symbolized the imminent demise of the Soviet Union over the next several months. During this transition the Air Force also had to reshuffle its organizations and resources to meet the shifting, although diminishing, threat. On 3 January 1990, SAC re-designated the 812th Combat Support Group as the 812th Strategic Support Wing (812 SSW), which, for a short time, became Ellsworth's fourth wing. The 812 SSW consolidated all combat support activities into one organization. On 31 July 1990, SAC replaced the 12th Air Division with the Strategic Warfare Center (SWC), which provided operational command and administrative control over Ellsworth's subordinate units. Then, as part of SAC's intermediate headquarters and base-level reorganization plan, on 1 September 1991, SAC renamed the 28 BMW the 28th Wing (28 WG), the 44 SMW the 44th Wing (44 WG) and the 99 SWW the 99th Tactics and Training Wing (99 TTW). Ten days later, SAC inactivated both the SWC and the 812 SSW. Once again, the 28th became Ellsworth's host organization and it soon absorbed all previous 812 SSW functions. It was also during this period that, in acknowledgment of the elimination of the Warsaw Pact, that the President, via the Secretary of Defense, ordered all strategic nuclear alert operations to stand-down. The decades-long Cold War was over.
On 1 June 1992, as part of the first major reorganization since the creation of USAF, the Air Force inactivated Strategic Air Command and assigned Ellsworth's organizations (including a renamed 28th Bomb Wing (28 BW)) to the newly activated Air Combat Command (ACC). After less than a year under the new command, the 28th’s mission changed from that of strategic bombardment to one of worldwide conventional munitions delivery. The mission of the 99th Tactics and Training Wing (later to become the 99th Wing) also continued, albeit slightly modified to fit the requirements of the new force concept.
The 44th Missile Wing, however, had ably accomplished its deterrence mission. On 3 December 1991, the wing permanently pulled the first Minuteman II missile from its silo and on 6 April 1992, the first Minuteman II launch control center shut down. Inactivation of the entire missile complex ended in April 1994. In keeping with its patriotic Minuteman tradition, the 44th Missile Wing formally inactivated on 4 July 1994. Under conditions of the Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty, all of the 44th Missile Wing's Minuteman silos and launch control centers were slated for demolition with the exception of Sites Delta-01 and Delta-09. These latter two sites were subsequently turned over to the National Park Service for preservation as part of the Minuteman Missile National Historic Site.[5]
In March 1994, Ellsworth welcomed the 34th Bomb Squadron, a geographically separated unit (GSU) that was awaiting airfield upgrades before it could return to its parent organization, the 366th Wing (366 WG), at Mountain Home Air Force Base, Idaho. While under the aegis of the 366 WG, the 34th's B-1Bs were part of one of the Air Force’s composite wings, which also included C/D and E model F-15 Eagles, C/D model F-16 Fighting Falcons, and R model KC-135 Stratotankers.
Also during 1994, the Air Force selected Ellsworth as the exclusive location from which to conduct a Congressionally mandated operational readiness assessment of the B-1B, known locally as "Dakota Challenge." After six months of hard work, under both peacetime and simulated wartime conditions, the 28 BW and Ellsworth, relying on extensive personnel, technical and logistical support from sister B-1 units at McConnell, Grand Forks and Dyess Air Force Bases, passed the test "with flying colors"; and proved the B-1 to be a reliable and capable weapons system; the mainstay of America's heavy bomber fleet for years to come.
In 1995, the 99th Wing departed Ellsworth for a new assignment at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada, although a small contingent formerly attached to that wing remained behind to continue bomber tactics training and radar munitions scoring from a handful of dispersed detachments. The year also saw the inactivation of one of Ellsworth’s oldest units, the 77th Bomb Squadron. While the unit (as an administrative entity) departed to save Air Force dollars for development of new follow-on B-1 munitions, the organization’s aircraft remained at Ellsworth (in a flying reserve status) under the able care of its sister unit, the 37th Bomb Squadron.
