Maine
| State of Maine État du Maine (French) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
|
Nickname(s): "The Pine Tree State" "Vacationland"[1] | |||||
|
Motto(s): "Dirigo" (Latin for "I lead", "I guide", or "I direct") | |||||
 | |||||
| Official language | None[2] | ||||
| Spoken languages | English (92%), French (5%) | ||||
| Demonym | Mainer[3] | ||||
| Capital | Augusta | ||||
| Largest city | Portland | ||||
| Largest metro | Portland-South Portland-Biddeford | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Total |
35,385 sq mi (91,646 km2) | ||||
| • Width | 210 miles (338 km) | ||||
| • Length | 320 miles (515 km) | ||||
| • % water | 13.5 | ||||
| • Latitude | 42° 58′ N to 47° 28′ N | ||||
| • Longitude | 66° 57′ W to 71° 5′ W | ||||
| Population | |||||
| • Total | 1,329,328 (2015 est)[4] | ||||
| • Density |
43.0/sq mi (16.6/km2) Ranked 38th | ||||
| Elevation | |||||
| • Highest point |
Mount Katahdin[5][6][7] 5,270 ft (1606.4 m) | ||||
| • Mean | 600 ft (180 m) | ||||
| • Lowest point |
Atlantic Ocean[6] sea level | ||||
| Before statehood | District of Maine (Massachusetts) | ||||
| Admission to Union | March 15, 1820 (23rd) | ||||
| Governor | Paul LePage (Republican) | ||||
| President of the Senate | Michael Thibodeau (Republican)[8] | ||||
| Legislature | |||||
| • Upper house | Senate | ||||
| • Lower house | House of Representatives | ||||
| U.S. Senators |
Susan Collins (Republican) Angus King (Independent) | ||||
| U.S. House delegation |
Chellie Pingree (Democrat) Bruce Poliquin (Republican) (list) | ||||
| Time zone | Eastern: UTC −5/−4 | ||||
| ISO 3166 | US-ME | ||||
| Abbreviations | ME | ||||
| Website |
www | ||||
| Maine state symbols | |
|---|---|
|
The Flag of Maine | |
|
The Seal of Maine | |
| Living insignia | |
| Bird | Chickadee |
| Fish | Atlantic salmon |
| Flower | White pine cone |
| Insect | Honey bee |
| Mammal | Moose |
| Tree | Eastern white pine |
| Inanimate insignia | |
| Beverage | Moxie |
| Food | Blueberry pie |
| Fossil | Pertica quadrifaria |
| Gemstone | Tourmaline |
| Motto | Dirigo (I Lead) |
| Soil | Chesuncook |
| Song | "State of Maine Song" |
| State route marker | |
 | |
| State quarter | |
|
Released in 2003 | |
| Lists of United States state symbols | |
Maine (/ˈmeɪn/; French: État du Maine) is the northernmost state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. Maine is the 39th most extensive and the 41st most populous of the U.S. states and territories. It is bordered by New Hampshire to the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the north. Maine is the easternmost state in the contiguous United States, and the northernmost east of the Great Lakes. It is known for its jagged, rocky coastline; low, rolling mountains; heavily forested interior, and picturesque waterways; and also its seafood cuisine, especially clams and lobster. There is a continental climate throughout the state, even in coastal areas such as its most populous city of Portland.[9] The capital is Augusta.
For thousands of years, indigenous peoples were the only inhabitants of the territory that is now Maine. At the time of European arrival in what is now Maine, several Algonquian-speaking peoples inhabited the area. The first European settlement in the area was by the French in 1604 on Saint Croix Island, by Pierre Dugua, Sieur de Mons. The first English settlement was the short-lived Popham Colony, established by the Plymouth Company in 1607. A number of English settlements were established along the coast of Maine in the 1620s, although the rugged climate, deprivations, and conflict with the local peoples caused many to fail over the years.
As Maine entered the 18th century, only a half dozen European settlements had survived. Loyalist and Patriot forces contended for Maine's territory during the American Revolution and the War of 1812. At the close of the War of 1812, it was occupied by British forces, but the territory of Maine was returned to the United States as part of a peace treaty that was to include dedicated land on the Michigan peninsula for Native American peoples. Maine was part of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts until 1820, when it voted to secede from Massachusetts to become an independent state. On March 15, 1820, it was admitted to the Union as the 23rd state under the Missouri Compromise.
Etymology
There is no definitive explanation for the origin of the name "Maine", but the most likely origin is the name given by early explorers after a province in France. Whatever the origin, the name was fixed for English settlers in 1665 when the English King's Commissioners ordered that the "Province of Maine" be entered from then on in official records.[10] The state legislature in 2001 adopted a resolution establishing Franco-American Day, which stated that the state was named after the former French province of Maine.[11]
Other theories mention earlier places with similar names, or claim it is a nautical reference to the mainland.[12] Attempts to uncover the history of the name of Maine began with James Sullivan's 1795 "History of the District of Maine". He made the unsubstantiated allegation that the Province of Maine was a compliment to the queen of Charles I, Henrietta Maria, who once "owned" the Province of Maine in France. This was quoted by Maine historians until the 1845 biography of that queen by Agnes Strickland[13] established that she had no connection to the Province of Maine in France; further, King Charles I married Henrietta Maria in 1625, three years after the name Maine first appeared on the charter.[14] A new theory, put forward by Carol B. Smith Fisher in 2002, is that Sir Ferdinando Gorges chose the name in 1622 to honor the village where his ancestors first lived in England, rather than the province in France. "MAINE" appears in the Domesday Book of 1086 in reference to the county of Dorset, which is today Broadmayne, just southeast of Dorchester.[14][15]
The view generally held among British place name scholars is that Mayne in Dorset is Brythonic, corresponding to modern Welsh "maen", plural "main" or "meini". Some early spellings are: MAINE 1086, MEINE 1200, MEINES 1204, MAYNE 1236. Today the village is known as Broadmayne, which is primitive Welsh or Brythonic, "main" meaning rock or stone, considered a reference to the many large sarsen stones still present around Little Mayne farm, half a mile northeast of Broadmayne village.[16][17]
The first known record of the name appears in an August 10, 1622, land charter to Sir Ferdinando Gorges and Captain John Mason, English Royal Navy veterans, who were granted a large tract in present-day Maine that Mason and Gorges "intend to name the Province of Maine". Mason had served with the Royal Navy in the Orkney Islands where the chief island is called Mainland, a possible name derivation for these English sailors.[10] In 1623, the English naval captain Christopher Levett, exploring the New England coast, wrote: "The first place I set my foote upon in New England was the Isle of Shoals, being Ilands [sic] in the sea, above two Leagues from the Mayne."[18] Initially, several tracts along the coast of New England were referred to as Main or Maine (cf. the Spanish Main). A reconfirmed and enhanced April 3, 1639, charter from England's King Charles I gave Sir Ferdinando Gorges increased powers over his new province and stated that it "shall forever hereafter, be called and named the PROVINCE OR COUNTIE OF MAINE, and not by any other name or names whatsoever..."[14][19] Maine is the only state whose name has exactly one syllable.[20][21]
History



The original inhabitants of the territory that is now Maine were Algonquian-speaking Wabanaki peoples, including the Abenaki, Passamaquoddy, Maliseet and Penobscot, who had a loose confederacy.
