List of religious sites
This article provides an incomplete list and broad overview of significant religious sites and places of spiritual importance throughout the world. Sites are listed alphabetically by religion.
Abrahamic religions
Abrahamic religions are those monotheistic faiths emphasizing and tracing their common origin to Abraham[1] or recognizing a spiritual tradition identified with him.[2][3][4] They constitute one of three major divisions in comparative religion, along with Indian religions (Dharmic) and East Asian religions (Taoic).

The three major Abrahamic faiths (in chronological order of revelation) are Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Some strict definitions of what constitutes an Abrahamic religion include only these three faiths. However, there are many other religions incorporating Abrahamic doctrine, theology, genealogy and history into their own belief systems.
For example, Samaritanism is a religion closely related to Judaism, as Druzism, Ahmadiyya or Alevism are to Islam. The Bahá'í Faith considers itself a successor to the traditional Abrahamic religions. Somewhat related to Christianity are many Gnostic sects, as well as Mandaeism. Kurdish religions such as the various Yazdani faiths are quasi- or post-Abrahamic, syncretic, and may trace some portions of their theology to Iranian religions and in some cases Zoroastrianism.

Generally speaking, sites significant to most, if not all Abrahamic religions include Mount Sinai (Arabic: طور سيناء Ṭūr Sīnā’, or جبل موسى Jabal Mūsá; Egyptian Arabic: Gabal Musa, lit. "Moses' Mountain" or "Mount Moses"; Hebrew: הר סיני Har Sinai; also known as "Mount Horeb"), a mountain in the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt that is the traditional and most accepted location of the Biblical Mount Sinai. The latter is mentioned many times in the Book of Exodus in the Torah, the Bible,[5] and the Qur'an.[6] According to Jewish, Christian and Islamic tradition, the biblical Mount Sinai was the place where Moses received the Ten Commandments., the Tomb of Abraham in the Cave of the Patriarchs, as well as many other places within the "Promised Land" region of the Eastern Mediterranean. Many of these locations are featured in the history of the Jewish people and the various Abrahamic sacred texts such as the Judaic and Samaritan Pentateuch, the Torah, Tanakh and Talmud; the Christian Bible; the Qur'an; and under some definitions Bahá'í literature, the Druze Kitab Al Hikma, as well as Yazdani, Ahmadiyya, Alevi and other texts and lore.
Bahá'í Faith and Bábism

The Bahá'í Faith (/bəˈhaɪ/;[7] Persian: بهائی, originally from the Arabic Bahá, meaning "glory" or "splendour"[8]) is a monotheistic religion founded by Bahá'u'lláh in 19th century Persia, and consider their religion to progress from or succeed Bábism or the Bábi Faith (Persian: بابی ها Bábí há) founded by the Báb earlier in the century – emphasizing the spiritual unity of all humankind.[9]



Located in Bahji, within the Arc building complex at the Bahá'í World Centre (BWC) on Mount Carmel in Haifa, near Acre, Israel, the Shrine of Bahá'u'lláh is the most holy place for Bahá'ís and their Qiblih, or direction of prayer. It contains the remains of Bahá'u'lláh and is near the spot where he died in the Mansion of Bahji. Bahá'ís regard Acre (He.: עַכּוֹ Akko; Ar.: عكّا ʻAkkā) itself as their holy city, mostly due to the fact that it serves as the location of Bahá'u'lláh and his family's many affairs. Within Acre, Bahá'í sites include the House of `Abbúd, the House of `Abdu'lláh Páshá, the Garden of Ridván and the Prison cell of Bahá'u'lláh – where Bahá'u'lláh was incarcerated.
The second holiest site in the Bahá'í Faith – which is also revered by the few remaining Azalis (post-Bahá'í/Bábi split followers of Bábism, who number just several thousand worldwide) – is the Shrine of the Báb, also at the BWC. The Báb's Shrine contains within its walls the temporary Shrine of `Abdu'l-Bahá.
The BWC also contains the Monument Gardens – wherein can be found the graves of some of Bahá'u'lláh's family – as well as a house in which `Abdu'l-Bahá lived, and the resting place of Rúhíyyih Khanum (August 8, 1910 – January 19, 2000; born Mary Sutherland Maxwell; the wife of Shoghi Effendi).
Bahá'u'lláh decreed pilgrimage in the Kitáb-i-Aqdas to two places: the House of Bahá'u'lláh in Baghdad, Iraq and the House of the Báb in Shiraz, Iran. While these major pilgrimages were later replaced (at least in terms of religious significance) by `Abdu'l-Bahá, many Bahá'ís still flocked to Bahá'u'lláh's home for pilgrimage until the house was confiscated by Muslim authorities hostile to the Bahá'í Faith in 1922. It has yet to be returned to the Bahá'í community. The House of the Báb was completely destroyed by Iranian Muslims during a state-sponsored persecution of Bahá'ís. A road and mosque were built over the house and a telephone pole now marks the spot where the Báb proclaimed his prophethood. The city of Baghdad also includes the Garden of Ridván, which shares the same name as – though is distinct from – the Garden of Ridván in Acre.
-

The city of Haifa from the Bahá'í gardens in late 2007.
-
.jpg)
A coastal area of Acre in 2005.
-