In early 1996 on 26 March, an announcement was made that the 77th Bomb Squadron would soon return to Ellsworth. On 1 April, the squadron again activated at Ellsworth as the geographically separated 34th Bomb Squadron completed its transfer to its new home with the 366th Wing at Mountain Home AFB, Idaho. By June 1998, the 77th had six of its B-1Bs out of the reconstitution reserve. This number balanced those lost by the 34th BS.
In March 1999, the Air Force announced a reorganization plan that makes Ellsworth AFB and the 28 BW partners in the new Expeditionary Air Force (EAF) concept, now known as the Air & Space Expeditionary Force (AEF). The 28 BW was named a lead wing in the EAF, which enabled the 77 BS to gain six additional B-1Bs, and Ellsworth AFB to gain approximately 100 additional military personnel. The expeditionary force construct enables the Air Force to respond quickly to any worldwide crisis while making life more predictable for military members.
The summer of 2007 marked the last time that Ellsworth hosted a college/university level Air Force Reserve Officer Training Corps Field Training (FT) encampment. All college AFROTC FT encampments were subsequently consolidated at the Air Force Officer Training School at Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama.
Operation Allied Force, 1999
It was not long before Ellsworth and the 28th Bomb Wing were taking the lead in the AEF concept. Five B-1Bs from the 28th Bomb Wing joined NATO forces in Operation Allied Force and began striking military targets in Kosovo on 1 April 1999. By the end of the conflict in June 1999, B-1Bs from Ellsworth flew 100 combat missions and dropped over 1,260 tons of Mk-82 general-purpose bombs.
Operation Enduring Freedom 2001-present
After the events of the September 11, 2001 attacks, Ellsworth deployed a number of B-1s in support of Operation Enduring Freedom. Aircraft from the 37th BS at Ellsworth AFB joined additional B-1s from the 34th BS at Mountain Home AFB and formed the 34th Expeditionary Bomb Squadron. This squadron, along with other elements from Ellsworth, deployed to Diego Garcia and joined the 28th Air Expeditionary Wing. Their combat mission effectiveness was greater than 95% and they flew 5% of the total strike aircraft missions. They dropped 39% of the total tonnage of bombs, which was more than any other platform. During their deployment the 28th EBS dropped 2,974 JDAMs, 1,471 Mk-82, 135 Mk-84, and 70 CBU-87 bombs. Currently, the 28th Bomb Wing and personnel from Ellsworth Air Force Base continue to be the lead wing for AEF 8, and Ellsworth personnel continue to prepare for ongoing deployments in support of operations around the globe.
34th BS replaces the 77th BS, 2001

On 19 September 2001 the "Thunderbirds" of the 34th Bomb Squadron arrived from Mountain Home AFB, Idaho to rejoin the Ellsworth team. Due to a drawdown in the number of active B-1B aircraft in the Air Force inventory, the 77th BS at Ellsworth was inactivated.
Base Realignment and Closure 2004-2005
During the 2004 Senate race in South Dakota, Republican challenger John Thune made Ellsworth a campaign issue, stating in a 16 April 2004 appearance at the base that if he were elected over incumbent Democrat and Senate Minority Leader Tom Daschle: “It puts Ellsworth in a lot stronger position than having someone who's going to be in the minority and someone who doesn't have a relationship with the President of the U.S.” In a debate between the two men broadcast on KSFY-TV and KOTA-TV television on 17 October 2004, Thune said: "I think we have got to have somebody that has a relationship with the President of the United States, can work constructively across party lines in the Congress to get this done if we're going save Ellsworth" and was later quoted in the "Rapid City Journal" newspaper on 27 October 2004 claiming that: "an all-Democratic congressional delegation would have little political influence if President Bush is elected to a second term.”
On 24 May 2004 campaigning in South Dakota for Thune, Senate Majority Leader Bill Frist said of Daschle: "Who is the president going to listen to more? The majority leader of the Senate, who he works with on almost a daily basis, or a senator from another party who every day is saying things on the floor that demonstrate a lack of support?" also adding: “This time around, the President is appointing who's on that BRAC commission, all of them."