European contact with what is now called Maine started around 1200 CE when Norwegians interacted with the native Penobscot in present-day Hancock County, most likely through trade. About 200 years earlier, from the settlements of Iceland and Greenland, Norwegians had discovered America and attempted to settle areas such as Newfoundland, but failed to establish a permanent settlement there. Archeological evidence suggests that Norwegians in Greenland returned to North America for several centuries after the initial discovery to collect timber and to trade, with the most relevant evidence being the Maine Penny, a 10th-century Norwegian coin found at a Native American dig site in 1954.[22]
The first European settlement in Maine was in 1604 on Saint Croix Island, led by French explorer Pierre Dugua, Sieur de Mons; his party included Samuel de Champlain, noted as an explorer. The French named the entire area Acadia, including the portion that later became the state of Maine. The first English settlement in Maine was established by the Plymouth Company at Popham in 1607, the same year as the settlement at Jamestown, Virginia. The Popham colonists returned to England after 14 months.[23]
The French established two Jesuit missions: one on Penobscot Bay in 1609, and the other on Mount Desert Island in 1613. The same year, Castine was established by Claude de La Tour. In 1625, Charles de Saint-Étienne de la Tour erected Fort Pentagouet to protect Castine. The coastal areas of western Maine first became the Province of Maine in a 1622 land patent. Eastern Maine north of the Kennebec River was more sparsely settled and was known in the 17th century as the Territory of Sagadahock. A second settlement was attempted at a place called York, in 1623 by English explorer and naval Captain Christopher Levett, granted 6,000 acres (24 km2) by King Charles I of England.[24] That settlement also failed.
Central Maine was formerly inhabited by people of the Androscoggin tribe, also known as Arosaguntacook. The Androscoggin were a tribe in the Abenaki nation. They were driven out of the area in 1690 during King William's War. They were relocated at St. Francis, Canada, which was destroyed by Rogers' Rangers in 1759, and is now Odanak. The other Abenaki tribes suffered several severe defeats, particularly during Dummer's War, with the capture of Norridgewock in 1724 and the defeat of the Pequawket in 1725, which greatly reduced their numbers. They finally withdrew to Canada, where they were settled at Bécancour and Sillery, and later at St. Francis, along with other refugee tribes from the south.[25]
The province within its current boundaries became part of Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1652. Maine was much fought over by the French, English and allied natives during the 17th and early 18th centuries, who conducted raids against each other, taking captives for ransom or, in some cases, adoption by Native American tribes. For instance, in early 1692, the Abenaki raided York, killing about 100 of the English settlers and taking another estimated 80 villagers hostage.[26] The Abenaki took captives taken during raids of Massachusetts in Queen Anne's War of the early 1700s to Kahnewake, a Catholic Mohawk village near Montreal, where some were adopted and others ransomed.[27][28]
After the British defeated the French in Acadia in the 1740s, the territory from the Penobscot River east fell under the nominal authority of the Province of Nova Scotia, and together with present-day New Brunswick formed the Nova Scotia county of Sunbury, with its court of general sessions at Campobello. American and British forces contended for Maine's territory during the American Revolution and the War of 1812, and British forces occupied eastern Maine in both conflicts.[29] The treaty concluding revolution was ambiguous about Maine's boundary with British North America. The territory of Maine was confirmed as part of Massachusetts when the United States was formed, although the final border with British territory was not established until the Webster–Ashburton Treaty of 1842.
Maine was physically separate from the rest of Massachusetts. Long-standing disagreements over land speculation and settlements led to Maine residents and their allies in Massachusetts proper forcing an 1807 vote in the Massachusetts Assembly on permitting Maine to secede; the vote failed. Secessionist sentiment in Maine was stoked during the War of 1812 when Massachusetts pro-British merchants opposed the war and refused to defend Maine from British invaders. In 1819, Massachusetts agreed to permit secession if voters in Maine approved. Due to these considerations and rapid population growth, in 1820 Maine voted to secede from Massachusetts. The secession and formation of the state of Maine as the 23rd state occurred on March 15, 1820, as part of the Missouri Compromise, which geographically limited the spread of slavery and enabled the admission to statehood of Missouri the following year, keeping a balance between slave and free states.[30][31][32]
Maine's original capital was Portland, Maine's largest city, until it was moved to Augusta in 1832 to make it more central within the state. The principal office of the Maine Supreme Judicial Court remains in Portland.
The 20th Maine, under the command of Colonel Joshua Lawrence Chamberlain, defended Little Round Top at the Battle of Gettysburg. Its soldiers prevented the Union Army from being flanked by the Confederate Army.
Four U.S. Navy ships have been named USS Maine in honor of the state.
Geography
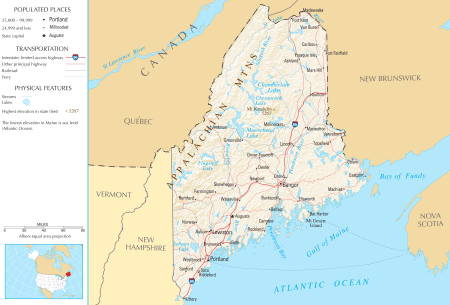
To the south and east is the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and northeast is New Brunswick, a province of Canada. The Canadian province of Quebec is to the northwest. Maine is both the northernmost state in New England and the largest, accounting for almost half the region's entire land area. Maine is the only state to border only one other state (New Hampshire to the west).
Maine is the easternmost state in the United States in both its extreme points and its geographic center. The municipalities of Eastport and Lubec are, respectively, the easternmost city and town in the United States. Estcourt Station is Maine's northernmost point, as well as the northernmost point in New England. (For more information see extreme points of the United States.)
Maine's Moosehead Lake is the largest lake wholly in New England, as Lake Champlain is located between Vermont, New York and Quebec. A number of other Maine lakes, such as South Twin Lake, are described by Thoreau in The Maine Woods (1864). Mount Katahdin is both the northern terminus of the Appalachian Trail, which extends southerly to Springer Mountain, Georgia, and the southern terminus of the new International Appalachian Trail which, when complete, will run to Belle Isle, Newfoundland and Labrador.
Maine has several unique geographical features. Machias Seal Island and North Rock, off its easternmost point, are claimed by both the U.S. and Canada and are within one of four areas between the two countries whose sovereignty is still in dispute, but it is the only one of the disputed areas containing land. Also in this easternmost area in the Bay of Fundy is the Old Sow, the largest tidal whirlpool in the Western Hemisphere.
Maine is the least densely populated U.S. state east of the Mississippi River. It is called the Pine Tree State; about 83% of its land is forested.[33] In the forested areas of the interior lies much uninhabited land, some of which does not have formal political organization into local units (a rarity in New England). The Northwest Aroostook, Maine unorganized territory in the northern part of the state, for example, has an area of 2,668 square miles (6,910 km2) and a population of 10, or one person for every 267 square miles (690 km2).
