1976 Republican National Convention
1976 presidential election | |
|
Nominees Ford and Dole | |
| Convention | |
|---|---|
| Date(s) | August 16–19, 1976 |
| City | Kansas City, Missouri |
| Venue | Kemper Arena |
| Candidates | |
| Presidential nominee | Gerald Ford of Michigan |
| Vice Presidential nominee | Bob Dole of Kansas |

The 1976 Republican National Convention was a United States political convention of the Republican Party that met from August 16 to August 19, 1976, to select the party's nominee for President. Held in Kemper Arena in Kansas City, Missouri, the convention nominated President Gerald Ford for a full term, but only after narrowly defeating a strong challenge from former California Governor Ronald Reagan. The convention also nominated Senator Robert J. Dole of Kansas for Vice President, instead of Vice President Nelson Rockefeller. The keynote address was delivered by Tennessee Senator Howard Baker. It is the last national convention by either of the two major parties to feature a seriously contested nomination between candidates.
History
The 1976 Republican National Convention was the last major party convention, as of 2016, where the party's nominee was not decided before the primary process concluded.

Situation at the opening of the convention
Going into the convention, Ford had won more primary delegates than Reagan, as well as a plurality in popular vote. However, Ford did not have enough to secure the nomination, and as the convention opened both candidates were seen as having a chance to win. Because of this, both Ford and Reagan arrived in Kansas City before the convention opened to woo the remaining uncommitted delegates in an effort to secure the nomination. Reagan benefited from his highly committed delegates, notably "Reagan's Raiders" of the Texas delegation. They and other conservative Western and Southern delegates particularly faulted the Ford Administration's foreign policy of détente towards the Soviet Union, criticizing his signing of the Helsinki Accords and indirectly blaming him for the April 1975 Fall of Saigon. The pro-Reagan Texas delegates worked hard to persuade delegates from other states to support Reagan. Ford, meanwhile, used all of the perks and patronage of the Presidency to win over wavering delegates, including trips aboard Air Force One and personal meetings with the President himself.
Richard Schweiker gambit and the search for an alternative
Reagan had promised, if nominated, to name Senator Richard Schweiker of Pennsylvania as his running mate, in a bid to attract liberals and centrists in the party. This move backfired, however, as many conservatives (such as Senator Jesse Helms) were infuriated by Reagan's choice of the "liberal" Schweiker, while few moderate delegates switched to Reagan. Helms promptly began a movement to draft Conservative Senator James L. Buckley of New York as the presidential nominee.
Platform and rules votes
The key vote of the convention occurred when Reagan's managers proposed a rules change that would have required Ford to publicly announce his running mate before the presidential balloting. Reagan's managers hoped that when Ford announced his choice for vice-president, it would anger one of the two factions of the party and thus help Reagan. Ford's supporters derisively described the proposed rules change as the "misery loves company" amendment.[1] The proposed rules change was defeated by a vote of 1180 to 1069, and Ford gained the momentum he needed to win the nomination. The balloting for president was still close, however, as Ford won the nomination with 1187 votes to 1070 votes for Reagan (and one for Elliot L. Richardson of Massachusetts).
Conservatives succeeded in inserting several key planks into the party platform, some of which were implicitly critical of the President's own policies.[2] Reagan and North Carolina Senator Jesse Helms successfully had a "moral foreign policy" plank inserted. In light of the 1973 Roe v. Wade decision, the 1976 Republican platform became the first to advocate a Human Life Amendment to the Constitution.
Nominations
Both Ford and Reagan's names were put into nomination.