Thune defeated Daschle with 51% of the vote in the election, and president Bush was elected to a second term. Nevertheless, on 13 May 2005, the Department of Defense recommended that Ellsworth Air Force Base be closed. Thune stated in protest he would vote against confirmation of the president's nominee for United Nations Ambassador, John Bolton.
On 26 August 2005 the nine-member BRAC commission voted 8–1 to spare Ellsworth from the closure list. Commissioner Harold Gehman said, "We have no savings, we're essentially moving the airplanes from one very, very good base to another very, very good base, which are essentially equal." Senator Thune called the move a good, nonpolitical decision.
Expansion of bomber training area
Since 2008, a bomber training area Powder River Training Complex is being expanded to about 28,000 square miles, including portions of Wyoming, Montana and the Dakota.[6]
Move to the Eighth Air Force
On October 1, 2015, Ellsworth became part of the Eighth Air Force and fell under the command of Global Strike Command.[7]
Previous names
- Established as Rapid City Army Air Base, December 1941
- Rapid City Army Air Field (unofficial designation), c. 1 September 1946
- Rapid City Air Field, 28 November 1947
- Weaver Air Force Base, 13 January 1948
- Rapid City Air Force Base, 24 June 1948
- Ellsworth Air Force Base, 1 June 1953–present
Major commands to which assigned
- Second Air Force, 9 June 1942
- Continental Air Forces, 16 April 1945
- Redesignated: Strategic Air Command, 21 March 1946
- Air Combat Command, 1 June 1992 – 30 September 2015
- Global Strike Command, 1 October 2015 – present
Major units assigned
|
|
Intercontinental ballistic missile facilities
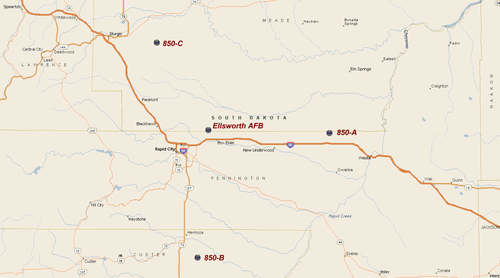

66th MS (Black)
67th MS (Blue)
68th MS (Blue)
The 850th Strategic Missile Squadron Operated three HGM-25A Titan I ICBM sites: (1 Dec 1960 – 25 Mar 1965)
- 850-A, 4 miles NNW of Wicksville, South Dakota 44°08′10″N 102°37′02″W / 44.13611°N 102.61722°W
- 850-B, 5 miles SSE of Hermosa, South Dakota 43°46′34″N 103°08′46″W / 43.77611°N 103.14611°W
- 850-C, 10 miles SE of Sturgis, South Dakota 44°23′51″N 103°18′48″W / 44.39750°N 103.31333°W
- 850-C has been destroyed- after trying to sell it for a few years, owner gave up and let a scrapper excavate and destroy the entire complex
LGM-30 Minuteman ICBM Missile Alert Facilities (MAF) (each controlling 10 missiles) were located as follows:
- 66th Missile Squadron (1 Sep 1962 – 1 Sep 1993)
- A-01 19.9 mi S of Howes, SD, 44°19′52″N 102°03′03″W / 44.33111°N 102.05083°W
- B-01 7.5 mi NxNW of Wall SD, 44°05′56″N 102°17′01″W / 44.09889°N 102.28361°W
- C-01 10.1 mi N of Philip SD, 44°11′01″N 101°42′09″W / 44.18361°N 101.70250°W
- *D-01 6.7 mi SxSW of Cottonwood SD, 43°52′40″N 101°57′42″W / 43.87778°N 101.96167°W
- *D-09 (Launch Facility) 4.4 mi SxSW of Quinn SD, 43°55′53″N 102°09′36″W / 43.93139°N 102.16000°W
- *Designated as part of the Minuteman Missile National Historic Site
- E-01 6.3 mi NxNE of Kadoka SD, 43°55′12″N 101°28′52″W / 43.92000°N 101.48111°W
- 67th Missile Squadron (1 Sep 1962 – 15 Aug 1992)
- F-01 61.0 mi NxNE of Ellsworth AFB, SD. 44°59′49″N 102°45′43″W / 44.99694°N 102.76194°W
- G-01 11.3 mi N of Union Center SD, 44°43′25″N 102°39′00″W / 44.72361°N 102.65000°W
- H-01 10.0 mi SW of Union Center SD, 44°27′43″N 102°48′55″W / 44.46194°N 102.81528°W
- I-01 5.7 mi E of White Owl SD, 44°36′10″N 102°18′57″W / 44.60278°N 102.31583°W
- J-01 13.8 mi SE of Maurine SD, 44°54′20″N 102°21′55″W / 44.90556°N 102.36528°W
- 68th Missile Squadron (1 Sep 1962 – 5 July 1994)
- K-01 5.6 mi N of Spearfish SD, 44°34′22″N 103°51′42″W / 44.57278°N 103.86167°W
