Ikebukuro Station
Ikebukuro Station 池袋駅 | |
|---|---|
|
The west side of Ikebukuro Station and the Tobu Department Store building, June 2012 | |
| Location |
1-28-1,2 Minami-Ikebukuro, Toshima, Tokyo Japan |
| Operated by |
|
| Line(s) | |
| Connections |
|
| History | |
| Opened | April 1, 1903 |
| Location | |
 Ikebukuro Station Location within Japan | |
Ikebukuro Station (池袋駅 Ikebukuro-eki) is a major railway station located in the Ikebukuro district of Toshima, Tokyo, Japan, shared by East Japan Railway Company (JR East), Tokyo subway operator Tokyo Metro, and the two private railway operators Seibu Railway and Tobu Railway. With 2.71 million passengers on an average daily in 2007, it is the second-busiest railway station in the world (after Shinjuku Station), and the busiest station in the Tobu, Seibu, and Tokyo Metro networks. It primarily serves commuters from Saitama Prefecture and other residential areas northwest of the city centre. It is the Tokyo terminal of the Seibu Ikebukuro Line and the Tobu Tojo Line.
Lines
JR East
- ■ Yamanote Line - along with Ōsaki, one of two stations where Yamanote loop trains are taken in and out of service
- ■ Saikyo Line
- ■■ Shonan-Shinjuku Line - through service to Takasaki Line and Utsunomiya Line; also used by Narita Express trains
Seibu Railway
![]() Seibu Ikebukuro Line (Ikebukuro to Hanno)
Seibu Ikebukuro Line (Ikebukuro to Hanno)
Tobu Railway
![]() Tobu Tojo Line (Ikebukuro to Yorii)
Tobu Tojo Line (Ikebukuro to Yorii)
Tokyo Metro
Station layout
Ikebukuro Station has two main entrances, the East exit and the West exit. There are a number of other secondary entrances such as the JR North exit, the various Seibu exits. and multiple subway exits.
The JR lines run north/south through the center. The Tobu platforms are to the northwest and the Seibu platforms are to the southeast. Both Tobu and Seibu operate department stores adjacent to their terminal stations. (Despite their names, "Seibu" (西武) starts with the kanji for "west" (西), but its platforms are in the eastern part of the station, while "Tōbu" (東武) starts with the character for "east" (東), but its platforms are in the western part of the station.)
The Marunouchi Line and Yurakucho Line run east/west two stories underground, while the Tokyo Metro Fukutoshin Line is four stories underground to the west of the main station complex. The latter line runs south toward Shinjuku and Shibuya along Meiji-dori, and offers through services to Motomachi-Chūkagai Station in Yokohama via the Tokyu Toyoko Line and Minatomirai Line.
Tokyo Metro's Echika underground mall is also located inside the station.[1]
 The Metropolitan Exit on the second-floor level
The Metropolitan Exit on the second-floor level
JR East
Ikebukuro Station 池袋駅 | |
|---|---|
| JR East station | |
 Yamatone Line platform | |
| Location |
1 Chome-28-2 Minamiikebukuro, Toshima, Tokyo Japan |
| Operated by | JR East |
| Line(s) | |
| Connections | |
| History | |
| Opened | 1903 |
| Traffic | |
| Passengers (2015) | 556,780 daily |
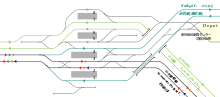
| 1 | ■ Saikyo Line | for Shinjuku, Shibuya, Ōsaki, and Shin-Kiba |
| 2 | ■ Shōnan-Shinjuku Line | for Shinjuku, Yokohama, Odawara, and Zushi |
| ■ Limited express Narita Express | for Narita Airport | |
| ■ Super View Odoriko | for Atami, Izukyū-Shimoda | |
| 3 | ■ Shōnan-Shinjuku Line | for Ōmiya, Utsunomiya, and Takasaki |
| 4 | ■ Saikyo Line | for Akabane, Ōmiya, and Kawagoe |
| 5/6 | ■ Yamanote Line | for Shinjuku, Shibuya, and Shinagawa |