Maine is in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome. The land near the southern and central Atlantic coast is covered by the mixed oaks of the Northeastern coastal forests. The remainder of the state, including the North Woods, is covered by the New England-Acadian forests.[34]
Maine has almost 230 miles (400 km) of coastline (and 3,500 miles (5,600 km) of tidal coastline).[35][36] West Quoddy Head, in Lubec, Maine, is the easternmost point of land in the 48 contiguous states. Along the famous rock-bound coast of Maine are lighthouses, beaches, fishing villages, and thousands of offshore islands, including the Isles of Shoals which straddle the New Hampshire border. There are jagged rocks and cliffs and many bays and inlets. Inland are lakes, rivers, forests, and mountains. This visual contrast of forested slopes sweeping down to the sea has been summed up by American poet Edna St. Vincent Millay of Rockland and Camden, Maine, in "Renascence":

- "All I could see from where I stood
- Was three long mountains and a wood;
- I turned and looked the other way,
- And saw three islands in a bay."
Geologists describe this type of landscape as a "drowned coast", where a rising sea level has invaded former land features, creating bays out of valleys and islands out of mountain tops.[37] A rise in the elevation of the land due to the melting of heavy glacier ice caused a slight rebounding effect of underlying rock; this land rise, however, was not enough to eliminate all the effect of the rising sea level and its invasion of former land features.
Much of Maine's geomorphology was created by extended glacial activity at the end of the last ice age. Prominent glacial features include Somes Sound and Bubble Rock, both part of Acadia National Park on Mount Desert Island. Carved by glaciers, Somes Sound is considered to be the only fjord on the eastern seaboard and reaches depths of 175 feet (50 m). The extreme depth and steep drop-off allow large ships to navigate almost the entire length of the sound. These features also have made it attractive for boat builders, such as the prestigious Hinckley Yachts.
Bubble Rock, a glacial erratic, is a large boulder perched on the edge of Bubble Mountain in Acadia National Park. By analyzing the type of granite, geologists were able to discover that glaciers carried Bubble Rock to its present location from near the town of Lucerne, Maine — 30 miles (48 km) away. The Iapetus Suture runs through the north and west of the state, being underlain by the ancient Laurentian terrane, and the south and east underlain by the Avalonian terrane.
Acadia National Park is the only national park in New England. Areas under the protection and management of the National Park Service include:[38]
- Acadia National Park near Bar Harbor
- Appalachian National Scenic Trail
- Maine Acadian Culture in St. John Valley
- Roosevelt Campobello International Park near Lubec
- Saint Croix Island International Historic Site at Calais
- Katahdin Woods and Waters National Monument
Climate


Maine has a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfb), with warm (although generally not hot), humid summers. Winters are cold and snowy throughout the state, and are especially severe in the northern parts of Maine. Coastal areas are moderated somewhat by the Atlantic Ocean, resulting in milder winters and cooler summers in immediate coastal areas. Daytime highs are generally in the 75–80 °F (24–27 °C) range throughout the state in July, with overnight lows in the high 50s °F (around 15 °C). January temperatures range from highs near 32 °F (0 °C) on the southern coast to overnight lows averaging below 0 °F (−18 °C) in the far north.[39]
The state's record high temperature is 105 °F (41 °C), set in July 1911, at North Bridgton.[40] Precipitation in Maine is evenly distributed year-round, but with a slight summer maximum in northern/northwestern Maine and a slight late-fall or early-winter maximum along the coast due to "nor'easters" or intense cold-season storms. In coastal Maine, the late spring and summer months are usually driest – a rarity across the Eastern United States. Maine has fewer days of thunderstorms than any other state east of the Rockies, with most of the state averaging less than 20 days of thunderstorms a year. Tornadoes are rare in Maine, with the state averaging fewer than two per year, mostly occurring in the southern part of the state.[41] Maine rarely sees tropical cyclones.
In January 2009, a new record low temperature for the state was set at Big Black River of −50 °F (−46 °C), tying the New England record.[39]
Annual precipitation varies from 909 mm (35.8 in) in Presque Isle, to 1,441 mm (56.7 in) in Acadia National Park.[42]
| Location | July (°F) | July (°C) | January (°F) | January (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portland | 78/59 | 26/15 | 31/13 | –0/–10 |
| Lewiston | 81/61 | 27/16 | 29/11 | –2/–12 |
| Bangor | 79/57 | 26/14 | 27/6 | –2/–14 |
| Augusta | 79/60 | 26/15 | 27/11 | –2/–11 |
| Presque Isle | 77/55 | 25/13 | 20/1 | –6/–17 |
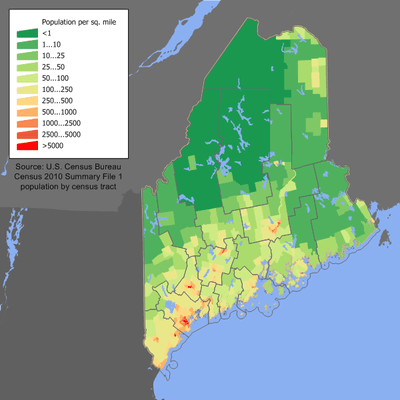
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 96,540 | — | |
| 1800 | 151,719 | 57.2% | |
| 1810 | 228,705 | 50.7% | |
| 1820 | 298,335 | 30.4% | |
| 1830 | 399,455 | 33.9% | |
| 1840 | 501,793 | 25.6% | |
| 1850 | 583,169 | 16.2% | |
| 1860 | 628,279 | 7.7% | |
| 1870 | 626,915 | −0.2% | |
| 1880 | 648,936 | 3.5% | |
| 1890 | 661,086 | 1.9% | |
| 1900 | 694,466 | 5.0% | |
| 1910 | 742,371 | 6.9% | |
| 1920 | 768,014 | 3.5% | |
| 1930 | 797,423 | 3.8% | |
| 1940 | 847,226 | 6.2% | |
| 1950 | 913,774 | 7.9% | |
| 1960 | 969,265 | 6.1% | |
| 1970 | 992,048 | 2.4% | |
| 1980 | 1,124,660 | 13.4% | |
| 1990 | 1,227,928 | 9.2% | |
| 2000 | 1,274,923 | 3.8% | |
| 2010 | 1,328,361 | 4.2% | |
| Est. 2015 | 1,329,328 | 0.1% | |
| Source: 1910-2010[44] 2015 estimate[4] | |||
The United States Census Bureau estimates that the population of Maine was 1,329,328 on July 1, 2015, a 0.07% increase since the 2010 United States Census.[4] The population density of the state is 41.3 people per square mile, making it the least densely populated state in New England, the American northeast, the eastern seaboard, of all of the states with an Atlantic coastline and of all of the states east of the Mississippi River.
The mean population center of Maine is located in Kennebec County, just east of Augusta.[45] The Greater Portland metropolitan area is the most densely populated with nearly 40% of Maine's population.[46] As explained in detail under "Geography", there are large tracts of uninhabited land in some remote parts of the interior.