The grave of Amatu'l-Bahá Rúhíyyih Khanum at the BWC in 2005.
-

The House of `Abdu'lláh Páshá in Acre in 2004.
-

The twin graves of Ásíyih Khánum (Bahá'u'lláh's wife) and Mírzá Mihdí (his youngest son) in the Monument Gardens of the BWC, in 2004.
-

Part of the Garden of Ridván in Acre, in 2006.
-

The Garden of Ridván in Baghdad, Iraq, where Bahá'u'lláh declared his mission in April 1863.
Christianity
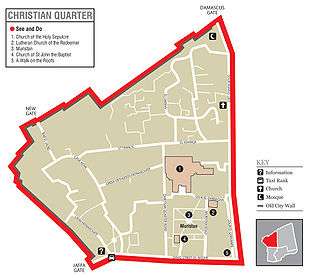
Located in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem, the Edicule, also known as the "Tomb of Christ") within the Church of the Holy Sepulchre is the most holy site for many mainstream denominations within Christianity. The area of the Church is regarded as the site, according to their understanding, where Jesus Christ suffered, was crucified, died, buried and resurrected from the dead along a temporal pathway known as the Via Dolorosa (from the Latin; lit. "way of sorrows"). The first eight Stations of the Cross can be followed along the route leading up to the Church, inside of which are the final five Stations.
The Greek Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, Roman Catholic Church, and Armenian Apostolic Church form the custodians of the Holy Sepulchre and collectively control the most holy pilgrimages within the church along with the Coptic, Syriac, and Ethiopian Orthodox churches who also hold some chapels. Within the walls of the church are the many traditional locations for the events associated with the Passion and death of Jesus: The Stone of Unction (the anointing place of Christ's body), the Prison of Christ (where Jesus was held, incarcerated, before his Passion), a treasure room which holds relics including fragments of the True Cross, and of course Calvary or Golgotha (where Christ was crucified) and the Sepulchre itself – to name a few.

Many Protestant and nontrinitarian denominations regard the nearby Garden Tomb to be the actual crucifixion and resurrection site of Jesus. Still others have claimed that Jesus's tomb is in Japan, or is really located outside of East Jerusalem. Some individuals in the Ahmadiyya Muslim community regard Roza Bal in Srinagar, India, to be Jesus's authentic grave.
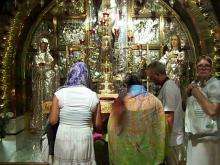
Other holy sites and shrines of pilgrimage exist in the Holy Land. In Jerusalem the Garden of Gethsemane, the Mount Zion Cenacle of the Last Supper and the Mount of Olives, as well as the Church of the Ascension prove spiritually important. Outside Jerusalem are pilgrimage places including the Sea of Galilee, as well as locations in Bethlehem, Nazareth, and Capernaum:
| Al-Maghtas | |
|---|---|
| Name as inscribed on the World Heritage List | |
|
Al-Maghtas ruins on the Jordanian side of the Jordan River are the location for the Baptism of Jesus and the ministry of John the Baptist. | |
| Location |
Balqa Governorate Jordan |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | iii, vi |
| Reference | 1446 |
| UNESCO region | Arab States |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 2015 (39th Session) |
- Bethlehem: The location of the Church of the Nativity in Manger Square, where Jesus was born.
- Capernaum: The town, bordering the Sea of Galilee, is cited in the Gospel of Luke where it was reported to have been the home of the apostles Simon Peter, Andrew, James and John, as well as the tax collector Matthew. In the Gospel of Matthew the town was reported to have been the home of Jesus. According to Luke [Luke 4:31–44], Jesus taught in the synagogue in Capernaum on Sabbath. Jesus then healed a man who had the spirit of an unclean devil and healed a fever in Simon Peter's mother-in-law. According to Luke [Luke 7:1–10], it is also the place where a Roman Centurion asked Jesus to heal his servant. Capernaum is also mentioned in the Gospel of Mark [Mark 2:1], in which it is the location of the famous healing of the paralytic lowered through the roof to reach Jesus. According to several Gospels, Jesus selected this town as the center of his public ministry in the Galilee after he left the small mountainous hamlet of Nazareth [Matthew 4:12–17]. Capernaum has no obvious advantages over any other city in the area, so he probably chose it because it was the home of his first disciples, Simon (Peter) and Andrew.
- Nazareth: The location of the Church of the Annunciation (in the Catholic tradition marks the site where the Archangel Gabriel announced the future birth of Jesus to the Virgin Mary [Luke 1:26–31]), St. Gabriel's Church (an Orthodox alternative site for the Annunciation), the Synagogue Church (The Melkite Greek Catholic Church lays claim to this site, which is traditionally that of the synagogue where Jesus preached [Luke 4]), the Church of St. Joseph's Carpentry (occupies the traditional location for the workshop of Saint Joseph); the Mensa Christi Church (run by the Franciscan religious order, commemorates the traditional location where Jesus dined with the Apostles after his Resurrection), the Basilica of Jesus the Adolescent (run by the Salesian religious order, occupies a hill overlooking the city), the Church of Christ (an Anglican church in Nazareth), and the Church of Our Lady of the Fright (marking the spot where Mary saw Jesus being taken to a cliff by the congregation of the synagogue and felt fear on his account). The "Jesus Trail" pilgrimage route connects many of the religious sites in Nazareth on a 60 km walking trail which ends in Capernaum.
Other important locations identified with the life of Jesus include areas around the Sea of Galilee – for instance Cana and the Church of the Multiplication in Tabgha – as well as the Mount of Temptation (in the Judean desert), Mount Tabor, Jacob's Well, Bethany and Bethabara (on the Jordan River). The town of Tzippori is where the Virgin Mary spent her childhood.
Still other revered places may exist within or outside the Holy Land, involving localities associated with the lives of the Twelve Apostles, the Church Fathers, the relatives and ancestors of Jesus, saints, or other figures or events featured in both the Old Testament (sharing religious significance with Judaism or other Abrahamic faiths) and New Testament. The reverence held for these sites may vary depending on denomination.
-