| 7/8 | ■ Yamanote Line | for Tabata, Ueno, and Tokyo |
Chest-high platform edge doors have been introduced on the Yamanote Line platforms since 2 March 2013.[2]
- Platform 1/2 (with Saikyo Line on the right), August 2014
Adjacent stations
| ← | Service | → | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yamanote Line | ||||
| Mejiro | - | Ōtsuka | ||
| Shonan-Shinjuku Line | ||||
| Ōmiya | Narita Express | Shinjuku | ||
| Terminus | Super View Odoriko | Shinjuku | ||
| Akabane | Special Rapid | Shinjuku | ||
| Akabane | Rapid | Shinjuku | ||
| Akabane | Local | Shinjuku | ||
| Saikyo Line | ||||
| Shinjuku | Commuter Rapid | Itabashi | ||
| Shinjuku | Rapid | Itabashi | ||
| Shinjuku | Local | Itabashi | ||
Tobu
Platforms
Ikebukuro Station 池袋駅 | |
|---|---|
| Tobu station | |
|
Ikebukuro Station Tobu South Gate | |
| Location |
1 Chome-21-1 Minamiikebukuro, Toshima, Tokyo Japan |
| Operated by | Tobu Railway |
| Line(s) | |
| Connections | |
| Other information | |
| Station code | TJ-01 |
| History | |
| Opened | 1914 |
| Traffic | |
| Passengers (2015) | 477,834 daily |
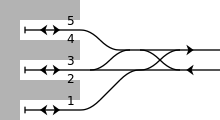
The Tobu station has three terminating tracks served by platforms 1 to 5, arranged as shown in the diagram on the right.
| 1-5 | ■ Tobu Tojo Line | for Narimasu, Shiki, Kawagoe, Sakado, and Ogawamachi |
Platforms 3 and 5 are normally used for disembarking passengers, although platform 5 is also used for passengers boarding the evening TJ Liner services, which require payment of a supplementary fare. From 14 June 2015, the departure melodies used when trains are about to depart from the station are to be changed to classical themes, with "Allegro" from "Divertimento in D major, K. 136" by Mozart used for platforms 1/2, "Menuetto" from "Eine kleine Nachtmusik" by Mozart used for platforms 3/4, and "Allegro ma non troppo" from the "Pastoral Symphony" by Beethoven used for TJ Liner services departing from platform 5.[3]
- The view from the buffer stops at the south end in April 2014
- Platform 1 and 2 viewed from platform 3 in April 2014
- PLatform 5 viewed from platform 4 in April 2014
- Platform 5 in the evening used by a TJ Liner service
Ticket barriers
There are three sets of ticket barriers giving access to the platforms: the "South Gate" at ground level (signposted in red), and the "Central Gate" (signposted in blue) and "North Gate" (signposted in green) on the first basement level.
- The ground-level south entrance and ticket barriers in December 2015
- The north gate ticket barriers in April 2014
- The stairs leading from the central gate to platform 5 for TJ Liner passengers in April 2014
Adjacent stations
| ← | Service | → | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobu Tojo Line | ||||
| Terminus | TJ Liner | Fujimino | ||
| Terminus | Rapid express | Wakōshi | ||
| Terminus | Rapid | Narimasu | ||
| Terminus | Express | Narimasu | ||
| Terminus | Semi express | Narimasu | ||
| Terminus | Local | Kita-Ikebukuro | ||
Seibu
Ikebukuro Station 池袋駅 | |
|---|---|
| Seibu station | |
 Ikebukuro Station Seibu platform | |
| Location |
1 Chome-28-1 Minamiikebukuro, Toshima, Tokyo Japan |
| Operated by | Seibu Railway |
| Line(s) | |
| Connections | |
| Other information | |
| Station code | SI-01 |
| History | |
| Opened | 1915 |
| Traffic | |
| Passengers (2015) | 483,407 daily |
| 1-7 | ■ Seibu Ikebukuro Line | for Nerima, Tokorozawa, and Hannō Chichibu Main Line for Mitsumineguchi |
Platforms 1, 4, and 6 are normally used for disembarking passengers only.
