Kashiwa
| Kashiwa 柏市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Core city | |||
|
Looking east from Kashiwa Station | |||
| |||
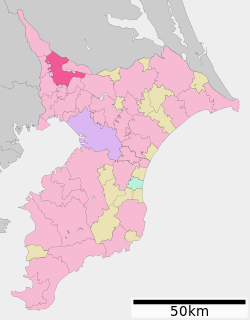 Location of Kashiwa in Chiba Prefecture | |||
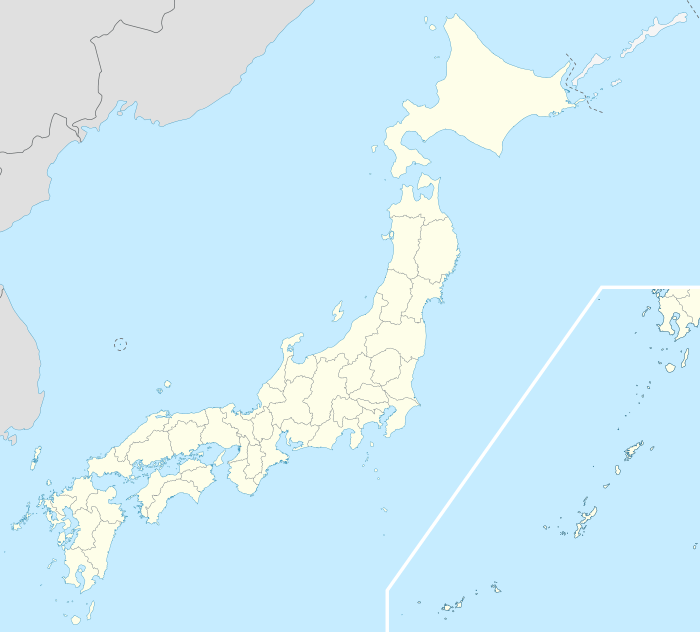 Kashiwa
| |||
| Coordinates: 35°52′3.3″N 139°58′32.7″E / 35.867583°N 139.975750°ECoordinates: 35°52′3.3″N 139°58′32.7″E / 35.867583°N 139.975750°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Kantō | ||
| Prefecture | Chiba Prefecture | ||
| Government | |||
| • -Mayor | Hiroyasu Akiyama (since November 2009) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 114.74 km2 (44.30 sq mi) | ||
| Population (December 1, 2015) | |||
| • Total | 411,602 | ||
| • Density | 3,590/km2 (9,300/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| City symbols | |||
| • tree | Daimyo oak, Castanopsis | ||
| • Flower | Phlox subulata; Erythronium japonicum; sunflower | ||
| • Bird | Azure-winged magpie | ||
| Phone number | 04-7167-1111 | ||
| Address | 5-10-1 Kashiwa, Kashiwa-shi, Chiba-ken 270-8505 | ||
| Website |
www | ||

Kashiwa (柏市 Kashiwa-shi) is a city located in northwestern Chiba Prefecture, Japan.[1] As of December 1, 2015, the city had an estimated population of 411,602 and a population density of 3,590 persons per km2. The total area was 114.72 square kilometres (44.29 sq mi).
The name of the city of Kashiwa in the Japanese language is written with a single kanji character, 柏, a reference to Quercus dentata, commonly known in English as the daimyo oak.
Geography
Kashiwa is located on the Shimōsa Plateau in the far northwestern corner of Chiba Prefecture.[2]
Neighboring municipalities
- Chiba Prefecture
- Ibaraki Prefecture
History
Early history
Kashiwa has been settled since ancient times, and was historically part of Shimōsa Province. The area around Kashiwa was the site of the Battle of Sakainehara in 1478 early in the Sengoku period (1467 – 1573). During the Edo period (1603 – 1868), the area was tenryō territory controlled directly by the Tokugawa shogunate. The shogunate established a number of horse ranches which provided war horses for the army of the shogunate. The Tokugawa shogunate put much effort into draining the marshy areas of Lake Tekanuma during the Edo period as part of large-scale land reclamation carried out across Japan.[2] Kashiwa was developed as a post station on the Mito Kaidō, which connected the capitol at Edo with Mito in present-day Ibaraki Prefecture.