The slab marking the place where Jesus was laid to rest and resurrected in the Tomb or Edicule of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in 2008.
-

The interior of the Garden Tomb, marking the place where many Protestants and other Christians believe Jesus was laid to rest and resurrected, in 2008.
-

The Stone of Unction – the traditional site of the anointing of Jesus's body after the crucifixion – in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in 2007.
-

The Prison of Christ in 2007. This prison is where it is believed Jesus was held, incarcerated, before his Passion, and is now located in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
-

The Garden of Gethsemane in Jerusalem in 2006, with the Russian Orthodox Church of Maria Magdalene in the background. According to Biblical texts, Jesus and his disciples are said to have prayed here the night before his crucifixion.
-

The Chapel of the Ascension in 2008, on the Mount of Olives in Jerusalem. The Mount of Olives is where Jesus is alleged to have preached the Sermon on the Mount and the chapel the place from which he ascended to Heaven.
-

The Silver Star marking the birthplace of Jesus in the Church of the Nativity in Manger Square, Bethlehem, in 2007.
-

A lithograph of fisherman on the Sea of Galilee in the late 19th century. The Lake and various sites bordering it (such as Cana, Capernaum and Tabgha) are where Jesus's ministry flourished and where he is supposed to have performed miracles.
-

A 2008 postcard image of the Mount of Temptation (or Mount Quarantania) near Jericho in the Judean desert, where Christ was tempted by Satan.
-
The Church of St. Photina near Jacob's Well, a New Testament landmark, in 2008. It is here that Jesus met a Samaritan woman and preached to her.
-

Mount Tabor in Lower Galilee, the site of the Transfiguration of Jesus, in 2010.
-

The Cenacle of Mount Zion in Jerusalem, the site of the Last Supper and Pentecost, in 2008.
-

Qasr el Yahud, one of the locations where Jesus was alleged to have been baptized by John the Baptist in the Jordan River, in 2007. Other locations associated with Jesus's baptism include Bethabara (or Ænon) and Al Maghtas. All are near to each other along the Jordan.
-
An 1859 Palestinian sketch of the site of Tzippori, where the Virgin Mary is said to have spent her childhood.
-
The Church of the Multiplication in Tabgha in 2008. The church is allegedly built upon the site where Christ fed the multitude.
Eastern Christianity
Orthodox or Eastern Christians, like many other Christians, regard the Sepulchre in Jerusalem to be the holiest of places. They place emphasis on Nazareth, Bethlehem, Capernaum and other parts of the Holy Land as sacred since apostolic times, and note as places of special sanctity the sanctuaries built on the tombs of the apostles and other saints. There are many shrines with the relics of Christian saints and martyrs which are sacred pilgrimage sites for Orthodox Christians as well.
Historically, four of the five major episcopal sees of the Roman Empire (the Pentarchy) represent the modern patriarchal centers of the majority of Orthodox churches. These are, namely, Alexandria, Antioch, Constantinople and Jerusalem – excluding Rome.
Among the Orthodox, there are many monasteries and convents which are held in high honor and sacred veneration.
Eastern Orthodox Church

If the Patriarch of Constantinople is taken to be one of the most prominent leaders in the Eastern Orthodox Communion, then the Church of St. George in Istanbul (Greek: Καθεδρικός ναός του Αγίου Γεωργίου Kathedrikós Naós tou Agíou Geōrgíou; Turkish: Aya Yorgi) – the seat of the Ecumenical Patriarch – may perhaps be one of the most important religious sites for Eastern Orthodox Christians.
Also of particular importance to the Eastern Orthodox Church and particularly the Greek Orthodox Church is the peninsular Mount Athos (Greek: Όρος Άθως, Oros Athos; /ˈæθɒs/, Greek pronunciation: [ˈaθos]), where the most masses in the world are celebrated daily in the Byzantine Rite. Mount Athos arguably comprises the largest community of Christian monastics, ascetics, and mystics (specifically hesychasts) in the world. It is home to twenty Eastern Orthodox monasteries under the direct jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarch.
Oriental Orthodox churches