- The Seibu Ikebukuro Line platforms in July 2014
 Seibu track and platform layout
Seibu track and platform layout
Adjacent stations
| ← | Service | → | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seibu Ikebukuro Line | ||||
| Terminus | Limited express | Tokorozawa | ||
| Terminus | Rapid express | Shakujii-kōen | ||
| Terminus | Express | Shakujii-kōen | ||
| Terminus | Commuter express | Shakujii-kōen | ||
| Terminus | Rapid | Nerima | ||
| Terminus | Commuter semi express | Nerima | ||
| Terminus | Semi express | Nerima | ||
| Terminus | Local | Shiinamachi | ||
Tokyo Metro
Platform
Ikebukuro Station 池袋駅 | |
|---|---|
| Tokyo Metro station | |
 Ikebukuro Station Fukutoshin Line platform | |
| Location |
3 Chome-28-1 Minamiikebukuro, Toshima (Marunouchi Line) 1 Chome-12-1 Nishiikebukuro, Toshima (Yurakucho Line) 3 Chome-28-14 Nishiikebukuro, Toshima (Fukutoshin Line) Japan |
| Operated by | Tokyo Metro |
| Line(s) | |
| Connections | |
| Other information | |
| Station code | M 25, Y 09, F 09 |
| History | |
| Opened | 1954 |
| Traffic | |
| Passengers (2015) | 548,839 daily |
This station consists of three island platforms, serving Marunouchi Line, Yūrakuchō Line and Fukutoshin Line.
Station layout
| 1/2 | ○ Tokyo Metro Marunouchi Line | for Ōtemachi, Tokyo, Ginza, Shinjuku, Ogikubo, and Hōnanchō |
| 3 | ○ Tokyo Metro Yurakucho Line | for Iidabashi, Nagatachō, Yūrakuchō, and Shin-Kiba |
| 4 | ○ Tokyo Metro Yurakucho Line | for Kotake-mukaihara, and Wakōshi |
| 5 | ○ Tokyo Metro Fukutoshin Line | for Shinjuku-sanchōme, Meiji-Jingūmae, and Shibuya |
| 6 | ○ Tokyo Metro Fukutoshin Line | for Kotake-mukaihara, and Wakōshi |
The Tokyo Metro platforms are equipped with chest-height platform edge doors.[4]
- The Yurakucho Line platforms in June 2016
Adjacent stations
| « | Service | » | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marunouchi Line (M-25) | ||||
| Shin-Ōtsuka (M-24) | Local | Terminus | ||
| Yurakucho Line (Y-09) | ||||
| Kanamechō (Y-08) | Local | Higashi-Ikebukuro (Y-10) | ||
| Fukutoshin Line (F-09) | ||||
| Kotake-Mukaihara (F-06) | Express | Shinjuku-sanchōme (F-13) | ||
| Kotake-Mukaihara (F-06) | Commuter express | Shinjuku-sanchōme (F-13) | ||
| Kanamechō (F-08) | Local | Zōshigaya (F-10) | ||
History

The station was opened on April 1, 1903 by the Japanese Government Railways (JGR). The Tōjō Railway Line (present-day Tobu Tojo Line) station opened on 1 May 1914 with the opening of the 33.5 km line to Tanomosawa (田面沢駅) in Saitama Prefecture (located between the present stations of Kawagoeshi and Kasumigaseki).[5] As the Tokyo terminus of the line was originally planned to be at Shimo-Itabashi, Ikebukuro Station is to this day marked by km post "-1.9" (the distance from Shimo-Itabashi Station where the "0 km" post for the line is located).[5]
Tobu opened a department store adjoining its station on 29 May 1962.[5] Around the same time, the Tobu station platforms were expanded with three tracks.[5]
In March 1992, automatic ticket barriers were installed at the north exit of the Tobu Station, and in June of the same year, the Tobu Department Store was expanded with the addition of the Metropolitan Plaza annex located on the south side.[5]
In June 2008, the Tobu station ticket barriers were colour-coded into three "zones": North, Central, and South.[5]
Chest-height platform edge doors were installed on the Tokyo Metro Yurakucho Line platforms in January 2011.[4]
Passenger statistics
The figures below are the official number of passengers entering and exiting each day released by each train operator.
