Hachiōji, Tokyo
| Hachiōji 八王子市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Core City | |||
|
View of top left, Downtown Hachioji, Komiya Park, Naganuma Park, Mount Takao, stone fence and bridge in Hachioji Castle site, Yakuoin in Mount Takao, Hachioji Ramen, Hachioji Traditional Festival on August | |||
| |||
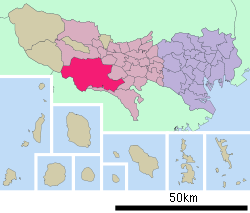 Location of Hachiōji in Tokyo | |||
 Hachiōji
| |||
| Coordinates: 35°39′59.2″N 139°18′57.6″E / 35.666444°N 139.316000°ECoordinates: 35°39′59.2″N 139°18′57.6″E / 35.666444°N 139.316000°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Kantō | ||
| Prefecture | Tokyo | ||
| Government | |||
| • -Mayor | Takayuki Ishimori (石森 孝志 Takayuki Ishimori) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 186.38 km2 (71.96 sq mi) | ||
| Population (February 2016) | |||
| • Total | 579,330 | ||
| • Density | 3,110/km2 (8,100/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| Symbols | |||
| • Tree | Ginkgo biloba | ||
| • Flower | Lilium auratum | ||
| • Bird | Blue-and-white flycatcher | ||
| Phone number | 042-626-3111 | ||
| Address | 3-24-1 Motohongo-cho, Hachiōji-shi, Tokyo 192-8501 | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Hachiōji (八王子市 Hachiōji-shi) is a city located in the western portion of Tokyo Metropolis, in the central Kantō region of Japan. As of 1 February 2016, the city had an estimated population of 579,330 and a population density of 3110 persons per km². Its total area was 186.38 square kilometres (71.96 sq mi).
Geography
Hachiōji is located in the foothills of the Okutama Mountains of western Tokyo, about 40 kilometers west of the center of the 23 special wards of Tokyo. The city is surrounded on three sides by mountains, forming the Hachioji Basin which opens up toward the east in the direction of Tokyo. The mountain ranges in the southwest include Mount Takao (599 m) and Mount Jinba (857 m), two popular hiking destinations which can be reached by train and bus, respectively.
Surrounding municipalities
Climate
| Climate data for Hachioji (1981 - 2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 19.9 (67.8) |
24.0 (75.2) |
25.5 (77.9) |
32.2 (90) |
37.1 (98.8) |
35.9 (96.6) |
39.0 (102.2) |
38.7 (101.7) |
39.2 (102.6) |
32.1 (89.8) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.0 (78.8) |
39.2 (102.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.2 (48.6) |
9.9 (49.8) |
13.0 (55.4) |
18.9 (66) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.6 (78.1) |
29.5 (85.1) |
31.2 (88.2) |
26.7 (80.1) |
21.2 (70.2) |
16.2 (61.2) |
11.8 (53.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.2 (37.8) |
4.1 (39.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
13.1 (55.6) |
17.6 (63.7) |
20.9 (69.6) |
24.7 (76.5) |
26.1 (79) |
22.2 (72) |
16.4 (61.5) |
10.7 (51.3) |
5.7 (42.3) |
14.4 (57.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.1 (28.2) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
2.2 (36) |
7.5 (45.5) |
12.6 (54.7) |
16.9 (62.4) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
18.5 (65.3) |
12.3 (54.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
0.5 (32.9) |
9.7 (49.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.3 (17.1) |
−8.6 (16.5) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−2 (28) |
2.6 (36.7) |
10.1 (50.2) |
13.3 (55.9) |
16.0 (60.8) |
7.9 (46.2) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−8.6 (16.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 48.3 (1.902) |
49.4 (1.945) |
103.4 (4.071) |
118.2 (4.654) |
121.5 (4.783) |
167.9 (6.61) |
176.0 (6.929) |
242.2 (9.535) |
256.7 (10.106) |
187.7 (7.39) |
88.8 (3.496) |
45.2 (1.78) |
1,602.3 (63.083) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 4.5 | 5.0 | 9.9 | 10.1 | 10.4 | 12.8 | 12.4 | 10.4 | 12.9 | 10.3 | 6.9 | 4.3 | 109.9 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 190.7 | 172.1 | 169.5 | 175.5 | 168.7 | 120.0 | 141.6 | 176.5 | 124.8 | 134.0 | 158.5 | 185.0 | 1,917.7 |
| Source #1: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: 観測史上1〜10位の値(年間を通じての値) | |||||||||||||
History
The area of present-day Hachiōji was part of ancient Musashi Province. It has been an important junction point and post town along the Kōshū Highway, the main road that connected the historical Edo (today's Tokyo) with western Japan. Hachioji Castle was built during the Sengoku period in 1584 by Hōjō Ujiteru, but was soon destroyed in 1590 by Toyotomi Hideyoshi. During the Edo period, the area was tenryo controlled directly by the Tokugawa shogunate.