Modern history
After the Meiji Restoration in 1868, Kashiwa Village was created in Chiba Prefecture on October 1, 1889. Kashiwa was connected to Tokyo by rail in 1896, and rail construction during the Meiji period (1868 – 1912) established the area as a commercial center.[1] Kashiwa became a town on September 15, 1926. Kashiwa, like much of northern Chiba Prefecture, saw the development of numerous military installations in the 1930s, notably after the Mukden Incident in 1931.[2] The Imperial Japanese Army established Kashiwa Air Field and Kashiwa Military Hospital, and Kashiwa became a military town. The air field was abandoned after the end of World War II, but the hospital continues to exist as the Kashiwa Public Hospital.[1]
On September 1, 1954, Kashiwa absorbed neighboring Kogane Town and Tsuchi and Tanaka villages to form the new city of Tokatsu (東葛市 Tokatsu-shi). However, many politicians in Kogane Town were vehemently opposed to the merger, and forced its dissolution on October 15, 1954 with most of former Kogane Town merging with Matsudo city instead.[2] On November 1, 1954, Fuse Village broke away from Tokatsu, eventually joining Abiko Town to form the city of Abiko. The remaining portion of Tokatsu was renamed Kashiwa on November 15, 1954. On December 25, 1955 a fire of unknown origin destroyed the former Kashiwa City Hall, and burned down most of the center of the city. In the 1960s, Kashiwa was designated for reconstruction with a special fund from the central government, which included Japan’s first pedestrian decks, completed at Kashiwa Station in 1973.
On April 1, 2008, Kashiwa was designated as a core city, with increased local autonomy. In August 2010, the city population exceeded 400,000 people.
Economy
Kashiwa is a regional commercial center and a bedroom community for nearby Chiba and Tokyo.[1] The city has a mixed industrial base, with food processing industries forming an important portion of the economy. Nikka Whisky Distilling, Asahi Soft Drinks, and Ito Ham all have production facilities in Kashiwa. There is some residual agriculture of turnips, onions and spinach.[1]
Education
Universities
- Chiba University, Kashiwa Campus
- University of Tokyo, Kashiwa Campus
- Reitaku University
- Nishōgakusha University
- Kaichi International University
Primary and secondary education
- Kashiwa has 42 public elementary schools, 21 public middle schools, three private combined middle/high schools and nine public and two private high schools.
Transportation
Rail
- East Japan Railway Company (JR East) - Jōban Line
- Tōbu Railway - Tōbu Noda Line
- Toyoshiki - Kashiwa - Shin-Kashiwa - Masuo - Sakasai - Takayanagi
- Metropolitan Intercity Railway Company - Tsukuba Express
Highways
Sports
Kashiwa is home to the professional football team Kashiwa Reysol.
Sister cities
 – Torrance, California, United States,[3] since February 20, 1973
– Torrance, California, United States,[3] since February 20, 1973 – Chengde, Hebei Province, China,[4] since November 1, 1983
– Chengde, Hebei Province, China,[4] since November 1, 1983 – Guam, United States,[4] since November 30, 1991
– Guam, United States,[4] since November 30, 1991 – Camden, New South Wales, Australia,[4] since April 11, 1997
– Camden, New South Wales, Australia,[4] since April 11, 1997 – Tsugaru, Aomori, Japan, since November 19, 1994
– Tsugaru, Aomori, Japan, since November 19, 1994
Notable people
- Shigeyuki Furuki, professional baseball player
- Fumio Imamura, Olympic race walker
- Naoki Ishikawa, professional soccer player
- Kirinji Kazuharu, sumo wrestler
- Masato Kobayashi, professional kickboxer
- Yuri Mitsui, actress, model
- Yōko Oginome, singer
- Takeshi Okano, manga artist
- Megumi Urawa, voice actress
- Kazunori Yamauchi, video game designer
- Shintaro Katsu, actor and singer, died in Kashiwa.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Kashiwa". Encyclopedia of Japan. Tokyo: Shogakukan. 2012. OCLC 56431036. Archived from the original on August 25, 2007. Retrieved 2012-07-17.
- 1 2 3 4 "柏" [Kashiwa]. Kokushi Daijiten (in Japanese). Tokyo: Shogakukan. 2012. OCLC 683276033. Archived from the original on August 25, 2007. Retrieved 2012-07-17.
- ↑ "US-Japan Sister Cities by State". Asia Matters for America. Honolulu, HI: East-West Center. Retrieved 20 November 2015.
- 1 2 3 "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Retrieved 21 November 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kashiwa, Chiba. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Kashiwa. |
- Official website (Japanese)
- Kashiwa City official website (English)
- Kashiwa International Relations Association in Japanese and English