Oriental Orthodoxy is the faith of those Eastern Christian churches that recognize only three ecumenical councils – the First Council of Nicaea, the First Council of Constantinople and the First Council of Ephesus. They rejected the dogmatic definitions of the Council of Chalcedon (c. 451). Hence, these Oriental Orthodox Churches are also called Old Oriental Churches, Miaphysite Churches, or the Non-Chalcedonian Churches, known to Western Christianity and much of Eastern Orthodoxy as Monophysite Churches.[10] These churches are generally not in communion with any of the multifarious Eastern Orthodox Churches but they are in dialogue for a return to unity.[11]
Despite the potentially confusing nomenclature (Oriental meaning Eastern), Oriental Orthodox churches are distinct from those that are collectively referred to as the Eastern Orthodox Church. The Oriental Orthodox communion comprises five basic groups: Coptic Orthodox, Ethiopian Orthodox, Eritrean Orthodox, Syriac Orthodox, and Armenian Apostolic churches.[12] These churches, while being in communion with one another, are hierarchically independent.[13]
The Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church or Indian Orthodox church is technically autonomous, but still shares some ties with the Syriac Orthodox church.
This being the case, each of the six communal churches has their own spiritual headquarters which act as the episcopal sees of their respective Popes or Patriarchs:
- Armenian Apostolic — Etchmiadzin Cathedral (Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin), Vagharshapat, Armenia
- Coptic Orthodox — St. Mark's Coptic Orthodox Cathedral in Abbassia in Cairo, Egypt (formerly St. Mark's Coptic Orthodox Cathedral in Alexandria, Egypt)
- Eritrean Orthodox — Asmara, Eritrea
- Ethiopian Orthodox — Holy Trinity Cathedral, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia (see also Rastafari movement)
- Indian Orthodox — Kottayam, India
- Syriac Orthodox (includes the Malankara Church and other Saint Thomas Christians) — Bab Tuma borough, Damascus, Syria (formerly Antioch; temporarily stationed in Homs, Mardin, et al.)
- The Syriac Patriarch himself resides in Dayro d-Mor Ephrem, a monastery near Damascus
-

The interior of St. Mark's Coptic Orthodox Cathedral in Cairo, Egypt, in 2008.
-

The interior of St. Mark's Coptic Orthodox Cathedral in Alexandria, Egypt, in 2006.
Latter-day Saints


Latter-day Saints regard with reverence such places as the Garden Tomb and the Garden of Gethsemane in Jerusalem, due their connections with the life and ministry of Jesus. Additionally, the most holy place for members of the mainstream LDS Church are the numerous temples around the world, particularly the "celestial room" located inside each temple. The purpose of these ordinance rooms is to act as a symbolic representation of the presence of God himself. Additionally, a room inside the Salt Lake Temple, designated as the Holy of Holies, is considered highly sacred due its primary function as a private meditation room for the church's president.
Mormon homes are also treated as sacred areas due the church's emphasis on the sacredness of family union and family-based ceremonies performed in LDS temples. On this subject, the Bible Dictionary in the LDS edition of the Bible states:
A temple is literally a house of the Lord, a holy sanctuary in which sacred ceremonies and ordinances of the gospel are performed by and for the living and also in behalf of the dead. A place where the Lord may come, it is the most holy of any place of worship on the earth. Only the home can compare with the temple in sacredness. ().
Once a Mormon family starts dwelling in a home, a special prayer is given by the head of the family (or a close member of the church) asking for the residence to be a shelter against temptation, and dedicating the place to God as long as the family inhabits it.
Other venerated sites for Latter-day Saints include historical locations throughout the United States, due to their particular connection to Mormon history and theology. However, no mandatory peregrinations nor worship ceremonies are performed in such places. Examples include the Sacred Grove (Palmyra, New York), the Kirtland Temple (Kirtland, Ohio) and Adam-ondi-Ahman (Daviess County, Missouri).
Other LDS movement sects
Mormon breakaway sects, sub-sects and fundamentalist groups sometimes hold the belief that their particular church alone can claim true authority and succession from Joseph Smith, and that other LDS denominations are therefore incorrect or heretical. Thus many sites throughout the United States represent the spiritual headquarters' of these churches: For example, the YFZ Ranch in Eldorado, Texas at one time represented the Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (FLDS) and the Apostolic United Brethren (AUB) base themselves in Bluffdale, Utah.
-
The Hill Cumorah Angel Moroni statue in 2005.
-

Adam-ondi-Ahman in Daviess County, Missouri in 2011.
-
.jpg)
The Sacred Grove, where Joseph Smith experienced his first theophany, in 1907.
-

The Kirtland Temple in 2005.
-
The Joseph Smith Birthplace Memorial in 2009.
-

The main temple of the YFZ Ranch – FLDS Church in Eldorado, Texas, in 2006.
Rastafari movement
Ethiopia is of considerable importance as the setting of the life and death of Haile Selassie. Many Rastas consider Ethiopia the Promised Land. The city of Shashamane is particularly significant. In the capital of Addis Ababa Haile Selassie is buried in the Holy Trinity Cathedral (often called Kidist Selassie, from the Amharic), which is also a significant religious site for Ethiopian Orthodox Christians (see also Oriental Orthodox churches), as it doubles as the seat of the primate of their church.
Catholic Church