Race, ancestry, and language
At the 2010 Census, 94.4% of the population was non-Hispanic White, 1.1% non-Hispanic Black or African American, 0.6% American Indian and Alaska Native, 1.0% Asian, 0.1% from some other race and 1.4% of two or more races. 1.3% of Maine's population was of Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish origin.[47]
| Racial composition | 1990[48] | 2000[49] | 2010[50] |
|---|---|---|---|
| White | 98.4% | 96.9% | 95.2% |
| Black | 0.4% | 0.5% | 1.2% |
| Asian | 0.5% | 0.7% | 1.0% |
| Native | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.6% |
| Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander | - | - | - |
| Other race | 0.1% | 0.2% | 0.3% |
| Two or more races | - | 1.0% | 1.6% |
| Largest ancestries (2011) [51] | Percent |
|---|---|
| English | 21.6% |
| Irish | 17.8% |
| French | 16.3% |
| American | 9.4% |
| German | 8.5% |
| French Canadian | 7.6% |
| Italian | 5.8% |
| Scottish | 5.5% |
| Polish | 2.1% |
| Swedish | 1.8% |
People citing that they are American are of overwhelmingly English descent, but have ancestry that has been in the region for so long (often since the 1600s) that they choose to identify simply as Americans.[52][53][54][55][56][57][58]
Maine has the highest percentage of French Americans among American states. It also has the highest percentage of non-Hispanic whites of any state, at 94.4% of the total population, according to the 2010 Census. In 2011, 89.0% of all births in the state were to non-Hispanic white parents.[59] The state also has the highest percentage of French-speakers of any state. Most of the French in Maine are of Canadian Origin, but in some cases have been living there prior to the Revolutionary War. There are particularly high concentrations of French in the northern part of Maine in Aroostook County, which is part of a cultural region known as Acadia that goes over the border into New Brunswick. Along with the Acadian population in the north, many French came from Quebec as immigrants between 1840 and 1930. Census figures show that Maine has the highest percentage of people speaking French at home of any state: 5.28% of Maine households are French-speaking, compared with 4.68% in Louisiana, which is the second highest state.[60] French-speakers are the state's chief linguistic minority; the 2000 Census reported 92.25% of Maine residents aged five and older spoke only English at home. Maine does not have an official language,[2] but the most widely spoken language in the state is English. Spanish is the third-most-spoken language in Maine, after English and French .
The upper Saint John River valley area was once part of the so-called Republic of Madawaska, before the frontier was decided in the Webster-Ashburton Treaty of 1842. Over one quarter of the population of Lewiston, Waterville, and Biddeford are Franco-American. Most of the residents of the Mid Coast and Down East sections are chiefly of British heritage. Smaller numbers of various other groups, including Irish, Italian and Polish, have settled throughout the state since the late 19th and early 20th century immigration waves.
Religion
According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA),[61] the religious affiliations of Maine in 2010 were:
- Catholic Church – 28%
- Protestant – 7%
- Evangelical Protestant - 4%
- Other religions – 1.7%
- Non-Christian religions include Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism and Bahá'í.
The Catholic Church was the largest religious institution with 202,106 members, the United Methodist Church had 28,329 members, the United Church of Christ had 22,747 members
In 2010, a study named Maine as the least religious state in the United States.[62]
Economy


The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that Maine's total gross state product for 2010 was $52 billion.[63] Its per capita personal income for 2007 was US$33,991, 34th in the nation. As of April 2016, Maine's unemployment rate is 3.4%[64]

Maine's agricultural outputs include poultry, eggs, dairy products, cattle, wild blueberries, apples, maple syrup and maple sugar. Aroostook County is known for its potato crops. Commercial fishing, once a mainstay of the state's economy, maintains a presence, particularly lobstering and groundfishing. Western Maine aquifers and springs are a major source of bottled water.
Maine's industrial outputs consist chiefly of paper, lumber and wood products, electronic equipment, leather products, food products, textiles, and bio-technology. Naval shipbuilding and construction remain key as well, with Bath Iron Works in Bath and Portsmouth Naval Shipyard in Kittery.
Brunswick Landing, formerly Naval Air Station Brunswick, is also in Maine. Formerly a large support base for the U.S. Navy, the BRAC campaign initiated the Naval Air Station's closing, despite a government-funded effort to upgrade its facilities. The former base has since been changed into a civilian business park, as well as a new satellite campus for Southern Maine Community College.[65]
Maine is the number one US producer of low-bush blueberries (Vaccinium angustifolium). Preliminary data from the USDA for 2012 also indicate Maine was the largest blueberry producer of the major blueberry producing states in the US, with 91,100,000 lbs.[66] This data includes both low (wild), and high-bush (cultivated) blueberries: Vaccinium corymbosum. The largest toothpick manufacturing plant in the United States used to be located in Strong, Maine. The Strong Wood Products plant produced 20 million toothpicks a day. It closed in May 2003.
Tourism and outdoor recreation play a major and increasingly important role in Maine's economy. The state is a popular destination for sport hunting (particularly deer, moose and bear), sport fishing, snowmobiling, skiing, boating, camping and hiking, among other activities.
Historically, Maine ports played a key role in national transportation. Beginning around 1880, Portland's rail link and ice-free port made it Canada's principal winter port, until the aggressive development of Halifax, Nova Scotia, in the mid-1900s. In 2013, 12,039,600 short tons passed into and out of Portland by sea,[67] which places it 45th out of the top 50 US water ports.[68] Portland Maine's Portland International Jetport was recently expanded, providing the state with increased air traffic from carriers such as JetBlue and Southwest Airlines.
Maine has very few large companies that maintain headquarters in the state, and that number has fallen due to consolidations and mergers, particularly in the pulp and paper industry. Some of the larger companies that do maintain headquarters in Maine include Fairchild Semiconductor in South Portland; IDEXX Laboratories, in Westbrook; Hannaford Bros. Co. in Scarborough, Unum in Portland; TD Bank, in Portland; L.L.Bean in Freeport; Cole Haan and DeLorme, both located in Yarmouth. Maine is also the home of The Jackson Laboratory, the world's largest non-profit mammalian genetic research facility and the world's largest supplier of genetically purebred mice.
Taxation
Maine has an income tax structure containing two brackets, 6.5% to 7.95% of personal income.[69] Before July 2013 Maine had four brackets: 2%, 4.5%, 7%, and 8.5%.[70] Maine's general sales tax rate is 5.5%. The state also levies charges of 7% on lodging and prepared food and 10% on short-term auto rentals. Commercial sellers of blueberries, a Maine staple, must keep records of their transactions and pay the state 1.5 cents per pound ($1.50 per 100 pounds) of the fruit sold each season. All real and tangible personal property located in the state of Maine is taxable unless specifically exempted by statute. The administration of property taxes is handled by the local assessor in incorporated cities and towns, while property taxes in the unorganized territories are handled by the State Tax Assessor.
Shipbuilding
Maine has a longstanding tradition of being home to many shipbuilding companies. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Maine was home to many shipyards that produced wooden sailing ships. The main function of these ships was to transport either cargos or passengers overseas. One of these yards was located in Pennellville Historic District in what is now Brunswick, Maine. This yard, owned by the Pennell family, was typical of the many family-owned shipbuilding companies of the time period. Other such examples of shipbuilding families were the Skolfields and the Morses. During the 18th and 19th centuries, wooden shipbuilding of this sort made up a sizable portion of the economy.