- L-01 6.2 mi SxSE of Vale SD, 44°32′29″N 103°20′42″W / 44.54139°N 103.34500°W
- M-01 17.7 mi NxNW of Belle Fourche SD, 44°55′09″N 103°56′07″W / 44.91917°N 103.93528°W
- N-01 6.7 mi NW of Newell SD, 44°47′41″N 103°30′09″W / 44.79472°N 103.50250°W
- O-01 38.5 mi W of opal, SD, 44°55′29″N 103°14′13″W / 44.92472°N 103.23694°W
A complete list of Minuteman missile launch control facilities and missile silos can be found here.
The Titan-I sites still exist, in various states of abandonment. Site "A" is still fenced, with all the missile silos capped and in place. Most of the concrete roads remain, along with what remains of the launch control blockhouse and several axillary buildings. Site "B" is in similar condition, abandoned with prairie grass in a very remote location. Site "C" also has the three missile silos capped, but much of the concrete has been removed and appears to be part of a grazing rangeland, the outlines of the missile site still very visible in aerial imagery.
The Minuteman Launch Control Facilities (with the exception of D-01) all appear to be still in federal government ownership, as after fifteen or more years of inactivation, all are standing but abandoned; the buildings still standing within the locked security fence. The missile sites (again, with the exception of D-09) are all in private ownership, most being used for agricultural use, the remainder abandoned and returning to a natural state.
Environmental contamination
Ellsworth Air Force Base is a military superfundsite, listed in August 1990. Contaminants are petroleum products, waste solvents and radioactive waste polluting soil and groundwater.[8] The Air Force has been cleaning up 12 areas, under supervision by EPA, including landfills, a fire protection training area, spill sites, industrial areas and an explosive-ordnance disposal area. Remedies have included groundwater pump-and-treat systems, bio-dechlorination, soil excavation, landfill covers, and institutional controls (fences/signs). In 2007, in-place reductive treatment for groundwater cleanup replaced the pump-and-treat systems. As of 2016 operation and maintenance activities and groundwater monitoring are ongoing.[9]
In February 2014 the air force found 12 places that needed more testing due to possible PFC contamination from A-FFF, a fire-fighting foam. 300 wells across Ellsworth are being sampled for PFC’s. in addition a site at the south end of the base, where former firefighters trained using A-FFF will be investigated with field work completed in August 2016.[10]
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of 1.9 mi² (4.9 km²), all land.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1970 | 5,805 | — | |
| 1980 | 4,766 | −17.9% | |
| 1990 | 7,017 | 47.2% | |
| 2000 | 4,165 | −40.6% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
As of the census[11] of 2000, there were 4,165 people, 1,056 households, and 991 families residing in the CDP. The population density was 2,217.8/ mi² (855.4/ km²). There were 1,076 housing units at an average density of 573.0/ mi² (221.0/ km²). The racial makeup of the CDP was 82.2% White, 6.7% Black or African American, 0.9% Native American, 2.3% Asian, 0.3% Pacific Islander, 2.6% from other races, and 5.1% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 6.6% of the population.
There were 1,056 households out of which 74.0% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 86.6% were married couples living together, 4.5% had a female householder with no husband present, and 6.1% were non-families. 4.5% of all households were made up of individuals, none of whom were 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.41 and the average family size was 3.51.