Catholics, like many other Christians, regards the Sepulchre in Jerusalem to be the holiest of places. It also places emphasis on Nazareth, Bethlehem, Capernaum, and other parts of the Holy Land as sacred since apostolic times, and notes as places of special sanctity the sanctuaries built on the tombs of the Apostles.
Mainstream Catholicism as a whole is represented by the Holy See (Latin: Sancta Sedes, "holy chair") of the Vatican City state (![]() i/ˈvætᵻkən ˈsɪti/;[14] Italian: Stato della Città del Vaticano (pronounced [ˈstaːto della t͡ʃitˈta del vatiˈkaːno])[15]), a walled enclave within Rome, Italy. Inside the Vatican the largest church in history, St. Peter's Basilica (L.: Basilica Sancti Petri), is the location of the Papal office and the living quarters of the Pope (in the Apostolic Palace), as well as Vatican Hill – atop which are Saint Peter's tomb and place of crucifixion, his throne, and his baldachin. Outside St. Peter's Square are many more churches throughout the Vatican and outlying Rome. One important landmark is the Sistine Chapel (L.: Sacellum Sixtinum; I.: Cappella Sistina), in which the Papal conclave takes place.
i/ˈvætᵻkən ˈsɪti/;[14] Italian: Stato della Città del Vaticano (pronounced [ˈstaːto della t͡ʃitˈta del vatiˈkaːno])[15]), a walled enclave within Rome, Italy. Inside the Vatican the largest church in history, St. Peter's Basilica (L.: Basilica Sancti Petri), is the location of the Papal office and the living quarters of the Pope (in the Apostolic Palace), as well as Vatican Hill – atop which are Saint Peter's tomb and place of crucifixion, his throne, and his baldachin. Outside St. Peter's Square are many more churches throughout the Vatican and outlying Rome. One important landmark is the Sistine Chapel (L.: Sacellum Sixtinum; I.: Cappella Sistina), in which the Papal conclave takes place.
Rome is the place from which Catholics believe the one, holy, catholic and apostolic church were formally founded and begun by St. Peter (whom they consider to be the "Prince of the Apostles") as the appointed successor and first vicar of Christ. Thus while the Holy Sepulchre is still the most sanctified of places for Catholics, the Vatican is an extremely sacred place to the faithful (those of the Latin Church, as well as the Churches sui iuris) as the seat of their supreme authority on Earth. Important papal territories include the four major basilicas (L.: Basilica maior, pl. -es; excluding St. Peter's) – namely the Archbasilica of St. John Lateran (the ecumenical Catholic mother church), St. Peter's Basilica, the Basilica of St. Paul Outside the Walls (containing the tomb of Paul the Apostle), and the Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore.
Other locations of reverence for ardent Catholics include Marian shrines, particularly the localities of Fátima and Lourdes, where miracles or apparitions attributed to the Virgin Mary took place.
-

St. Peter's baldachin in 2005. Beneath is the high altar, built atop St. Peter's tomb.
-

The Cathedra Petri, or throne of St. Peter, in 2005.
-
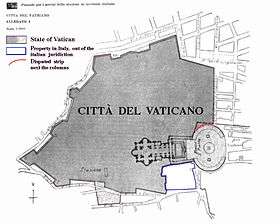
A map of the territory of the Vatican City state (in dark grey) according to the Lateran Treaty.
-
The interior of the Sistine Chapel in 2010.
-

The Sanctuary of Our Lady of Fátima in Fátima, Portugal in 2006.
-

The Our Lady of Lourdes Basilica in Lourdes, France in 2004.
-

The Basilica of St. John Lateran in 2007.
-
The façade of the Basilica of St. Paul Outside the Walls in 2007.
-

The Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore in 2006.
Islam
The Kaaba, a cuboid structure located within the Masjid al-Ḥarām (Sacred Mosque) in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, according to Islamic tradition was rebuilt by Ibrahim (Abraham) and his son Ismail (Ishmael), and is one of the holiest places in Islam. During his life the Prophet Muhammad laid the Black Stone in one of the corners of the building. Many millions of Muslims visit Mecca and the surrounding areas each year during a pilgrimage known as the Hajj – the fifth and final pillar of Islam – during which they circumambulate the Kaaba as part of the ritual.
Other significant areas within or surrounding Mecca include areas in which the Hajj takes place, including the Well of Zamzam, Mina and its bridge, Muzdalifah and Mount Arafat.
The second holiest place for Muslims is the Masjid al-Nabawi in Medina, which is where the Prophet Muhammad is buried under the Green Dome. Caliphs Umar and Abu Bakr are also said to be buried in the Masjid al-Nabawi. The Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem is a sacred place in Sunni traditions as the site from which Muhammad ascended to heaven in the Isra and Mi'raj and was also the first qibla. Mount Sinai also holds significance in Islam.[16] Among Shias, the Imam Ali Mosque and Imam Husayn Shrine also hold high significance.
.jpg)
Other sites in the Arabian Hejaz are associated with Muhammad: near Mecca, on the mountain of Jabal al-Nour the cave Hira is the place of the Prophet's first revelation. Many other former places of devotion that are historically associated with Muhammad were destroyed under the alleged anti-idolatrous policies of the Wahhabi Saudi government.