Transportation
Airports
Maine receives passenger jet service at its two largest airports, the Portland International Jetport in Portland, and the Bangor International Airport in Bangor. Both are served daily by many major airlines to destinations such as New York, Atlanta, and Orlando. Essential Air Service also subsidizes service to a number of smaller airports in Maine, bringing small turboprop aircraft to regional airports such as the Augusta State Airport, Hancock County-Bar Harbor Airport, Knox County Regional Airport, and the Northern Maine Regional Airport at Presque Isle. These airports are served by Cape Air with Cessna 402s and Penair with Saab 340s.
Many smaller airports are scattered throughout Maine, only serving general aviation traffic. The Eastport Municipal Airport, for example, is a city-owned public-use airport with 1,200 general aviation aircraft operations each year from single-engine and ultralight aircraft.[71]
Highways

Interstate 95 (I-95) travels through Maine, as well as its easterly branch I-295 and spurs 195, 395 and the unsigned I-495. In addition, U.S. Route 1 (US 1) starts in Fort Kent and travels to Florida. The eastern terminus of the eastern section of US 2 starts in Houlton, near the New Brunswick, Canada border to Rouses Point, New York, at US 11. US 2A connects Old Town and Orono, primarily serving the University of Maine campus. US 201 and US 202 flow through the state. US 2, Maine State Route 6 (Route 6), and Route 9 are often used by truckers and other motorists of the Maritime Provinces en route to other destinations in the United States or as a short cut to Central Canada.
Rail
Passenger

The Downeaster passenger train, operated by Amtrak, provides passenger service between Brunswick and Boston's North Station, with stops in Freeport, Portland, Old Orchard Beach, Saco, and Wells. The Downeaster makes five daily trips, two of which continue past Portland to Brunswick.[72]
Freight
Freight service throughout the state is provided by a handful of regional and shortline carriers: Pan Am Railways (formerly known as Guilford Rail System), which operates the former Boston & Maine and Maine Central railroads; St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad; Maine Eastern Railroad; Central Maine and Quebec Railway; and New Brunswick Southern Railway.
Law and government
The Maine Constitution structures Maine's state government, composed of three co-equal branches—the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The state of Maine also has three Constitutional Officers (the Secretary of State, the State Treasurer, and the State Attorney General) and one Statutory Officer (the State Auditor).
The legislative branch is the Maine Legislature, a bicameral body composed of the Maine House of Representatives, with 151 members, and the Maine Senate, with 35 members. The Legislature is charged with introducing and passing laws.
The executive branch is responsible for the execution of the laws created by the Legislature and is headed by the Governor of Maine (currently Paul LePage). The Governor is elected every four years; no individual may serve more than two consecutive terms in this office. The current attorney general of Maine is Janet Mills. As with other state legislatures, the Maine Legislature can by a two-thirds majority vote from both the House and Senate override a gubernatorial veto. Maine is one of seven states that do not have a lieutenant governor.
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting state laws. The highest court of the state is the Maine Supreme Judicial Court. The lower courts are the District Court, Superior Court and Probate Court. All judges except for probate judges serve full-time, are nominated by the Governor and confirmed by the Legislature for terms of seven years. Probate judges serve part-time and are elected by the voters of each county for four-year terms.
Counties
Maine is divided into political jurisdictions designated as counties. In 1860 there were 16 counties in the state, ranging in size from 370 to 6,829 square miles (958 to 17,700 km2).
| Maine counties | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| County name | County seat | Year founded | 2010 population[73] | Percent of total | Area (sq. mi.) | Percent of total |
| Androscoggin | Auburn | 1854 | 107,702 | 8.11% | 497 | 1.44% |
| Aroostook | Houlton | 1839 | 71,870 | 5.41% | 6,829 | 19.76% |
| Cumberland | Portland | 1760 | 281,674 | 21.20% | 1,217 | 3.52% |
| Franklin | Farmington | 1838 | 30,768 | 2.32% | 1,744 | 5.05% |
| Hancock | Ellsworth | 1789 | 54,418 | 4.10% | 1,522 | 4.40% |
| Kennebec | Augusta | 1799 | 122,151 | 9.20% | 951 | 2.75% |
| Knox | Rockland | 1860 | 39,736 | 2.99% | 1,142 | 3.30% |
| Lincoln | Wiscasset | 1760 | 34,457 | 2.59% | 700 | 2.03% |
| Oxford | Paris | 1805 | 57,833 | 4.35% | 2,175 | 6.29% |
| Penobscot | Bangor | 1816 | 153,923 | 11.59% | 3,556 | 10.29% |
| Piscataquis | Dover-Foxcroft | 1838 | 17,535 | 1.32% | 4,377 | 12.67% |
| Sagadahoc | Bath | 1854 | 35,293 | 2.66% | 370 | 1.07% |
| Somerset | Skowhegan | 1809 | 52,228 | 3.93% | 4,095 | 11.85% |
| Waldo | Belfast | 1827 | 38,786 | 2.92% | 853 | 2.47% |
| Washington | Machias | 1790 | 32,856 | 2.47% | 3,255 | 9.42% |
| York | Alfred | 1636 | 197,131 | 14.84% | 1,271 | 3.68% |
| Total counties: 16 | Total 2010 population: 1,328,361 | Total state area: 34,554 square miles (89,494 km2) | ||||
State and local politics
In state general elections, Maine voters tend to accept independent and third-party candidates more frequently than most states. Maine has had two independent governors recently (James B. Longley, 1975–1979 and Angus King, 1995–2003). Maine state politicians, Republicans and Democrats alike, are noted for having more moderate views than many in the national wings of their respective parties.
Maine is an alcoholic beverage control state.
On May 6, 2009, Maine became the fifth state to legalize same-sex marriage; however, the law was repealed by voters on November 3, 2009. On November 6, 2012, Maine, along with Maryland and Washington, became the first state to legalize same-sex marriage at the ballot box.[74]
Federal politics
| Year | Democratic | Republican |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 47.85% 352,485 | 45.15% 332,591 |
| 2012 | 56.27% 401,306 | 40.98% 292,276 |
| 2008 | 57.71% 421,923 | 40.38% 295,283 |
| 2004 | 53.57% 396,842 | 44.58% 330,201 |
| 2000 | 49.09% 319,951 | 43.97% 286,616 |
| 1996 | 51.62% 312,788 | 30.76% 186,378 |
| 1992 | 38.77% 263,420 | 30.39% 206,504 |
| 1988 | 43.88% 243,569 | 55.34% 307,131 |
| 1984 | 38.78% 214,515 | 60.83% 336,500 |
| 1980 | 42.25% 220,974 | 45.61% 238,522 |
| 1976 | 48.07% 232,279 | 48.91% 236,320 |
| 1972 | 38.48% 160,584 | 61.46% 256,458 |
| 1968 | 55.30% 217,312 | 43.07% 169,254 |
| 1964 | 68.84% 262,264 | 31.16% 118,701 |
| 1960 | 42.95% 181,159 | 57.05% 240,608 |
In the 1930s, Maine was one of very few states which retained Republican sentiments. In the 1936 presidential election, Franklin D. Roosevelt received the electoral votes of every state other than Maine and Vermont; these were the only two states in the nation that never voted for Roosevelt in any of his presidential campaigns, though Maine was closely fought in 1940 and 1944. In the 1960s, Maine began to lean toward the Democrats, especially in presidential elections. In 1968, Hubert Humphrey became just the second Democrat in half a century to carry Maine, perhaps because of the presence of his running mate, Maine Senator Edmund Muskie, although the state voted Republican in every presidential election in the 1970s and 1980s.
