Arles-sur-Tech
| Arles-sur-Tech Arles | |
|---|---|
|
Shops in Arles-sur-Tech, with the Tour Saint-Sauveur in the background | |
 Arles-sur-Tech | |
|
Location within Occitanie region 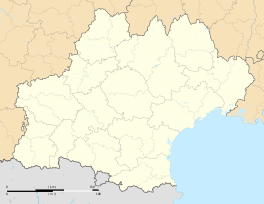 Arles-sur-Tech | |
| Coordinates: 42°27′27″N 2°38′04″E / 42.4575°N 2.6344°ECoordinates: 42°27′27″N 2°38′04″E / 42.4575°N 2.6344°E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Occitanie |
| Department | Pyrénées-Orientales |
| Arrondissement | Céret |
| Canton | Arles-sur-Tech |
| Intercommunality | Haut Vallespir |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2014–2020) | René Bantoure |
| Area1 | 28.82 km2 (11.13 sq mi) |
| Population (2012)2 | 2,671 |
| • Density | 93/km2 (240/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) |
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 66009 / 66150 |
| Elevation |
226–1,302 m (741–4,272 ft) (avg. 300 m or 980 ft) |
|
1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km² (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. 2 Population without double counting: residents of multiple communes (e.g., students and military personnel) only counted once. | |
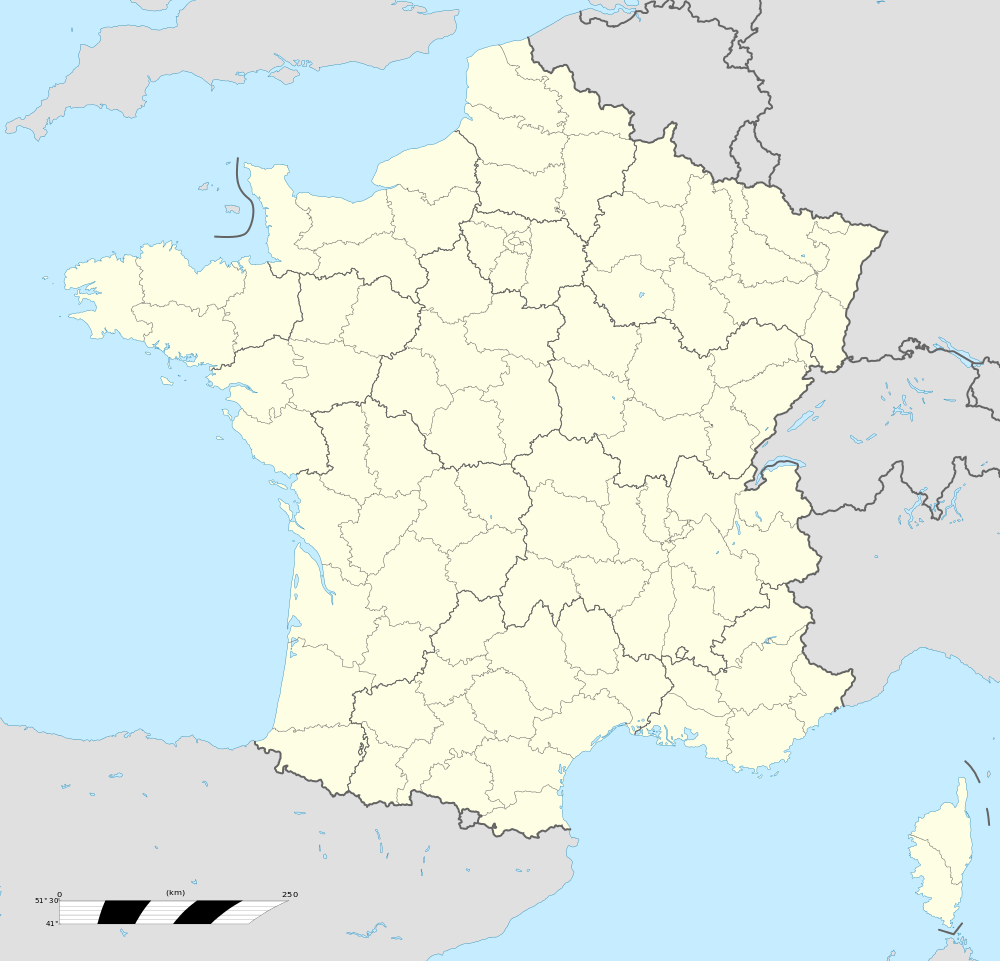
Arles-sur-Tech (Catalan: Arles de Tec) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France.