-

The Plain of Mount Arafat during the Hajj.
-
Pilgrims at the Well of Zamzam.
-

The Stoning of the Devil at Jamaraat Bridge.
-
Masjid al-Nabawi. Muhammad's tomb is located beneath the Green Dome.
-
Muhammad's tomb.
-

The Dome of the Rock (center) and the Al-Aqsa Mosque (surrounding) in Jerusalem.
Druzism

Druzism is a highly distinguished sect of Ismāʿīli Shi'a Islam, practiced by the Druze community. Most Druze consider themselves Muslims, however most non-Druze Muslims (most Sunnis and many Shi'as) do not regard the Druze as practicing Islam – and may even condemn their beliefs as shirk (polytheism).
The Nabi Shu'ayb, or Tomb of Jethro, near Tiberias in Israel is the most important religious site for the Druze. They have held religious festivals there for centuries and it has been a place of annual pilgrimage.
Judaism

The Kodesh Hakodashim, Judaism's Holy of Holies, was the inner sanctuary of the Tabernacle in the time of Moses as described in the Torah; the term now refers to the space on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem where this sanctuary was located in the Temple in Jerusalem. (This location is often, but controversially, identified as being inaccessible within the footprint of the Islamic Dome of the Rock.) Historically, it could be entered by the High Priest only on Yom Kippur. Orthodox Judaism and Conservative Judaism continue to regard the location as retaining some or all of its sanctity despite the destruction of the Temple in 70 CE. Entry into sanctified areas has been prohibited in recent times by powerful elements within traditional Judaism, and as a result many religious authorities prohibit or restrict entry into the Temple Mount by observant Jews.
Today, Jews recognize the Jewish Quarter of the city, wherein the Mount is located, to be a location of profound spiritual importance. Within the area a stone artifact known as the Western Wall is paramount as the last standing remains of the temple. Along the wall notable featured include the Western Stone and Wilson's Arch. Beneath it a tunnel runs closer toward what was the original Kodesh Hakodashim, ending approximately 150 ft. inward at a place called Warren's Gate. In an alley the Muslim Quarter of the city is a semi-concelead section of the Wall called the Little Western Wall.
The Cave of the Patriarchs in Hebron is the second holiest site in Judaism. Other significant sites include a number of temples within the Jewish quarter of Old Jerusalem, namely the Hurva, Belz, Tiferet Yisrael and the Four Sephardic synagogues. The Beit El Synagogue is of special importance to students of Kaballah. The Biblical Mount Sinai is believed to be the place where Moses received the Ten Commandments from God – although there is considerable debate as to the location of the mountain. (Scholarly opinion places it at either the mountain historically known as "Sinai" or Mount Seir.)
Samaritanism

Samaritanism is an Abrahamic or Semitic religion closely related to – or by some considered an early derivative of – Judaism, practiced by the Samaritan (Hebrew: שומרונים Shomronim, Arabic: السامريون as-Sāmariyyūn) ethnoreligious group, who mostly reside in the region of the Levant and claim ancestry to Israelites with connections to the ancient Eastern Mediterranean kingdom of Samaria. The Samaritan ethnoreligious group and the subsequent Samaritan religion are considered to be, demographically, the smallest of their kind in modern times, with the number of Samaritans worldwide totalling at just 712 as of late 2007.
Adherents of Samaritanism consider a formation known as the Holy Rock, atop the summit of Mount Gerizim (Samaritan Hebrew: Ar-garízim, Arabic: جبل جرزيم Jabal Jarizīm, T.H.: הַר גְּרִזִּים Har Gərizzîm, S.H.: הַר גְּרִיזִּים Har Gərizzim; also romanized as Jirziem), to be their "holy of holies". This is comparable with the Temple Mount of Jerusalem as idealized and revered by mainstream Jews – however Gerizim is located near the Samaritan village of Kiryat Luza (الطيبه), adjacent to the Palestinian city of Nablus (present-day Biblical Shechem), in the West Bank.
Indian religions
Buddhism
Lumbinī is a Buddhist pilgrimage site in the Rupandehi District of Nepal. It is the place where, according to Buddhist tradition, Queen Mayadevi gave birth to Siddhartha Gautama in 563 BCE. Gautama, who achieved Enlightenment some time around 528 BCE, became the Gautama Buddha and founded Buddhism. Lumbini is one of many magnets for pilgrimage that sprang up in places pivotal to the life of Gautama Buddha.

Bodhgaya, in the state of Bihar in India, is considered by many adherents of Buddhism to be their most holy site. Gautama Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment while sitting under a peepal tree, called the Bodhi tree, located in Bodhgaya. At this site of his purported enlightenment the Mahabodhi temple now stands. Every year, many Buddhists make pilgrimages from all over the world to visit and meditate at the temple.
Shugendō

Shugendō is a small, syncretic, highly esoteric and ascetic sect or sub-sect of Buddhism (mostly related to, and often considered a distinct branch of the Tendai and Shingon schools) combining elements of Zen, Taoism, Koshintō, Japanese folk animism and shamanism. The faith is traditionally believed to have been founded by the śramaṇa and mystic-sorcerer En no Gyōja in the 7th or 8th century. In the same manner as the religion of Shintō, Shugendō is largely relegated to Japan.
The lay practitioners and monks of Shugendō, called Shugenja or yamabushi respectively, venerate mountains as both spiritual areas and, along with nature as a whole, "natural maṇḍalas" .
Adherents of Shugendō consider the collective Three Mountains of Dewa (consisting of Mount Haguro, Mount Gassan, and Mount Yudono), located in the remote Dewa Province of Japan, to be their most sacred of places. The three mountains are also sacred in Shintō.
Hinduism