Since 1969, two of Maine's four electoral votes have been awarded based on the winner of the statewide election; the other two go to the highest vote-getter in each of the state's two congressional districts. Every other state except Nebraska gives all its electoral votes to the candidate who wins the popular vote in the state at large, without regard to performance within districts.
Ross Perot achieved a great deal of success in Maine in the presidential elections of 1992 and 1996. In 1992, as an independent candidate, Perot came in second to Democrat Bill Clinton, despite the longtime presence of the Bush family summer home in Kennebunkport. In 1996, as the nominee of the Reform Party, Perot did better in Maine than in any other state.
Maine has voted for the Democratic candidate in six successive presidential elections, casting its votes for Bill Clinton twice, Al Gore in 2000, John Kerry in 2004, and Barack Obama in 2008 and 2012. Although Democrats have carried the state in presidential elections in recent years, Republicans have largely maintained their control of the state's U.S. Senate seats, with Edmund Muskie, William Hathaway and George J. Mitchell being the only Maine Democrats serving in the U.S. Senate in the past fifty years.
In the 2010 midterm elections, Republicans made major gains in Maine. They captured the governor's office as well as majorities in both chambers of the state legislature for the first time since the early 1970s. However, in 2012 elections Democrats managed to recapture both houses of Maine Legislature.
Maine's U.S. senators are Republican Susan Collins and Independent Angus King. The governor is Republican Paul LePage. The state's two members of the United States House of Representatives are Democrat Chellie Pingree and Republican Bruce Poliquin.
Municipalities
Organized municipalities
An organized municipality has a form of elected local government which administers and provides local services, keeps records, collects licensing fees, and can pass locally binding ordinances, among other responsibilities of self-government. The governmental format of most organized towns and plantations is the town meeting, while the format of most cities is the council-manager form. As of 2013 the organized municipalities of Maine consist of 23 cities, 431 towns, and 34 plantations. Collectively these 488 organized municipalities cover less than half of the state's territory. Maine also has 3 Reservations: Indian Island, Indian Township Reservation, and Pleasant Point Indian Reservation.[76]
- The largest municipality in Maine, by population, is the city of Portland (pop. 66,318).
- The smallest city by population is Eastport (pop. 1,331).
- The largest town by population is Brunswick (pop. 20,278).
- The smallest town by population is Frye Island, a resort town which reported zero year-round population in the 2000 Census; one plantation, Glenwood Plantation, Maine, also reported a permanent population of zero.
- In the 2000 census, the smallest town aside from Frye Island was Centerville with a population of 26, but since that census, Centerville voted to disincorporate and therefore is no longer a town. The next smallest town with a population listed in that census is Beddington (pop. 50 at the 2010 census).
- The largest municipality by land area is the town of Allagash, at 128 square miles (332 km2).
- The smallest municipality by land area is the plantation of Monhegan Island, at 0.86 square miles (2.2 km2). The smallest municipality by area that is not an island is Randolph, at 2.23 square miles (6 km2).
Unorganized territory
Unorganized territory has no local government. Administration, services, licensing, and ordinances are handled by the state government. The unorganized territory of Maine consists of over 400 townships (towns are incorporated, townships are unincorporated), plus many coastal islands that do not lie within any municipal bounds. The UT land area is slightly over one half the entire area of the State of Maine. Year-round residents in the UT number approximately 9,000, about 1.3% of the state's total population, with many more people residing only seasonally within the UT. Only four of Maine's sixteen counties (Androscoggin, Cumberland, Waldo and York) are entirely incorporated, although a few others are nearly so, and most of the unincorporated area is in the vast and sparsely populated Great North Woods of Maine.[77]
Most populous cities and towns
QuickFacts US Census Maine Portland:
| Portland (66,194) |
Lewiston (36,592) |
Bangor (33,039) |
South Portland (25,002) |
Auburn (23,055) |
Biddeford (21,277) |
Sanford (20,798) |
| Brunswick (20,278) |
Augusta (19,136) |
Scarborough (18,919) |
Saco (18,482) |
Westbrook (17,494) |
Windham (17,001) |
Gorham (16,381) |
| Waterville (15,722) |
York (12,529) |
Falmouth (11,185) |
Kennebunk (10,798) |
Orono (10,362) |
Standish (9,874) |
Presque Isle (9,692) |
| Wells (9,589) |
Kittery (9,490) |
Brewer (9,482) |
Buxton (9,093) |
Cape Elizabeth (9,015) |
Lisbon (9,009) |
Topsham (8,794) |
| Old Orchard Beach (8,624) |
Skowhegan (8,589) |
Bath (8,514) |
Yarmouth (8,349) |
Caribou (8,189) |
Freeport (7,879) |
Old Town (7,840) |
| Winslow (7,794) |
Gray (7,761) |
Farmington (7,760) |
Ellsworth (7,741) |
Waterboro (7,693) |
Rockland (7,297) |
Hampden (7,257) |
| Berwick (7,246) |
South Berwick (7,220) |
Cumberland (7,211) |
Fairfield (6,735) |
Belfast (6,668) |
Oakland (6,240) |
Eliot (6,204) |
Throughout Maine, many municipalities, although each separate governmental entities, nevertheless form portions of a much larger population base. There are many such population clusters throughout Maine, but some examples from the municipalities appearing in the above listing are:
- Portland, South Portland, Cape Elizabeth, Westbrook, Scarborough, and Falmouth
- Lewiston and Auburn
- Bangor, Orono, Brewer, Old Town, and Hampden
- Biddeford, Saco and Old Orchard Beach
- Brunswick and Topsham
- Waterville, Winslow, Fairfield, and Oakland
- Presque Isle and Caribou[78]
Education
There are thirty institutions of higher learning in Maine.[79] These institutions include the University of Maine, which is the oldest, largest and only research university in the state. UMaine was founded in 1865 and is the state's only land grant and sea grant college. The University of Maine is located in the town of Orono and is the flagship of Maine. There are also branch campuses in Augusta, Farmington, Fort Kent, Machias, and Presque Isle.[80]
Bowdoin College is a liberal arts college founded in 1794 in Brunswick, making it the oldest institution of higher learning in the state. Colby College in Waterville was founded in 1813 making it the second oldest college in Maine.[81] Bates College in Lewiston was founded in 1855 making it the third oldest institution in the state and the oldest coeducational college in New England.[82] The three colleges collectively form the Colby-Bates-Bowdoin Consortium and are ranked among the best colleges in the United States; often placing in the top 10% of all liberal arts colleges.[83][84][85]

Maine' per-student public expenditure for elementary and secondary schools was 21st in the nation in 2012, at $12,344.[86]
The collegiate system of Maine also includes numerous baccalaureate colleges such as: the Maine Maritime Academcy (MMA), Unity College, and Thomas College. There is only one medical school in the state, (University of New England's College of Osteopathic Medicine) and only one law school (The University of Maine School of Law).