Geography
Localisation
Arles-sur-Tech is located in the canton of Arles-sur-Tech and in the arrondissement of Céret.
Arles-sur-Tech is situated in the southernmost valley in mainland France before Spain, the Vallespir, through which the 84 km (52 mi) long river "Tech" flows. This small town is surrounded by the eastern Pyrenees which dominate skyline around Arles-sur-Tech. The town sits on the only main road which passes through the valley, the D 115, making it accessible from Spain in the west and the plane of Roussillon and Perpignan in the east. It is located close to the larger and more well-known spa town of Amélie-les-Bains-Palalda.

Neighbouring communes
| Corsavy | Montbolo | ||
| Montferrer | |
Amélie-les-Bains-Palalda | |
| |||
| | |||
| Saint-Laurent-de-Cerdans |
Government and politics
Mayors
| Mayor | Term start | Term end |
|---|---|---|
| Jean-Baptiste Serradell | 1807 | 1808 |
| Abdon Desclaus | 1808 | 1813 |
| Jean-Baptiste Serradell[1] | 1813 | 1815 |
| Jean Galangau | 1815 | 1827 |
| Dominique Jofre | 1827 | 1830 |
| Jean Pujade | 1830 | 1832 |
| Etienne Grau | 1832 | 1835 |
| Pierre Mouchart | 1835 | 1837 |
| Jacques Dubois | 1837 | 1839 |
| Jean Serreclare | 1839 | 1840 |
| François Comaills | 1840 | 1848 |
| Etienne Douffiagues | 1848 | 1849 |
| Joseph Boix | 1849 | 1850 |
| Joseph Pallarès | 1892 | 1908 |
| Jean Vilar | 1908 | 1914 |
| Baptiste Pams | 1914 | 1941 |
| Lucien Trenet (father of Charles Trenet) | 1941 | 1942 |
| Pierre Sola | 1942 | 1944 |
| Baptiste Pams | 1944 | 1967 |
| Paul Lavanga | 1967 | 1983 |
| Marcel Charlet | 1983 | 1989 |
| Albert Costa | 1989 | 2001 |
| René Ala | 2001 | 2008 |
| René Bantoure | 2008 |
International relations
Arles-sur-Tech is twinned with:
Population
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1962 | 2,604 | — |
| 1968 | 2,760 | +6.0% |
| 1975 | 2,945 | +6.7% |
| 1982 | 2,889 | −1.9% |
| 1990 | 2,837 | −1.8% |
| 1999 | 2,700 | −4.8% |
| 2006 | 2,767 | +2.5% |
| 2009 | 2,757 | −0.4% |
Sites of interest
- Saint-Mary Abbey : Arles-sur-Tech is best known for its abbey, which allegedly holds the relics of Saints Abdon and Sennen in a sarcophagus called Sainte Tombe, traditionally believed to have been brought from Rome by Abbot Arnulf in the middle of the tenth century.[3] Its waters are traditionally believed to hold miraculous healing properties.[4]
- The Caixa de Rotllan, a dolmen.
- Saint-Stephen church
- Saint-Saviour church
- Saint-Peter church
- Holy Cross church
- The Fou canyon, said to be the world's narrowest.
Bibliography
- Abbé Adolphe Crastre, Histoire du martyre des saints Abdon et Sennen, de leurs reliques, de leurs miracles, de leur culte et de l'eau miraculeuse du sarcophage (Amélie-les-Bains, 1932). Facsimile reprint, Nîmes: Les Éditions Lacour-Ollé, 2005. ISBN 2-7504-1045-2
See also
References
- ↑ (French) Fabricio Cardenas, Vieux papiers des Pyrénées-Orientales, Arles, le 11 juin 1815, 14 january 2014
- ↑ (Catalan) Infos on Cubelles municipal website Archived September 21, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Joan Evans, Cluniac Art of The Romanesque Period (Cambridge University Press, 1950). Citing L'abbé Joseph Gibrat, Aperçu historique sur l'abbaye d'Arles-sur-Tech, page 15 (Céret, L. Roque, 1922. In-8°, 93 p.).
- ↑ Milburg Francisco Mansfield, Castles and chateaux of old Navarre and the Basque provinces: including also Foix, Roussillon and Béarn (I. Pitman, 1908).
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Arles-sur-Tech. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Arles-sur-Tech. |