The Indian cities of Allahabad, Varanasi, Ayodhya, Mathura, Haridwar, Kanchipuram, Ujjain and Dwarka are said to be the major Pilgrim cities in Hinduism; as stated in the Vedas. Of these Varanasi; Uttar Pradesh is considered the Holiest ancient site and it is considered by many to be the most sacred place of pilgrimage for Hindus irrespective of denomination.
Shaivas in South India, especially Tamil Nadu, consider Chidambaram as the heart of the world and temple of temples. Although all temples are referred to as kovil, the holy city of Chidambaram is the true kovil. All recitations of the Thirumurai (12 holy scriptures of Shaivism) begin and end with the phrase "Thirucchittrambalam" (the auspicious holy of holies: chidambaram). Vaishnavites on the other hand consider Sri Rangam as the holiest city and refer to it as the earthly Vaikunta.
The "garbha griha" (literally womb-house or womb-chamber), the shrine inside a temple complex where the main deity is installed in an area that is in a separate building by itself inside the complex, is the most sacred site within the temple complex.
The garbha griha usually contains the murti (idol or icon), the primary focus of prayer. In temples with a spire or vimana, this chamber is placed directly underneath it, and the two them form a main vertical axis of the temple. These together may be understood to represent the axis of the world through Mount Meru. The garbha griha is usually also on the main horizontal axis of the temple which generally is an east-west axis. In those temples where there is also a cross-axis, the garbha griha is generally at their intersection. Tirumala Venkateswara Temple is a Hindu temple in the hill town of Tirumala, near Tirupati in the Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh. It is around 600 km (370 mi) from Hyderabad, 138 km (86 mi) from Chennai and 291 km (181 mi) from Bangalore.
The Tirumala Hill is 853m above sea level and is about 10.33 square miles (27 km2) in area. It comprises seven peaks, representing the seven heads of Adisesha, thus earning the name Seshachalam. The seven peaks are called Seshadri, Neeladri, Garudadri, Anjanadri, Vrushabhadri, Narayanadri, and Venkatadri. The temple is on Venkatadri (also known as Venkatachala or Venkata Hill), the seventh peak, and is also known as the "Temple of Seven Hills". The presiding deity of the temple is Lord Venkateswara, a form of the Hindu god Vishnu. Venkateswara is known by other names: Balaji, Govinda, and Srinivasa. The temple lies on the southern banks of Sri Swami Pushkarini, a holy water tank. The temple complex comprises a traditional temple building, with a number of modern queue and pilgrim lodging sites.
The temple is the richest pilgrimage center, after the Padmanabhaswamy Temple in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, of any faith (at more than INR 50,000 crore) and the most-visited place of worship in the world. The temple is visited by about 50,000 to 100,000 pilgrims daily (30 to 40 million people annually on average), while on special occasions and festivals, like the annual Brahmotsavam, the number of pilgrims shoots up to 500,000, making it the most-visited holy place in the world.
There are yearly pilgrimage gatherings such as Kumbh Mela Pilgrimage(3 year or 12),[17][18] Shabarimala Pilgrimage,[19][20] Kottiyoor Vysakha Pilgrimage[21] where in thousands of people gather in a certain period of a year for pilfrimage.
Jainism

The Palitana temples on Mount Shatrunjaya, located by the city of Palitana, in Bhavnagar district, Gujarat, India are considered one of the holiest places for Jains. Jains believes that a visit to this group of temples is essential once in a life time to achieve nirvana or salvation, much like the Hajj for Muslims.
Shikharji or Śrī Sammed Śikharjī (श्री सम्मेद शिखरजी), also known as the Parasnath Hill, located in Giridih district in Jharkhand, India, is a major Jain pilgrimage destination and is one of the most sacred place for Jains in the world. According to Jain belief, twenty of the twenty-four Tirthankaras (teachers of the Jains) attained Moksha (Nirvana) from this place. Parasnath Hill, with a height of 1,350 metres (4,430 ft)), is the highest mountain in the state of Jharkhand. The number of Tirthankars who attained nirvana at Shri Sammet Shikharji is 20. For each of them there is a shrine on the hill.
The hill is also known as Parasnath, a name derived from Parshva, the 23rd Tirthankara who attained Nirvana there. The present temple is not very old, although the idol in the main temple is ancient. The Sanskrit inscriptions at the foot of the images indicate that they were installed in the temple in 1678 AD.
Archaeologists believe some of the existing temple edifices on Parasnath Hill date from 1765 AD although the place is of greater antiquity. It is certain that the present edifices replace older edifices, which were demolished. Jain temples are often pulled down and re-built.
Sikhism
.jpg)
Harmandir Sahib, or Darbar Sahib (also known as the Golden Temple), is culturally the most important shrine in Sikhism, considered the spiritual and cultural centre of Sikhs. Located in Amritsar, Punjab, India. It is one of the oldest Sikh gurdwaras. It is located in the city of Amritsar, India, which was established by Guru Ram Das, the fourth guru of the Sikhs and the city was also built around the shrine, known as "Guru Di Nagri" meaning city of the Sikh Guru. It is made from white marble to keep the ground cool and pleasant. It was later laid with real Gold which was provided by the emperor of Sikh Empire, Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
Another significant place is the village of Nankana Sahib in Pakistan,the birthplace of Guru Nanak, founder of Sikhism. Each of Nankana Sahib's gurdwaras are associated with different events in Guru Nanak Dev's life. The town remains an important site of pilgrimage for Sikhs worldwide. Punjab province of Pakistan is also the location of many important religious and historical sites for Sikhs, including the place of martyrdom of fifth Sikh Guru, Guru Arjan Dev. Many other important Sikh Shrines are located in the Punjab state of India as well as other parts in India.
East Asian religions
Confucianism