Private schools in Maine are funded independently of the state and its furthered domains. Private schools are less common than public schools. A large number of private elementary schools with under 20 students exist, but most private high schools in Maine can be described as "semi-private."
Culture
.jpg)
Sports teams
Professional
- Maine Red Claws, basketball, NBA Development League
- Portland Sea Dogs, minor league baseball, Eastern League (U.S. baseball)
- Portland Pirates, hockey, NHL Development League, Florida Panthers
Non-professional
- Portland Phoenix FC, soccer, Premier Developmental League
- Maine Roller Derby, roller derby, Women's Flat Track Derby Association

NCAA
State symbols
Adapted from the Maine facts site.[87]

- State berry: Wild blueberry[88]
- State bird: Black-capped chickadee
- State cat: Maine Coon
- State dessert: Blueberry pie made with wild Maine blueberries
- State fish: Land-locked salmon
- State flower: White Pinecone and Tassel
- State fossil: Pertica quadrifaria
- State gemstone: Tourmaline
- State herb: Wintergreen[89]
- State insect: European honey bee
- State mammal: Moose
- State soft drink: Moxie
- State soil: Chesuncook soil series
- State song: State of Maine Song
- State treat: Whoopie pie[90]
- State tree: Eastern White Pine
- State vessel: Arctic exploration schooner Bowdoin
- State motto: Dirigo ("I lead")
In popular culture
Notable people
A citizen of Maine is known as a "Mainer",[3] though the term is often reserved for those whose roots in Maine go back at least three generations.[91] The term "Downeaster" may be applied to residents of the northeast coast of the state. The term "Mainiac" is considered by some to be derogatory, but embraced with pride by others,[92] and is used for a variety of organizations and for events such as the YMCA Mainiac Sprint Triathlon & Duathlon.[93]
See also
References
- ↑ "Maine for Vacation". USA Today. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
There's a reason it's called "Vacationland..."
- 1 2 "Maine History, Language and Culture". worldtravelguide.net. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- 1 2 "Dictionary.com - definition of "Mainer"". Dictionary.com. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
- 1 2 3 "Table 1. Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for the United States, Regions, States, and Puerto Rico: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015" (CSV). U.S. Census Bureau. December 26, 2015. Retrieved December 26, 2015.
- ↑ "Katahdin 2". NGS data sheet. U.S. National Geodetic Survey. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- 1 2 "Elevations and Distances in the United States". United States Geological Survey. 2001. Archived from the original on October 15, 2011. Retrieved October 21, 2011.
- ↑ Elevation adjusted to North American Vertical Datum of 1988.
- ↑ In the event of a vacancy in the office of Governor, the President of the State Senate is first in line for succession.
- ↑ "Portland, Maine Climate Summary". Weatherbase. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- 1 2 Stewart, George (1982) [1945]. Names on the Land: A Historical Account of Place-Naming in the United States. New York: Random House. pp. 41–42. ISBN 978-0-938530-02-2.
- ↑ "Journal of the Senate" (doc). State of Maine, HP1629, item 1, 123rd Maine State Legislature. March 6, 2002. Retrieved September 20, 2007.
WHEREAS, the State of Maine is named after the Province of Maine in France...
- ↑ Schroeder, Emily A. "Origin of Maine's Name". Maine State Library. Archived from the original on July 16, 2007. Retrieved September 20, 2007.
- ↑ Strickland, Agnes (1845). Lives of the Queens of England, Henrietta Maria. VIII. ISBN 978-0217842747.
- 1 2 3 Fisher, Carol B. Smith (February 26, 2002). "Who Really Named Maine?". Bangor Daily News. p. A8.
- ↑ Guyton, Kathy (2009). The U. S. State Names: The Stories of How Our States Were Named. Nederland, Colorado: Mountain Storm Press. pp. 193–201. ISBN 978-0982523902.
- ↑ correspondence to Carol B. Smith Fisher, 26 April 2002, from Hywel Wyn Owen, Director and Professor of the Place-Name Research Center, University of Wales Bangor
- ↑ Ekwall, Eilert, ed. (1960). The Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Place Names (4th ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 319. ISBN 978-0198691037.
- ↑ Shain, Samuella (August 1, 1997). The Maine Reader: The Down East Experience from 1614 to the Present. David R. Godine Publisher. ISBN 978-1-56792-078-9. Retrieved July 3, 2010.
- ↑ Baxter, James Phinney (1890). Sir Ferdinando Gorges and his Province of Maine. Boston: Prince Society. p. 180.
- ↑ "Real Fact #922". Snapple. Retrieved September 21, 2016.
- ↑ "Maine Facts and Trivia". Waltham, Massachusetts: Digital Properties. Retrieved September 11, 2015.
- ↑ "Science: Bye, Columbus". TIME.com. December 11, 1978.
- ↑ MPBN, "Rolling Back the Frontier", The Story of Maine; accessed January 3, 2011
- ↑ "Proceedings of the Massachusetts Historical Society". google.com. Retrieved September 11, 2015.
- ↑ Bruce G. Trigger (ed.): Handbook of North American Indians. Vol. 15. Northeast. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington D.C. 1978 ISBN 0-16-004575-4
- ↑ "York commemorates Candlemas Raid". The Portsmouth Herald. February 1, 2001.
- ↑ John Demos, The Unredeemed Captive: A Family Story from Early America, New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1994, pp. 186 and 224
- ↑ Darren Bonaparte, "The History of Akwesasne", The Wampum Chronicles, accessed February 1, 2010
- ↑ Woodard, Colin. The Lobster Coast. New York. Viking/Penguin, ISBN 0-670-03324-3, 2004, pp. 139–140, 150-151
- ↑ Woodard, Colin. "Parallel 44: Origins of the Mass Effect", The Working Waterfront, August 31, 2010.
- ↑ Woodard, Colin. The Lobster Coast: Rebels, Rusticators and the Forgotten Frontier (2004) Penguin Books. ISBN 0-670-03324-3
- ↑ "Maine History (Statehood)". www.maine.gov. Retrieved April 13, 2008.
- ↑ "Tree and impervious cover in the United States" (PDF). USDA. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ↑ Olson; D. M; E. Dinerstein; et al. (2001). "Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth". BioScience. 51 (11): 933–938. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0933:TEOTWA]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0006-3568. Archived from the original on October 14, 2011.
- ↑ "Maine.gov: Facts About Maine". State of Maine. Retrieved September 17, 2010.
- ↑ "Length of the U.S. Coastline by State". fen.com. Retrieved September 11, 2015.
- ↑ "Answers - The Most Trusted Place for Answering Life's Questions". Answers.com. Retrieved September 11, 2015.
- ↑ "Maine". National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 3, 2008. Retrieved July 16, 2008.
- 1 2 Lent, Robert (February 10, 2009). "New All Time Low Temperature Recorded in Maine". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved November 6, 2011.
- ↑ "Each state's high temperature record". USA Today. August 2006. Retrieved February 11, 2009.
- ↑ NOAA National Climatic Data Center. Retrieved on October 24, 2006.