| Operator | Number | Fiscal year | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JR East | 550,350 | 2013 | Boarding passengers only. Second busiest JR East station.[6] | |
| Tobu | 472,132 | 2014 | Busiest Tobu station.[7] | |
| Seibu | 484,446 | 2013 | Busiest Seibu station.[8] | |
| Tokyo Metro | 523,834 | 2013 | Busiest Tokyo Metro station. (Excludes stations which allow through services onto non-Tokyo Metro lines)[9] | |
Annual passenger figures for the station between fiscal 1903 and 1965 are as shown below. Note that the figures only consider boarding passengers and a blank indicates that no data is available.
| Fiscal year | Annual total | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JGR/JNR | Tobu | Musashino/Seibu | TRTA | ||
| 1903 | 27,941 | Not in operation | Not in operation | Not in operation | [10] |
| 1905 | 33,877 | [11] | |||
| 1915 | 545,473 | [12] | |||
| 1925 | 6,842,992 | 192,380 | 1,228,881 | [13] | |
| 1935 | 11,554,661 | 500,476 | 3,558,958 | [14] | |
| 1955 | 34,428,803 | [15] | |||
| 1965 | 144,996,156 | 72,559,157 | 77,873,226 | 55,093,466 | [16][17] |
The daily passenger figures for the JR East, Seibu, Tobu, and Tokyo Metro station after fiscal 2000 are as shown below. Note that the JR East figures only consider boarding passengers whereas the Seibu, Tobu, and Tokyo Metro figures consider both entering and exiting passengers.
| Fiscal year | JR East | Seibu | Tobu | Tokyo Metro |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 570,255[18] | |||
| 2005 | 564,669[19] | 511,078[20] | ||
| 2010 | 544,222[21] | 476,989[22] | 467,770[23] | |
| 2011 | 544,762[24] | 472,022[25] | 464,908[26] | 470,284[27] |
| 2012 | 550,756[28] | 479,467[29] | 471,990[30] | 483,952[31] |
| 2013 | 550,350[6] | 484,446[8] | 476,756[32] | 523,834[9] |
| 2014 | 472,132[7] |
Surrounding area

The surrounding Ikebukuro district is a major commercial centre. Seibu department store, Sunshine City, Parco, Mitsukoshi, and Bic Camera are located to the east of the station, while the Tobu department store and Metropolitan Plaza are located to the west.
Education
- Rikkyo University
- Tokyo College of Music
- Teikyo Heisei University Ikebukuro Campus
- Tokyo University of Social Welfare Ikebukuro Campus
- Shukutoku University Ikebukuro Satellite Campus
- Tokyo College of Transport Studies
- Toshimagaoka-joshigakuen Junior and Senior High School
Retail
- Seibu Department Store
- Parco Department Store
- Tobu Department Store
- Sunshine City
Hotels
- Hotel Metropolitan
Civic
- Toshima Tax Office
- Toshima Civic Centre
- Tokyo Metropolitan Theatre
- Ikebukuro Library
- Ikebukuro Fire Station
Other stations
See also
References
- JR全線全駅ステーション倶楽部編(上) [Complete JR Line/Station Compendium (Vol. 1)] (in Japanese). Tokyo, Japan: 文春文庫 (Bunshun Bunko). September 1988. pp. 37–38. ISBN 4-16-748701-2.
- ↑ Echika Ikebukuro Retrieved on 21 July 2009. (Japanese)
- ↑ 山手線池袋駅 ホームドア使用開始日決定 [Start date fixed for platform edge doors on Ikebukuro Station Yamanote Line platforms]. Tetsudo Hobidas (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing. 25 December 2012. Retrieved 28 December 2012.
- ↑ 6月14日(日) 池袋駅 発車メロディがクラシック音楽に変わります [Ikebukuro Station departure melodies to be changed to classical tunes from 14 June] (pdf). News release (in Japanese). Japan: Tobu Railway. 8 June 2015. Retrieved 9 June 2015.
- 1 2 有楽町線:和光市駅に設置! [Installation at Yurakucho Line Wakoshi Station] (pdf) (in Japanese). Japan: Tokyo Metro. 27 March 2012. Retrieved 15 April 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 週刊私鉄全駅・全車両基地 No.08 [Weekly All Private Railway Stations and Depots No.8]. Japan: Asahi Shimbun Publications Inc. 9 February 2014. p. 9. EAN 4910234820243.