Confucianism is often regarded as either a religion, philosophy or quasi-religious system of beliefs based upon the teachings of the ancient Chinese sage Confucius. Confucius's philosophy stresses a firm sense of ethical and political order and how to achieve these ends in order to benefit society.
While Confucianism is no longer as organized of an ideology as it once was, it still continues as a quasi-religious tradition and temples of Confucius exist throughout China. The most important is the Temple of Confucius in Confucius's hometown of Qufu.
Shinto
Ise Shrine is the formal home of Amaterasu ōmikami, the primary deity of Shinto and traditionally believed to be a direct ancestor of the Japanese Imperial Family. It is located in the city of Ise in Mie prefecture, Japan. Access is strictly limited, with the public allowed to see merely the thatched roofs of the central structures, hidden behind three tall wooden fences. The Ise Shrine is purportedly the home of the Sacred Mirror.
Taoism
Four sacred mountains of Taoism:
Wudang Mountains, in Shiyan, Hubei Province of China;
Mount Qingcheng, in Dujiangyan, Sichuan Province;
Mount Longhu, in Yingtan, Jiangxi Province;
Mount Qiyun, in Huangshan, Anhui Province.
Neopaganism

Neodruids
Stonehenge is a site of religious significance in Neo-Druidism as Druids perform pilgrimage there. The first modern Druids to perform ceremonies at this site were the Ancient Order of Druids.
Zoroastrianism
Udvada is a town in Gujarat, renowned for its Zoroastrian Atash Behram. This place of worship is the oldest still-functioning example of its kind, and has established Udvada as a pilgrimage center for Zoroastrians the world over.
See also
- Burial places of founders of world religions
- Holy places
- Honden
- List of founders of religious traditions
- List of religions
- List of religious texts
- List of sacred languages
- List of shrines
- Pilgrimage
- Place of worship
- Religious symbolism
- Sacred architecture
- Sacred travel
References
- ↑ "Philosophy of Religion". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2010. Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ↑ Massignon 1949, pp. 20–23
- ↑ Smith 1998, p. 276
- ↑ Derrida 2002, p. 3
- ↑ Joseph J. Hobbs, Mount Sinai (University of Texas Press) 1995, discusses Mount Sinai as geography, history, ethnology and religion.
- ↑ "Tafsir Ibn Kathir". Tafsir.com. 2002-10-26. Retrieved 2011-03-21.
- ↑ In English /bəˈhaɪ/ with two syllables, in Persian Persian: بهائی [bæhɒːʔiː] with three syllables. The exact realization of the English pronunciation varies. The Oxford English Dictionary has /bæˈhɑːiː/ ba-HAH-ee, Merriam-Webster has /bɑːˈhɑːiː/ bah-HAH-ee, and the Random House Dictionary has /bəˈhɑːiː/ bə-HAH-ee. See Banani, Amin. "A Baha'i Glossary and Pronunciation Guide" (MP3). Bahá’i Study and Shahrokh, Darius. "Complete List and Downloads of Windows to the Past Programs". Bahá'i Library. Windows to the Past – A Guide to Pronunciation part 1 and 2, for more pronunciation instructions
- ↑ Bahá'ís prefer the orthographies "Bahá'í", "Bahá'ís", "the Báb", "Bahá'u'lláh", and "`Abdu'l-Bahá", using a particular transcription of the Arabic and Persian in publications. "Bahai", "Bahais", "Baha'i", "the Bab", "Bahaullah" and "Baha'u'llah" are often used when diacriticals are unavailable.
- ↑ Houghton 2004
- ↑ Davis, SJ, Leo Donald (1990). The First Seven Ecumenical Councils (325-787): Their History and Theology (Theology and Life Series 21). Collegeville, MN: Michael Glazier/Liturgical Press. p. 342. ISBN 978-0814656167.
- ↑ Syrian Orthodox Resources – Middle Eastern Oriental Orthodox Common Declaration
- ↑ Oriental Orthodox Churches
- ↑ An Introduction to the Oriental Orthodox Churches
- ↑ "Homepage of Vatican City State". Vaticanstate.va. Retrieved 15 October 2010.
- ↑ "Stato della Città del Vaticano" is the name used in the state's founding document, the Treaty between the Holy See and Italy, article 26.
- ↑ Mount Sinai (Mount Moses) in the Sinai of Egypt
- ↑ Enormous crowd at Kumbh Mela - ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)
- ↑ Kumbh Mela (Hindu festival) - Encyclopedia Britannica
- ↑ "Sabarimala pilgrimage - News Stories, Latest News Headlines on Times of India". The Times Of India.
- ↑ "Sabarimala sees heavy rush". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 18 August 2013.
- ↑ "Thousands throng Kottiyur temple". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 7 June 2005.
External links
- Bible study from basicsteps.org
- The Purpose of Temples: The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
- Endangered Sacred Sites
- History of the Holy Sepulchre
- Holy Sepulchre
- Top religious sites

.svg.png)