- ↑ National Climatic Data Center. NOAA's 1981-2010 Climate Normals. http://www.currentresults.com/Weather/Maine/average-yearly-precipitation.php
- ↑ "Maine climate averages". Weatherbase. Retrieved November 9, 2015.
- ↑ Resident Population Data. "Resident Population Data - 2010 Census". 2010.census.gov. Archived from the original on October 28, 2011. Retrieved March 15, 2012.
- ↑ "Population and Population Centers by State: 2010 (US Census Bureau)". Retrieved April 9, 2011.
- ↑ "census.gov" (PDF). Retrieved August 3, 2013.
- ↑ "2010_State_Profile_TEMPLATE" (PDF). Retrieved October 25, 2012.
- ↑ Historical Census Statistics on Population Totals By Race, 1790 to 1990, and By Hispanic Origin, 1970 to 1990, For The United States, Regions, Divisions, and States
- ↑ Population of Maine: Census 2010 and 2000 Interactive Map, Demographics, Statistics, Quick Facts
- ↑ Center for New Media and Promotions(C2PO). "2010 Census Data". census.gov. Retrieved September 11, 2015.
- ↑ "Selected Social Characteristics in the United States: 2011 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates (DP02): Maine". U.S. Census Bureau American Factfinder. Retrieved January 4, 2013.
- ↑ Sharing the Dream: White Males in a Multicultural America By Dominic J. Pulera.
- ↑ Reynolds Farley, "The New Census Question about Ancestry: What Did It Tell Us?", Demography, Vol. 28, No. 3 (August 1991), pp. 414, 421.
- ↑ Stanley Lieberson and Lawrence Santi, "The Use of Nativity Data to Estimate Ethnic Characteristics and Patterns", Social Science Research, Vol. 14, No. 1 (1985), pp. 44-6.
- ↑ Stanley Lieberson and Mary C. Waters, "Ethnic Groups in Flux: The Changing Ethnic Responses of American Whites", Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, Vol. 487, No. 79 (September 1986), pp. 82-86.
- ↑ Mary C. Waters, Ethnic Options: Choosing Identities in America (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1990), p. 36.
- ↑ French Canadian Emigration to the United States 1840-1930. Claude Bélanger, Department of History, Marianopolis College
- ↑ French-Canadian Americans by Marianne Fedunkiw
- ↑ "Americans under age 1 now mostly minorities, but not in Ohio: Statistical Snapshot". The Plain Dealer. June 3, 2012.
- ↑ "MLA Language Map Data Center". Modern Language Association.
- ↑ "The Association of Religion Data Archives | State Membership Report". www.thearda.com. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- ↑ Hendrickson, Dyke (August 19, 2010). "The Role of Religion in Maine". Maine Public Broadcasting Network. Retrieved October 19, 2011.
- ↑ "GDP by State". Greyhill Advisors. Retrieved September 13, 2011.
- ↑ "Bureau of Labor Statistics Data". data.bls.gov. Retrieved 2016-05-23.
- ↑ "Brunswick Landing - Midcoast Regional Redevelopment Authority". Midcoast Regional Redevelopment Authority. Retrieved September 11, 2015.
- ↑ http://usda.mannlib.cornell.edu/usda/ers/blueberry/table02.xls
- ↑ Part1_Ports_tonsbycommCY2013.htm
- ↑ Table 1-57: Tonnage of Top 50 U.S. Water Ports, Ranked by Total Tons(a) | Bureau of Transportation Statistics
- ↑ https://maine.gov/revenue/forms/1040/2013/1040RateSched_13RevJan13.pdf
- ↑ https://maine.gov/revenue/forms/1040/2012/RateSched_12.pdf
- ↑ KEPM - Eastport, Maine - Eastport Municipal Airport". Great Circle Mapper. http://gc.kls2.com/airport/KEPM. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Downeaster Schedule, effective November 1, 2012" (PDF). Amtrak Train Schedules, Timetables. Amtrak. Retrieved November 10, 2012.
- ↑ "Maine QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". State & County QuickFacts. United States Census Bureau. January 17, 2012. Retrieved February 12, 2012.
- ↑ "Maine Passes Gay Marriage in Historic 'Question 1' Vote". The Huffington Post. November 7, 2012.
- ↑ "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". Archived from the original on June 4, 2011. Retrieved June 11, 2011.
- ↑ "Maine.gov: Local". maine.gov. Retrieved September 11, 2015.
- ↑ "Unorganized Territory". maine.gov. Retrieved September 11, 2015.
- ↑ Fact Finder US Census Maine Portland Archived November 3, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Carnegie Classifications | Basic Classification". carnegieclassifications.iu.edu. Retrieved 2016-08-12.
- ↑ "About UMaine". Umaine.edu. Retrieved 2016-07-18.
- ↑ "About". Retrieved 2016-08-19.
- ↑ "Bates College". Forbes. Retrieved 2016-06-16.
[Bates College] was the first coeducational college in New England.
- ↑ "National Liberal Arts College Rankings | Top Liberal Arts Colleges | US News Best Colleges". colleges.usnews.rankingsandreviews.com. Retrieved 2016-08-12.
- ↑ "College Guide Rankings 2015 – Liberal Arts Colleges". Washington Monthly. Retrieved 2016-08-12.
- ↑ "America's Top Colleges". Retrieved 2016-08-12.
- ↑ Bidwell, Allie. "How States Are Spending Money in Education". U.S. News & World Report - News. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ↑ "Facts About Maine". Maine.gov. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- ↑ "Maine State Berry - Wild Blueberry". Statesymbolsusa.org. Retrieved March 15, 2012.
- ↑ "Maine State Symbols and Emblems". maine.gov. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Whoopie pie to become Maine state 'treat'". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on October 25, 2011.
- ↑ "Maine: A Spiritual Frontier Opens for Business". Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ↑ Louise Dickinson Rich. State o'Maine. Harper & Row, 1964, p ix
- ↑ "Mainiac Tri". Archived from the original on August 14, 2014. Retrieved August 13, 2014.
External links
State government
- Maine government
- Maine Office of Tourism Search for tourism-related businesses
- Visit Maine (agriculture) Maine fairs, festivals, etc. - Agricultural Dept.
U.S. government
- Maine State Guide, from the Library of Congress
- U.S. EIA Energy Profile for Maine - economic, environmental and energy data
- U.S. Geological Survey Real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Maine
- U.S. Dept. of Agriculture Maine State Facts - agricultural
- U.S. Census Bureau Quick facts on Maine
- Portland Magazine Editorial on Maine news, events, and people
Information
- Maine at DMOZ
- Maine Historical Society
- Old USGS maps of Maine.
- 1860 Map of Maine by Mitchell.
- 1876 Panoramic Birdseye View of Portland by Warner at LOC.,
- Portland Stage Company
- Comprehensive compilation of media sources in Maine.
-
 Geographic data related to Maine at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Maine at OpenStreetMap
 |
Saint Lawrence River | |
Gulf of Saint Lawrence |  |
| |
|
Bay of Fundy | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| |
Atlantic Ocean |
| Preceded by Alabama |
List of U.S. states by date of statehood Admitted on March 15, 1820 (23rd) |
Succeeded by Missouri |
Coordinates: 45°30′N 69°00′W / 45.5°N 69°W