In the CDP the population was spread out with 36.4% under the age of 18, 24.7% from 18 to 24, 36.3% from 25 to 44, 2.4% from 45 to 64, and 0.2% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 22 years. For every 100 females there were 119.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 131.0 males.
The median income for a household in the CDP was $31,919, and the median income for a family was $31,941. Males have a median income of $20,721 versus $15,238 for females. The per capita income for the CDP was $11,362. About 3.4% of the population and 4.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 3.9% of those under the age of 18 and none of those 65 and older.
Nearby installations
The nearest major military installations to Ellsworth are F.E. Warren AFB in Cheyenne, Wyoming and Minot AFB in Minot, North Dakota, both over 200 mi (300 km) away.
Smaller installations include Camp Rapid in Rapid City, which serves as the headquarters for the South Dakota National Guard. The 114th Fighter Wing (114 FW), an Air Combat Command-gained unit of the South Dakota Air National Guard flying the F-16 Fighting Falcon, is located at Sioux Falls Regional Airport / Joe Foss Field Air National Guard Station in Sioux Falls. The South Dakota Army National Guard also operates the South Dakota Military Academy located at Fort Meade, South Dakota, approximately 20 miles (32 km) NNW of Ellsworth AFB.
See also
- South Dakota World War II Army Airfields
- List of USAF Aerospace Defense Command General Surveillance Radar Stations
- South Dakota Air and Space Museum Originally located inside the Ellsworth AFB, now located outside the front gate.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency website http://www.afhra.af.mil/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency website http://www.afhra.af.mil/.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Government document "Ellsworth Air Force Base".
This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Government document "Ellsworth Air Force Base".
- ↑ "Colonel Gentry Boswell". US AirForce. June 2015. Archived from the original on 18 September 2016. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ↑ "CMSgt Sonia Lee". US AirForce. August 2015. Archived from the original on 18 September 2016. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- ↑ A Handbook of Aerospace Defense Organization 1946 – 1980, by Lloyd H. Cornett and Mildred W. Johnson, Office of History, Aerospace Defense Center, Peterson Air Force Base, Colorado
- ↑ Winkler, David F. (1997), Searching the skies: the legacy of the United States Cold War defense radar program. Prepared for United States Air Force Headquarters Air Combat Command.
- ↑ "Minuteman Missile National Historic Site (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved 2016-09-18.
- ↑ Brown, Matthew (July 20, 2014). "Air Force says decision near on four-state bomber training area over Northern Plains". Associated Press. ABC News .com.
- ↑ "Ellsworth B-1 bombers under La. command". Associated Press. 28 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ↑ "Ellsworth Air Force Base:". South Dakota DENR. n.d. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- ↑ "Site Information for ELLSWORTH AIR FORCE BASE". Superfund Information Systems. EPA. 29 April 2016. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- ↑ http://www.kotatv.com/content/news/Health-and-safety-constant-concerns-for-Ellsworth-Air-Force-Base--377474501.html (29 April 2016). "Health and safety constant concerns for Ellsworth Air Force Base". KOTA Territory News. Gray Digital Media -. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- Maurer, Maurer. Air Force Combat Units of World War II. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office 1961 (republished 1983, Office of Air Force History, ISBN 0-912799-02-1).
- Ravenstein, Charles A. Air Force Combat Wings Lineage and Honors Histories 1947–1977. Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama: Office of Air Force History 1984. ISBN 0-912799-12-9.
- Mueller, Robert, Air Force Bases Volume I, Active Air Force Bases Within the United States of America on 17 September 1982, Office of Air Force History, 1989
- Ellsworth AFB history
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ellsworth Air Force Base. |
- Ellsworth Air Force Base at GlobalSecurity.org
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective December 8, 2016
- FAA Terminal Procedures for RCA, effective December 8, 2016
- Resources for this U.S. military airport:
- FAA airport information for RCA
- AirNav airport information for KRCA
- ASN accident history for RCA
- NOAA/NWS latest weather observations
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KRCA
 Media related to Ellsworth Air Force Base (HAER images) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ellsworth Air Force Base (HAER images) at Wikimedia Commons- Ellsworth Air Force Base EPA Superfund program