- 1 2 各駅の乗車人員 (2013年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2013)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Archived from the original on 1970-01-01. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- 1 2 駅情報(乗降人員) [Station information: Passenger figures] (in Japanese). Japan: Tobu Railway. 2015. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- 1 2 駅別乗降人員 2013(平成25)年度 1日平均 [Average daily station usage figures (fiscal 2013)] (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan: Seibu Railway. Retrieved 22 June 2014.
- 1 2 各駅の乗降人員ランキング [Station usage ranking] (in Japanese). Tokyo Metro. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ 東京府 編 (1905). 東京府統計書. 明治36年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1903)] (in Japanese). 1. 東京府. p. 323. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) (digital page number 183)
- ↑ 東京府 編 (1906). 東京府統計書. 明治38年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1905)] (in Japanese). 1. 東京府. p. 357. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) (digital page number 196)
- ↑ 東京府 編 (1917). 東京府統計書. 大正4年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1915)] (in Japanese). 1. 東京府. p. 681. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) (digital page number 347)
- ↑ 東京府 編 (1927). 東京府統計書. 大正14年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1925)] (in Japanese). 1. 東京府. pp. 561–3. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) (digital page number 326)
- ↑ 東京府 編 (1937). 東京府統計書. 昭和10年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1935)] (in Japanese). 1. 東京府. pp. 569–70. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) (digital page numbers 340-1)
- ↑ 東京都統計昭和30年 [Tokyo Metropolis Statistics (1955)] (pdf) (in Japanese). Japan: Tokyo Metropolitan Government. p. 173. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ↑ 東京都統計昭和40年 [Tokyo Metropolis Statistics (1965)] (pdf) (in Japanese and English). Japan: Tokyo Metropolitan Government. p. 223. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ↑ 東京都統計昭和40年 [Tokyo Metropolis Statistics (1965)] (pdf) (in Japanese and English). Japan: Tokyo Metropolitan Government. pp. 228–34. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2000年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2000)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Archived from the original on 2014-10-09. Retrieved 26 January 2013.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2005年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2005)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Archived from the original on 2014-10-09. Retrieved 26 January 2013.
- ↑ 駅別乗降人員 2005(平成17)年度 1日平均 [Average daily station usage figures (fiscal 2005)] (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan: Seibu Railway. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2010年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2010)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Archived from the original on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 26 January 2013.
- ↑ 駅別乗降人員 2010(平成22)年度 1日平均 [Average daily station usage figures (fiscal 2010)] (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan: Seibu Railway. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ 駅情報(乗降人員) [Station information: Passenger figures] (in Japanese). Japan: Tobu Railway. 2011. Archived from the original on 5 April 2012. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2011年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2011)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Archived from the original on 2014-10-08. Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- ↑ 駅別乗降人員 2011(平成23)年度 1日平均 [Average daily station usage figures (fiscal 2011)] (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan: Seibu Railway. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ 駅情報(乗降人員) [Station information: Passenger figures] (in Japanese). Japan: Tobu Railway. 2012. Archived from the original on 23 August 2013. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ↑ 各駅の乗降人員ランキング [Station usage ranking] (in Japanese). Tokyo Metro. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2012年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2012)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Archived from the original on 2014-10-07. Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- ↑ 駅別乗降人員 2012(平成24)年度 1日平均 [Average daily station usage figures (fiscal 2012)] (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan: Seibu Railway. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ 駅情報(乗降人員) [Station information: Passenger figures] (in Japanese). Japan: Tobu Railway. 2013. Archived from the original on 25 April 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ↑ 各駅の乗降人員ランキング [Station usage ranking] (in Japanese). Tokyo Metro. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ 駅情報(乗降人員) [Station information: Passenger figures] (in Japanese). Japan: Tobu Railway. 2014. Archived from the original on 30 October 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ikebukuro Station. |
- JR Ikebukuro Station map
- Ikebukuro Station information (Seibu) (Japanese)
- Ikebukuro Station information (Tobu) (Japanese)
- Ikebukuro Station information (Tokyo Metro) (Japanese)
Coordinates: 35°43′49″N 139°42′41″E / 35.73028°N 139.71139°E