In the post-Meiji Restoration cadastral reform of July 22, 1878, the area became part of Minamitama District in Kanagawa Prefecture. The town of Hachiōji was created on April 1, 1889 with the establishment of municipalities law. Minaitama District was transferred to the administrative control of Tokyo Metropolis on April 1, 1893. Hachiōji gained city status on September 1, 1917.
During the 1964 Summer Olympics, the city played host to the road cycling events. A velodrome in the city played host to the track cycling events.[1]
Economy
During the Meiji period, Hachiōji prospered as an important location for the production of silk and silk textiles. The industry faded away, however, in the 1960s. Today, Hachiōji mainly serves as a commuter town for people working in Tokyo, and as a location for many large colleges and universities.
Education
Colleges and universities
- Chuo University (Tama Campus)
- Digital Hollywood University
- Kogakuin University (Hachioji Campus)
- Kyorin University (Hachioji Campus)
- Meisei University (Hino Campus)
- Nihon Bunka University
- Soka University
- Tama Art University (Hachioji Campus)
- Takushoku University (Hachioji Campus)
- Teikyo University (Hachioji Campus)
- Tokyo Junshin University
- Tokyo Kasei-Gakuin University (Machida Campus)
- Tokyo Metropolitan University (Minamiōsawa Campus)
- Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology
- Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences
- Tokyo University of Technology (Hachiōji Campus)
- Tokyo Zokei University of Art and Design
- Nippon Engineering College
Primary and secondary education
Hachiōji has 70 public elementary schools and 37 public middle schools operated by the city government, as well as four public combined elementary/middle schools. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education operates nine public high schools, and there are also eleven private high schools.
he metropolis also operates the Hachioji School for the Blind.
Transportation
Railways
- JR East- Chūō Main Line
- JR East- Yokohama Line
- JR East- Hachikō Line
- Keio Corporation - Keio Line
- Keio Corporation - Keio Takao Line
- Kitano - Keiō-Katakura - Yamada - Mejirodai - Hazama - Takao - Takaosanguchi
- Keio Corporation - Sagamihara Line
- Tama Toshi Monorail Line
- Takaotozan Railway
Highways
- Chūō Expressway
- Ken-Ō Expressway
- Japan National Route 16
- Japan National Route 20
- Japan National Route 411
Sister city relations
 - Kaohsiung, Taiwan[2] - friendship city since November 1, 2006
- Kaohsiung, Taiwan[2] - friendship city since November 1, 2006.svg.png) - Siheung, Gyeonggi Province, Korea[2] - friendship city since November 7, 2006
- Siheung, Gyeonggi Province, Korea[2] - friendship city since November 7, 2006 - Tai'an, Shandong Province, China[2] - friendship city since September 23, 2006
- Tai'an, Shandong Province, China[2] - friendship city since September 23, 2006
Local attractions
Hachioji stretches over a large area, combining such diverse parts as the densely populated city center and its shopping district with the hardly populated rural areas in the west.
- Mt. Takao (599 m) is a popular hiking destination in the southwest, easily accessible through the Keio Takao Line. It is famous for the Shingon Buddhist temple Takao-san Yakuōin Yūkiji (高尾山薬王院有喜寺).
- Mt. Jinba (855 m) is more difficult to reach, requiring a one-hour bus ride from the city center. It is popular, however, because of the scenic view toward Mt. Fuji.
- Tama Forest Science Garden
- Tokyo Fuji Art Museum
- Musashi Imperial Graveyard houses the remains of the Taishō and Shōwa emperors.

- Shōwa emperor's grave
- Taishō emperor's grave
References
- 1964 Summer Olympics official report. Volume 2. Part 1. p. 263.
- ↑ 1964 Summer Olympics official report. Volume 1. Part 1. p. 115.
- 1 2 3 "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Retrieved 1 July 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hachioji, Tokyo. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Hachioji. |
- Official website (English)



_pictogram.svg.png)