Balloting
With the outcome not a foregone conclusion, the balloting would be the most exciting it would be for the rest of the 20th century and into the 21st.
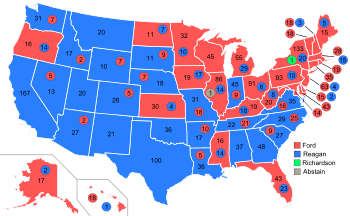
| Republican National Convention Presidential nominee vote, 1976[3] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Candidate | Votes | Percentage |
| President Gerald Ford | 1,187 | 52.57% |
| Ronald Reagan | 1,070 | 47.39% |
| Elliot Richardson | 1 | 0.04% |
| Totals | 2,258 | 100.00% |
Vice Presidential
While desperately trying to secure enough delegates to be nominated, the President's campaign did not neglect the selection of a running mate, especially with Reagan's Schweiker ploy. Among the many people considered were;
- Representative John B. Anderson of Illinois
- Senator Howard Baker of Tennessee
- Governor Kit Bond of Missouri
- Senator William Brock of Tennessee
- Senator Edward Brooke of Massachusetts
- Senator James Buckley of New York
- CIA Director George H.W. Bush of Texas
- Former Secretary of the Treasury John B. Connally of Texas
- Governor Daniel Evans of Washington
- Secretary of Housing and Urban Development Carla Anderson Hills of Wisconsin
- Governor James Holshouser of North Carolina
- Former Secretary of Defense Melvin Laird of Wisconsin
- Senator Charles Mathias of Maryland
- Senator Charles Percy of Illinois
- Governor Robert Ray of Iowa
- Former Governor Ronald Reagan of California
- Secretary of Commerce Elliot Richardson of Massachusetts
- Vice President Nelson A. Rockefeller of New York
- Former FBI Director William Ruckelshaus
- Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld of Illinois
- Former Secretary of the Treasury George Shultz of New York
- Secretary of Treasury William E. Simon of New Jersey
- Former Governor William W. Scranton of Pennsylvania
- Senator Lowell Weicker of Connecticut
Ford selected Kansas Senator Robert J. Dole as his running-mate in preference to Vice President Nelson Rockefeller; Rockefeller had announced that he did not wish to be a candidate for Vice President in 1976 the previous fall, in no small part because it was believed that Rockefeller was too far to the left to be acceptable to the G.O.P. base.
Some of the Reagan delegates, angry with the loss of their candidate, decided to scatter their votes among over 30 people. Jesse Helms' name was put into nomination.[4]
- Bob Dole – 1,921 (85.04%)
- Abstaining – 103 (4.56%)
- Jesse Helms – 103 (4.56%)
- Ronald Reagan – 27 (1.20%)
- Phil Crane – 23 (1.02%)
- John Grady – 19 (0.84%)
- Louis Frey – 9 (0.40%)
- Anne Armstrong – 6 (0.27%)
- Howard Baker – 6 (0.27%)
- James L. Buckley – 4 (0.18%)
- John B. Connally – 4 (0.18%)
- David C. Treen – 4 (0.18%)
- Alan Steelman – 3 (0.13%)
- Bob Bauman – 2 (0.09%)
- Bill Brock – 2 (0.09%)
- Paul Laxalt – 2 (0.09%)
- Elliot Richardson – 2 (0.09%)
- Richard Schweiker – 2 (0.09%)
- William E. Simon – 2 (0.09%)
- Jack Wellborn – 2 (0.09%)
- James Allen – 1 (0.04%)
- Ray Barnhardt – 1 (0.04%)
- George H. W. Bush – 1 (0.04%)
- Pete Domenici – 1 (0.04%)
- James B. Edwards – 1 (0.04%)
- Frank S. Glenn – 1 (0.04%)
- David Keene – 1 (0.04%)
- James McClure – 1 (0.04%)
- Nancy Palm – 1 (0.04%)
- Donald Rumsfeld – 1 (0.04%)
- John W. Sears – 1 (0.04%)
- Roger Staubach – 1 (0.04%)
- Steve Symms – 1 (0.04%)
Reagan's concession speech

Reagan gave an eloquent and stirring speech that overshadowed Ford's own acceptance address. Some delegates later stated that they left the convention wondering if they had voted for the wrong candidate.[5] A contemporary media account stated that if a motion to reconsider the nomination had been in order, it might have passed.[6]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1976 Republican National Convention. |
References
- ↑ "Instant Replay: How Ford won It", Time Magazine, Monday, Aug. 30, 1976, p 16
- ↑ World Almanac and Book of Facts, 1977
- ↑ "US President – R Convention Race – Aug 16, 1976". Our Campaigns. Retrieved 2015-08-25.
- ↑ "US Vice President – R Convention Race – Aug 16, 1976". Our Campaigns. Retrieved 2015-08-25.
- ↑ "Reagan's Impromptu Speech at 1976 GOP Convention". YouTube. 1980-07-17. Retrieved 2015-08-25.
- ↑ Dickenson, James R. (1976-08-21). "Hearts Are with Reagan". The Times-News. Hendersonville, N.C. Washington Star. p. 2. Retrieved 2015-07-06.
External links
- Republican Party platform of 1976 at The American Presidency Project
- Ford acceptance speech at The American Presidency Project
- NPR's "1976: Reagan Takes on a GOP Incumbent" page
- Gerald Ford Presidential Library's 1976 Republican Presidential Nomination Acceptance Speech
| Preceded by 1972 Miami Beach, Florida |
Republican National Conventions | Succeeded by 1980 Detroit, Michigan |



